Singing a tumor test song
Monitoring the stiffness of the tissue near a patient's thyroid while they sing a note can allow medical professionals to determine the presence of a tumor.
2021-01-12
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, January 12, 2021 -- Singing may be the next-generation, noninvasive approach to determining the health of a patient's thyroid.
Typically, a fine needle is used to detect the presence of a tumor in the thyroid, which most commonly affects children and younger women. However, this method can only detect about 5% of thyroid cancers.
Researchers from Université de Tours, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Dijon-Bourgogne, and Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté suggest a simpler approach: singing. They demonstrate the technique in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
"Developing noninvasive methods would reduce the stress of patients during their medical exams," said Steve Beuve, one of the authors. "Having to sing during a medical exam can perhaps help release some of the nervous tension even more."
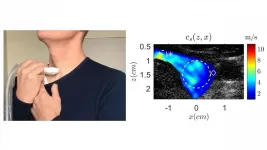
When a person sings, the vibrations from their voice create waves in the tissue near the vocal tract called shear waves. If a tumor is present in the thyroid, the elasticity of its surrounding tissue increases, stiffening, and causing the shear waves to accelerate.
Using ultrasound imaging to measure the speed of these waves, the researchers can determine the elasticity of the thyroid tissue. This method, which the authors call vocal passive elastography, is an extension of passive elastography, a shear wave propagation tracking technique used in seismology.
"The propagation of shear waves gives us information about mechanical properties of soft tissues," Beuve said.
Because the elasticity of biological tissues depends on the speed of the shear waves, by asking a volunteer to sing and maintain an "eeee" sound at 150 hertz, approximately the frequency of D3, the group was able to characterize the thyroid and find any abnormally stiff areas.
A key benefit of V-PE is how quick and easy it is. It requires no specialized or complex equipment added to the ultrasound scanner and only needs about one second of data acquisition to complete. Analyzing the data is the longest step, but a computer program that the team developed does the computation automatically.
The group is working on improving the user friendliness of the computer interface and potentially expanding V-PE to include other areas near the vocal tract, such as the brain.
"We want to cooperate with physicians to propose protocols to verify the relevance of elasticity as a biomarker of pathogens," Beuve said.
INFORMATION:
The article "Natural shear wave imaging using vocal tract vibrations: introducing vocal passive elastography (V-PE) to thyroid elasticity mapping" is authored by Steve Beuve, Samuel Callé, Elise Khoury, Emmanuel Simon, and Jean Pierre Remenieras. The article will appear in Applied Physics Letters on Jan. 12, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0031169). After that date, it can be accessed at
https://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0031169.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Letters features rapid reports on significant discoveries in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/apl.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-12
What The Study Did: National register data from Denmark were used to examine if people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) have higher rates of suicide attempts and suicide compared to those without ASD and to identify potential risk factors.
Author: Kairi Kõlves, Ph.D., of Griffith University in Brisbane, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33565)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict ...
2021-01-12
BOSTON -- For women hoping to achieve a pregnancy using freshly retrieved donor eggs, a new retrospective study led by researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital may provide important insight. Brigham senior author Janis H. Fox, MD, had observed that when freshly retrieved donor eggs were used, pregnancy rates were higher for fresh compared to frozen embryo transfers. Fox and her colleagues were intrigued by this observation. The team set out to scientifically determine if this observation would be replicated in a larger sample of recipients. Leveraging national data from the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART), the Brigham researchers found that, in cycles using freshly retrieved donor eggs, fresh embryo transfers were indeed ...
2021-01-12
A detailed analysis of the burden of osteoporosis in eight Eurasian countries has found that osteoporosis is a significant and growing health problem in the region that will escalate in the future due to expected demographic changes.
The authors of the Audit report [1] carried out a review of the available literature and a survey of the representatives of the national osteoporosis societies in eight Eurasian countries. The Audit reviews both the burden and the differences between Armenia, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, the Russian Federation, and Uzbekistan with regard to the prevalence of osteoporosis and incidence of osteoporotic fractures, future demographic changes, diagnostic resources, and treatment availability.
