INFORMATION:
Pregnancy Medicaid Improvements in a Nonexpansion State After the Affordable Care Act
Jonas J. Swartz, MD, MPH, et al
Duke University, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Durham, North Carolina
https://www.annfammed.org/content/19/1/38
North Carolina simplifies medicaid enrollment, improves coverage for pregnant women
Pregnant women in North Carolina gain access to more comprehensive coverage through simplified full Medicaid enrollment
2021-01-12
(Press-News.org) North Carolina did not expand Medicaid eligibility under the Affordable Care Act, which continued to put many low-income women at risk for losing health care coverage post partum. The state did comply with ACA standards for simplifying Medicaid enrollment, automating the process and removing a stringent and often cumbersome financial assessment process. Analysis from researchers at Duke University found that these reforms enabled more low-income women to qualify for full Medicaid and reduced the number of women who instead qualified for more limited benefits under the state's Medicaid for Pregnant Women program. Researchers examined Medicaid claims and vital statistics in North Carolina from 2011 to 2017 and determined that, after changing the full Medicaid enrollment process in 2013 to adhere to the ACA standards, enrollment in full Medicaid during pregnancy doubled and Medicaid for Pregnant Women fell. Full Medicaid does not expire after 60 days and allows women access to crucial preventative health services that include primary care and contraception.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reviewing the evidence for cloth mask use among health care workers
2021-01-12
A rapid, evidence-based review summarizes the effectiveness of cloth masks in protecting health care clinicians from respiratory viral infections, such as COVID-19. Nine studies were included in the review, and all but one were conducted prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. The only randomized trial of cloth face masks published at the time of this review compared the infection rates of influenza-like illness among groups of health care professionals who wore cloth masks, medical masks, or inconsistent mask use in the hospital setting. That study reported wide-ranging confidence intervals ...
Primary care plays key role in managing COVID-19 in three Asian cities
2021-01-12
Despite having some of the densest living spaces and the highest number of international visitors, Hong Kong, Singapore, and Beijing have utilized their respective primary health care systems to keep their COVID-19 cases and deaths relatively low. Researchers studied the primary health care systems in the three cities to identify features of each system that other cities can use as examples to prepare for and prevent deaths in future health crises. Wong et al write that all three cities have made use of primary care in performing public health surveillance and ...
Treatment for chronic pain must address both physical and social pain
2021-01-12
Physical pain and social pain may be more closely related than previously thought. Social pain, which typically results from interpersonal rejection or abuse, has been viewed as a non-medical response to external factors. However, recent research suggests that some physical and social stress responses may arise because of shared processing in the brain. Long-term usage of opioid medications could perpetuate a cycle of experiencing both physical and social pain and may increase risk of addiction. The authors, both of whom prescribe opioid medications, caution, "We must recognize ...
Fewer patient encounters drive decline in total primary care office visits
2021-01-12
Despite seeing gains in insurance coverage for preventive health services under the Affordable Care Act, the US has seen a declining rate of primary care visits over the past fifteen years. Are fewer individuals seeing primary care physicians? The authors of this study compared two factors that contribute to that decline to determine whether it was the number of primary care patients or the frequency of their clinical visits that contributed most to the overall decline. Over a fifteen year period from 2002 to 2017, both the number of unique patients seeing PCPs and the number of visits per patient declined. At the start of their analysis in 2002, most Americans saw a primary care physician about 4.3 times in a two-year span. By the end of the study in 2016, frequency ...
Consent forms design influences patient willingness to share personal health information
2021-01-12
Patients are sometimes asked to share their personal health information for research purposes. Informed consent and trust are critical components in a patient's decision to participate in research. Researchers at the University of Florida conducted a three-arm randomized controlled trial to compare the effects on patient experiences of three electronic consent (e-consent) designs that asked them to share PHI for research purposes. Participants were randomized to a standard e-consent form (standard); an e-consent that contained standard information plus hyperlinks to additional interactive details (interactive); or an e-consent that contained standard information, interactive hyperlinks, and factual ...
No-till practices in vulnerable areas significantly reduce soil erosion
2021-01-12
URBANA, Ill. - Soil erosion is a major challenge in agricultural production. It affects soil quality and carries nutrient sediments that pollute waterways. While soil erosion is a naturally occurring process, agricultural activities such as conventional tilling exacerbate it. Farmers implementing no-till practices can significantly reduce soil erosion rates, a new University of Illinois study shows.
Completely shifting to no-till would reduce soil loss and sediment yield by more than 70%, says Sanghyun Lee, doctoral student in the Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering at U of I and lead author on the study, published in Journal of Environmental Management.
But even a partial change in tilling practices could have significant results, he adds.
"If we ...
New study examines medical practice patterns over time
2021-01-12
Harmful medical practices, like inappropriate prescribing of opioids and racial and income-based discrimination in clinical settings, can vary across medical practices and individuals. Patients may find that even common primary care health services, like getting a chest x-rays or a referral to a heart or lung specialist, can differ widely depending on your doctor or clinic location. These variations in medical practice can have serious consequences for the quality, equity and cost of one's health care; however, it's unclear whether these disparities can be attributed to individual differences, from one ...
Researchers speed up analysis of Arctic ice and snow data through AI
2021-01-12
Researchers at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) have developed a technique to more quickly analyze extensive data from Arctic ice sheets in order to gain insight and useful knowledge on patterns and trends. Over the years, vast amounts of data have been collected about the Arctic and Antarctic ice. These data are essential for scientists and policymakers seeking to understand climate change and the current trend of melting. Masoud Yari, research assistant professor, and Maryam Rahnemoonfar, associate professor of information systems, have utilized new AI technology to develop a fully automatic technique to analyze ice data, published in the Journal ...
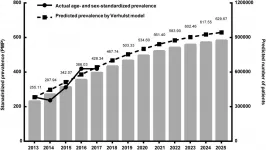
Prevalence of patients receiving dialysis in China may exceed 800,000 by 2025
2021-01-12
Study published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD) projects that prevalence of patients receiving dialysis in China will increase from 384.4 patients per million (PPM) in 2017 to 629.7 PMP in 2025 with a predicted 874,373 patients receiving dialysis in 2025.
The national prevalence of dialysis in China has not been well studied due to its large population and limited resources. Insurance claims data provide a unique opportunity to understand the burden of kidney failure and have been used to characterize dialysis patients in the ...
Metabolism may play role in recurrent major depression
2021-01-12
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, in collaboration with Dutch scientists, have found that certain metabolites -- small molecules produced by the process of metabolism -- may be predictive indicators for persons at risk for recurrent major depressive disorder.
The findings were published in the January 11, 2021 online issue of Translational Psychiatry.
"This is evidence for a mitochondrial nexus at the heart of depression," said senior author Robert K. Naviaux, MD, PhD, professor of medicine, pediatrics and pathology at UC San Diego School of Medicine. "It's a small study, but it is the first to show the potential of using metabolic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
[Press-News.org] North Carolina simplifies medicaid enrollment, improves coverage for pregnant womenPregnant women in North Carolina gain access to more comprehensive coverage through simplified full Medicaid enrollment