Fetal-maternal discordance in APOL1 genotype contributes to preeclampsia risk
2021-01-12
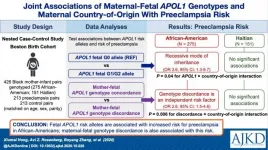
(Press-News.org) Fetal APOL1 kidney risk alleles are associated with increased risk for preeclampsia in African Americans and maternal fetal genotype discordance is also associated with this risk.
Preeclampsia, characterized by increased blood pressure after 20 weeks of pregnancy, as well as other abnormalities (e.g., protein in the urine), is dangerous to mothers and their infants. Previous studies found that individuals with African ancestry may carry APOL1 genetic variants that increase risk for chronic kidney disease. This study published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD) found that fetal high-risk APOL1 genotypes and maternal-fetal APOL1 genotype discordance independently contribute to preeclampsia risk in African-American mothers. This association was not observed in Haitian mother-infant pairs possibly because of different environmental exposures and cultural milieu. Additional studies are required to understand why APOL1 associations with preeclampsia differ by maternal country of origin and to improve management of mothers at risk for preeclampsia.
INFORMATION:
ARTICLE TITLE: Joint Associations of Maternal-Fetal APOL1 Genotypes and Maternal Country of Origin With Preeclampsia Risk
AUTHORS: Xiumei Hong, MD, PhD, Avi Z. Rosenberg, MD, PhD, Boyang Zhang, BS, Elizabeth Binns-Roemer, Victor David, MS, Yiming Lv, BS, Rebecca C. Hjorten, MD, Kimberly J. Reidy, MD, Teresa K. Chen, MD, MHS, Guoying Wang, MD, PhD, Yuelong Ji, PhD, Claire L. Simpson, PhD, Robert L. Davis, MD, MPH, Jeffrey B. Kopp, MD, Xiaobin Wang, MD, MPH, and Cheryl A. Winkler, PhD
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.10.020
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-12
TROY, N.Y. -- An analysis of an exhaustive dataset on cells essential to the mammalian immune system shows that our ability to fight disease may rely more heavily on daily circadian cycles than previously assumed.
Malfunctions in circadian rhythms, the process that keeps our bodies in tune with the day/night cycles, are increasingly associated with diabetes, cancer, Alzheimer's, and many other diseases. An investigation published today in Genome Research shows that the activity of macrophages -- cells within us that seek and destroy intruders like bacteria -- may time daily changes in their responses to pathogens and stress through the circadian control of metabolism.
In this study, ...
2021-01-12
Organizations seeking to fill internal roles traditionally have two options: promote from within or hire externally. Internal promotions benefit from being vetted talent who possess firm-specific skills while outside hires harbor external knowledge that can infuse an organization with new energy. Though this dichotomy is often accepted as unavoidable, there is a third option: boomerang employees.
Boomerang employees are those who return to an organization after an amicable absence. Whether the absence was for personal or professional reasons, their return provides unique value to an ...
2021-01-12
A team of astronomers led by the University of Arizona has observed a luminous quasar 13.03 billion light-years from Earth - the most distant quasar discovered to date. Dating back to 670 million years after the Big Bang, when the universe was only 5% its current age, the quasar hosts a supermassive black hole equivalent to the combined mass of 1.6 billion suns.
In addition to being the most distant - and by extension, earliest - quasar known, the object is the first of its kind to show evidence of an outflowing wind of super-heated gas escaping from the surroundings of the black hole at a fifth of the speed of light. In ...
2021-01-12
An international team of astronomers has discovered the most distant quasar yet found -- a cosmic monster more than 13 billion light-years from Earth powered by a supermassive black hole more than 1.6 billion times more massive than the Sun and more than 1,000 times brighter than our entire Milky Way Galaxy.
The quasar, called J0313-1806, is seen as it was when the Universe was only 670 million years old and is providing astronomers with valuable insight on how massive galaxies -- and the supermassive black holes at their cores -- formed in the early Universe. The scientists presented their findings to the American Astronomical Society's meeting, now underway virtually, and in a paper accepted to ...
2021-01-12
Maunakea, Hawaii - The most distant quasar known has been discovered. The quasar, seen just 670 million years after the Big Bang, is 1000 times more luminous than the Milky Way, and is powered by the earliest known supermassive black hole, which weighs in at more than 1.6 billion times the mass of the Sun. Seen more than 13 billion years ago, this fully formed distant quasar is also the earliest yet discovered, providing astronomers with insight into the formation of massive galaxies in the early universe. The result was released today at the January 2021 meeting of the American Astronomical Society (AAS).
Quasars, which are powered by the feeding frenzies of colossal supermassive black holes, are the most energetic objects ...
2021-01-12
The American Society of Hematology (ASH), the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH), National Hemophilia Foundation (NHF), and World Federation of Hemophilia (WFH) have developed joint clinical practice guidelines on the diagnosis and management of von Willebrand Disease (VWD), the world's most common inherited bleeding disorder. The guidelines were published today in Blood Advances.
VWD affects approximately 1% of the world's population, and it is the most common bleeding disorder. Although VWD occurs among men and women equally, women are more likely to notice the symptoms because of heavy or abnormal bleeding during their menstrual periods and after childbirth. This inherited condition results in the ...
2021-01-12
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - Jan 12, 2020 - Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute have identified the sensor in human lungs that detects SARS-CoV-2 and signals that it's time to mount an antiviral response. The study, published today in Cell Reports, provides insights into the molecular basis of severe disease and may enable new strategies for the treatment and prevention of COVID-19.
"Our research has shown that MDA-5 is the immune cop that's tasked to keep an eye out for SARS-CoV-2 and call for back-up," says Sumit Chanda, Ph.D., director of the Immunity and Pathogenesis Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys and senior author of the study. ...
2021-01-12
Key Takeaways:
Machine learning can be an effective tool to set competitive prices.
Artificial intelligence has its limits on how to set the most effective prices due to variables beyond the seller's control.
Over the long term, supracompetitive pricing can result.
CATONSVILLE, MD, January 12, 2021 - Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are perfectly suited to help companies and marketers monitor and set prices based on real-time dynamic pricing. But new research has identified some possible unintended consequences of AI in this area.
Machine learning algorithms don't always account for factors outside of the seller's control, such as competitor prices. Researchers ...
2021-01-12
The daily toll of COVID-19, as measured by new cases and the growing number of deaths, overlooks a shadowy set of casualties: the rising risk of mental health problems among health care professionals working on the frontlines of the pandemic.
A new study, led by University of Utah Health scientists, suggests more than half of doctors, nurses, and emergency responders involved in COVID-19 care could be at risk for one or more mental health problems, including acute traumatic stress, depression, anxiety, problematic alcohol use, and insomnia. The researchers found that the risk of these mental health conditions was comparable to rates observed during natural disasters, such as 9/11 and Hurricane Katrina.
"What health care workers are experiencing is akin to domestic combat," says ...
2021-01-12
LOS ANGELES (Jan. 11, 2021) -- Cell-derived exosomes are effective in treating disease when mixed with the dominant protein in breast milk and given orally, a new Smidt Heart Institute study of laboratory mice shows. The findings, published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, could help develop new oral medications for treating patients with muscular dystrophy and heart failure.
The study builds on more than a decade of research led by Eduardo Marbán, MD, PhD, executive director of the Smidt Heart Institute and Cedars-Sinai professor of Cardiology. The research has focused on human cardiosphere-derived ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fetal-maternal discordance in APOL1 genotype contributes to preeclampsia risk