The findings ...
2021-01-12
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a new laser-based process for 3D printing intricate parts made of glass. With further development, the new method could be useful for making complex optics for vision, imaging, illumination or laser-based applications.
"Most 3D printing processes build up an object layer by layer," said research team leader Laurent Gallais from The Fresnel Institute and Ecole Centrale Marseille in France. "Our new process avoids the limitations of these processes by using a laser beam to transform -- or polymerize -- a liquid precursor into solid glass."
In The Optical Society (OSA) journal Optics Letters, Gallais and research team members Thomas Doualle and Jean-Claude Andre demonstrate how they used the new technique to create detailed objects in ...
2021-01-12
The abundant presence of an enzyme known as low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase (LMWPTP) in tumor cells has long been considered an indicator of cancer aggressiveness and metastatic potential. It is also known to perform important functions in cells under normal conditions, participating in both the proliferation process and the regulation of intracellular systems. Research continues on its role in cancer progression.
In Brazil, a group of researchers at the University of Campinas’s In Vitro Bioassay and Signal Transduction Laboratory led by Professor Carmen Veríssima Ferreira-Halder are studying the possibility of inhibiting this protein phosphatase ...
2021-01-12
Scientists have determined the optimal conditions following a stem cell transplant that could control HIV without the need of an everyday pill, according to a study published today in eLife.
Finding the right balance of stem cell dose, cell type and timing of antiretroviral therapy (ART) could potentially lead to a spontaneous cure of HIV.
There are only two cases of HIV cure to date: the Berlin Patient and the London Patient, who both received stem cell transplants with stem cells from donors that lack a molecule called CCR5, which HIV is attracted to.
"The major obstacle to HIV eradication is a latent reservoir of long-lived infected cells, and cure strategies aim to eliminate all infected cells or permanently prevent viral reactivation ...
2021-01-12
Understanding the immune systems of oysters and clams is important in monitoring the effects of pollution and climate change on the health of molluscan species and the potential impacts on the aquaculture industry. Their immune responses also can serve as indicators of changes in ocean environments.
A new study involving the University of Maine assessed immune responses in four economically important marine mollusc species -- the blue mussel, soft-shell clam, Eastern oyster, and Atlantic jackknife clam -- and identified new biomarkers relating to changes ...
2021-01-12
BOSTON -- Reprogramming the rich connective tissue microenvironment of a liver cancer known as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) inhibits its progression and resistance to standard chemotherapy in animal models, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have found. This new treatment for a disease with extremely poor outcomes uses antibodies to block placental growth factor (PlGF), a member of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family, which has been widely studied for its role in new vessel formation in cancers. PlGF is highly expressed ...
2021-01-12
ORLANDO, Jan. 12, 2021 -Vehicles have evolved to become more efficient and sophisticated, but their fuel hasn't necessarily evolved along with them. The Department of Energy is determined to identify cleaner burning and renewable alternatives to gasoline, and through the work of two UCF researchers, the DOE is one step closer to that goal.
Research engineer Anthony C. Terracciano and Associate Professor Subith Vasu have developed a model that will help engine designers, fuel chemists and federal agencies determine whether certain biofuels should be implemented as an alternative fuel ...
2021-01-12
January 12, 2021 - A change in evidence-based guidelines for vasectomy may have led to a reduction in the number of follow-up tests to confirm the procedure was successful, reports a study in Urology Practice®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Originally published in 2012, and then updated in 2015, the AUA clinical guideline could significantly reduce the number of men undergoing multiple postvasectomy semen analyses (PVSAs) to confirm it's safe to stop using other methods of birth control, according to new research by Tony Chen, MD, of University of Washington, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Singing a tumor test song
Monitoring the stiffness of the tissue near a patient's thyroid while they sing a note can allow medical professionals to determine the presence of a tumor.

