Scientists reveal how gut microbes can influence bone strength in mice
New findings could aid the development of therapies that change the gut microbiome to allow healthy skeletal growth in humans
2021-01-12
(Press-News.org) Gut microbes passed from female mice to their offspring, or shared between mice that live together, may influence the animals' bone mass, says a new study published today in eLife.
The findings suggest that treatments which alter the gut microbiome could help improve bone structure or treat conditions that weaken bones, such as osteoporosis.
"Genetics account for most of the variability in human bone density, but non-genetic factors such as gut microbes may also play a role," says lead author Abdul Malik Tyagi, Assistant Staff Scientist at the Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism, and Lipids at Emory Microbiome Research Center, Emory University, Georgia, US. "We wanted to investigate the influence of the microbiome on skeletal growth and bone mass development."
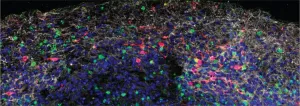
To do this, Tyagi and colleagues studied mice that lacked any gut microbes. They transferred fecal material containing a gut microbe called segmented filamentous bacteria (SFB), which stimulates the breakdown of bone, into the animals. Their studies revealed that the offspring of the SFB-treated mice were colonised with these bacteria at birth and had poorer bone structure than identical mice that lacked SFB.
Additionally, mice that lived with others carrying SFB became colonised with the bacteria within four weeks, and developed poorer bone structure as a result. "Our work shows that microbes can be either inherited or transmitted between individuals and significantly affects skeletal development in the animals," Tyagi says.
"Further studies are now needed to determine if the same is true in humans," adds senior author Roberto Pacifici, Garland Herndon Professor of Medicine, and Director of the Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism, and Lipids, at Emory University. "If it is, then it could be possible to develop therapies that change the gut microbiome early in life to allow for healthy skeletal growth.
"It would also suggest the need for caution in the current use of fecal transplants to treat other conditions in patients, to ensure that bone-weakening bacteria aren't inadvertently introduced," Pacifici concludes.
INFORMATION:
Reference
The paper 'The gut microbiota is a transmissible determinant of skeletal maturation' can be freely accessed online at https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.64237. Contents, including text, figures and data, are free to reuse under a CC BY 4.0 license.
Media contact
Emily Packer, Media Relations Manager
eLife
e.packer@elifesciences.org
01223 855373
About eLife
eLife is a non-profit organisation created by funders and led by researchers. Our mission is to accelerate discovery by operating a platform for research communication that encourages and recognises the most responsible behaviours. We work across three major areas: publishing, technology and research culture. We aim to publish work of the highest standards and importance in all areas of biology and medicine, while exploring creative new ways to improve how research is assessed and published. We also invest in open-source technology innovation to modernise the infrastructure for science publishing and improve online tools for sharing, using and interacting with new results. eLife receives financial support and strategic guidance from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Max Planck Society and Wellcome. Learn more at https://elifesciences.org/about.
To read the latest Medicine research published in eLife, visit https://elifesciences.org/subjects/medicine.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-12
Using both mouse and human brain tissue, researchers at Yale School of Medicine have discovered that SARS-CoV-2 can directly infect the central nervous system and have begun to unravel some of the virus's effects on brain cells. The study, published today in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), may help researchers develop treatments for the various neurological symptoms associated with COVID-19.
Though COVID-19 is considered to primarily be a respiratory disease, SARS-CoV-2 can affect many other organs in the body, including, in some patients, the central nervous system, where infection is associated with ...
2021-01-12
The first step in treating cancer is understanding how it starts, grows and spreads throughout the body. A relatively new cancer research approach is the study of metabolites, the products of different steps in cancer cell metabolism, and how those substances interact.
To date, research like this has focused mostly on cancerous tissues; however, normal tissues that surround tumors, known as the extratumoral microenvironment (EM), may have conditions favorable for tumor formation and should also be studied.
In a new study published in the journal PLOS ONE, researchers investigated the metabolites involved in the growth and spread of melanoma, a rare but deadly ...
2021-01-12
Almost 18,000 Americans experience traumatic spinal cord injuries every year. Many of these people are unable to use their hands and arms and can't do everyday tasks such as eating, grooming or drinking water without help.
Using physical therapy combined with a noninvasive method of stimulating nerve cells in the spinal cord, University of Washington researchers helped six Seattle area participants regain some hand and arm mobility. That increased mobility lasted at least three to six months after treatment had ended. The research team published these findings Jan. 5 in the journal ...
