INFORMATION:
When Physical and Social Pain Coexist: Insights Into Opioid Therapy
Mark D. Sullivan, MD, PhD and Jane C. Ballantyne, MD
University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
https://www.annfammed.org/content/19/1/63
Treatment for chronic pain must address both physical and social pain
2021-01-12
(Press-News.org) Physical pain and social pain may be more closely related than previously thought. Social pain, which typically results from interpersonal rejection or abuse, has been viewed as a non-medical response to external factors. However, recent research suggests that some physical and social stress responses may arise because of shared processing in the brain. Long-term usage of opioid medications could perpetuate a cycle of experiencing both physical and social pain and may increase risk of addiction. The authors, both of whom prescribe opioid medications, caution, "We must recognize that when physical and social pain coexist, long-term opioid therapy is more likely to harm than help." They advocate a move "toward chronic pain care models that do not separate physical pain (as a medical issue) from social pain (as a non-medical issue)."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fewer patient encounters drive decline in total primary care office visits
2021-01-12
Despite seeing gains in insurance coverage for preventive health services under the Affordable Care Act, the US has seen a declining rate of primary care visits over the past fifteen years. Are fewer individuals seeing primary care physicians? The authors of this study compared two factors that contribute to that decline to determine whether it was the number of primary care patients or the frequency of their clinical visits that contributed most to the overall decline. Over a fifteen year period from 2002 to 2017, both the number of unique patients seeing PCPs and the number of visits per patient declined. At the start of their analysis in 2002, most Americans saw a primary care physician about 4.3 times in a two-year span. By the end of the study in 2016, frequency ...
Consent forms design influences patient willingness to share personal health information
2021-01-12
Patients are sometimes asked to share their personal health information for research purposes. Informed consent and trust are critical components in a patient's decision to participate in research. Researchers at the University of Florida conducted a three-arm randomized controlled trial to compare the effects on patient experiences of three electronic consent (e-consent) designs that asked them to share PHI for research purposes. Participants were randomized to a standard e-consent form (standard); an e-consent that contained standard information plus hyperlinks to additional interactive details (interactive); or an e-consent that contained standard information, interactive hyperlinks, and factual ...
No-till practices in vulnerable areas significantly reduce soil erosion
2021-01-12
URBANA, Ill. - Soil erosion is a major challenge in agricultural production. It affects soil quality and carries nutrient sediments that pollute waterways. While soil erosion is a naturally occurring process, agricultural activities such as conventional tilling exacerbate it. Farmers implementing no-till practices can significantly reduce soil erosion rates, a new University of Illinois study shows.
Completely shifting to no-till would reduce soil loss and sediment yield by more than 70%, says Sanghyun Lee, doctoral student in the Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering at U of I and lead author on the study, published in Journal of Environmental Management.
But even a partial change in tilling practices could have significant results, he adds.
"If we ...
New study examines medical practice patterns over time
2021-01-12
Harmful medical practices, like inappropriate prescribing of opioids and racial and income-based discrimination in clinical settings, can vary across medical practices and individuals. Patients may find that even common primary care health services, like getting a chest x-rays or a referral to a heart or lung specialist, can differ widely depending on your doctor or clinic location. These variations in medical practice can have serious consequences for the quality, equity and cost of one's health care; however, it's unclear whether these disparities can be attributed to individual differences, from one ...
Researchers speed up analysis of Arctic ice and snow data through AI
2021-01-12
Researchers at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) have developed a technique to more quickly analyze extensive data from Arctic ice sheets in order to gain insight and useful knowledge on patterns and trends. Over the years, vast amounts of data have been collected about the Arctic and Antarctic ice. These data are essential for scientists and policymakers seeking to understand climate change and the current trend of melting. Masoud Yari, research assistant professor, and Maryam Rahnemoonfar, associate professor of information systems, have utilized new AI technology to develop a fully automatic technique to analyze ice data, published in the Journal ...
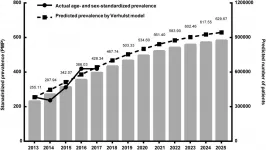
Prevalence of patients receiving dialysis in China may exceed 800,000 by 2025
2021-01-12
Study published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD) projects that prevalence of patients receiving dialysis in China will increase from 384.4 patients per million (PPM) in 2017 to 629.7 PMP in 2025 with a predicted 874,373 patients receiving dialysis in 2025.
The national prevalence of dialysis in China has not been well studied due to its large population and limited resources. Insurance claims data provide a unique opportunity to understand the burden of kidney failure and have been used to characterize dialysis patients in the ...
Metabolism may play role in recurrent major depression
2021-01-12
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, in collaboration with Dutch scientists, have found that certain metabolites -- small molecules produced by the process of metabolism -- may be predictive indicators for persons at risk for recurrent major depressive disorder.
The findings were published in the January 11, 2021 online issue of Translational Psychiatry.
"This is evidence for a mitochondrial nexus at the heart of depression," said senior author Robert K. Naviaux, MD, PhD, professor of medicine, pediatrics and pathology at UC San Diego School of Medicine. "It's a small study, but it is the first to show the potential of using metabolic ...
CDC report: removing unnecessary medical barriers to contraception
2021-01-12
New Rochelle, NY, January 12, 2021--The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is committed to removing unnecessary medical barriers to contraception use by people with certain characteristics or medical conditions. The CDC is celebrating the 10th anniversary of the release of its U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use (MEC), with an exclusive article published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women's Health. Click here to read the article now.
The CDC has updated the MEC recommendations over the past decade based on new evidence. It has collaborated with national partners to disseminate and implement the guidelines and has conducted surveys of health ...
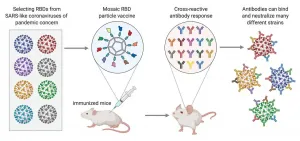
Nanoparticle immunization technology could protect against many strains of coronaviruses
2021-01-12
The SARS-CoV-2 virus that is causing the COVID-19 pandemic is just one of many different viruses in the coronavirus family. Many of these are circulating in populations of animals like bats and have the potential to "jump" into the human population, just as SARS-CoV-2 did. Researchers in the laboratory of Pamela Björkman, the David Baltimore Professor of Biology and Bioengineering, are working on developing vaccines for a wide range of related coronaviruses, with the aim of preventing future pandemics.
Now, led by graduate student Alex Cohen, a Caltech ...
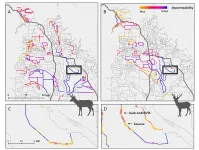
New study reveals how fences hinder migratory wildlife in the West
2021-01-12
Berkeley -- Each year, thousands of migratory mule deer and pronghorn antelope journey northwest from their winter homes in the Green River Basin, a grassland valley in western Wyoming, to their summer homes in the mountainous landscape near Grand Teton National Park.
But to reach their destination, these ungulates must successfully navigate the more than 6,000 kilometers (3,728 miles) of fencing that crisscrosses the region. That's enough distance to span nearly twice the length of the U.S.-Mexico border.
In a new study, wildlife biologists at the University of California, Berkeley, combined GPS location data of tagged mule deer and pronghorn with satellite imagery of ...