2021-01-12
A recent study finds that, in the wake of a mass shooting, National Rifle Association (NRA) employees, donors and volunteers had extremely mixed emotions about the organization - reporting higher levels of both positive and negative feelings about the NRA, as compared to people with no NRA affiliation.
"We wanted to see what effect 'in-group' affiliation and political identity had on how people responded to the NRA's actions after a mass shooting," says Yang Cheng, co-author of the study and an assistant professor of communication at North Carolina State University. "The political findings were predictable - Republicans thought more favorably of the NRA than Democrats did. But the in-group affiliation was a lot more complex than ...
2021-01-12
Stroke survivors who had ceased to benefit from conventional rehabilitation gained clinically significant arm movement and control by using an external robotic device powered by the patients' own brains.
The results of the clinical trial were described in the journal NeuroImage: Clinical.
Jose Luis Contreras-Vidal, director of the Non-Invasive Brain Machine Interface Systems Laboratory at the University of Houston, said testing showed most patients retained the benefits for at least two months after the therapy sessions ended, suggesting the potential for long-lasting gains. He is also Hugh Roy and Lillie Cranz Cullen Distinguished Professor of electrical and computer engineering.
The trial involved training stroke survivors with limited movement in one arm to use a brain-machine interface ...
2021-01-12
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Entomologist Akito Kawahara's message is straightforward: We can't live without insects. They're in trouble. And there's something all of us can do to help.
Kawahara's research has primarily focused on answering fundamental questions about moth and butterfly evolution. But he's increasingly haunted by studies that sound the alarm about plummeting insect numbers and diversity.
Kawahara has witnessed the loss himself. As a child, he collected insects with his father every weekend, often traveling to a famous oak outside Tokyo ...
2021-01-12
MANHATTAN, KANSAS -- Kyle Goerl, the medical director of Kansas State University's Lafene Health Center, is part of a collaborative team that is providing research-based guidance during the COVID-19 pandemic. The team's latest research contributed to the updated quarantine guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Goerl is a co-author of the publication "Time from Start of Quarantine to SARS-CoV-2 Positive Test Among Quarantined College and University Athletes." The publication appeared in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the CDC on Friday, Jan. 8, and involved researchers from multiple organizations and universities.
The publication was one of many that the ...
2021-01-12
Osaka, Japan -- Ultra-intense lasers with ultra-short pulses and ultra-high energies are powerful tools for exploring unknowns in physics, cosmology, material science, etc. With the help of the famous technology "Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA)" (2018 Nobel Prize in Physics), the current record has reached 10 Petawatts (or 10^16 Watts). In a study recently published in Scientific Reports, researchers from Osaka University proposed a concept for next-generation ultra-intense lasers with a simulated peak power up to the Exawatt class (1 Exawatt equals 1000 Petawatts).
The laser, which was invented by Dr. T. H. Maiman in 1960, has one important characteristic of high intensity (or high peak power for pulse lasers): historically, laser peak ...
2021-01-12
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed insulin nanoparticles that may one day become the basis for an oral medicine, and an alternative to insulin injections for diabetic patients.
In a pre-clinical study, the NTU Singapore team fed insulin-containing nanoparticles to rats and found that insulin increased in their blood minutes later.
Insulin therapy is often an important part of treatment for diabetes, a metabolic disease that affects 422 million people globally . In Singapore, the number of diabetics is expected to grow to 1 million - almost a fifth of the population - in 2050 .
Delivering insulin orally would be preferable over insulin jabs for patients because it causes less ...
2021-01-12
Anthropogenic, or human-made, heat flux in the near-surface atmosphere has changed urban thermal environments. Much of this fluctuation has been noted with rapid development of the global economy and urbanization since the turn of the 21st century. Meanwhile, the number of extreme temperature events in the first decade of the 21st century grew faster than in the last 10 years of the 20th century. During this period, urban extreme heat events have become more frequent, breaking temperature records more often.
"We found the relationships between anthropogenic heat flux and extreme temperature events..." said Prof. Zhenghui Xie, a scientist with the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. "...including ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists reveal how gut microbes can influence bone strength in mice
New findings could aid the development of therapies that change the gut microbiome to allow healthy skeletal growth in humans