Need to reduce work-related stress? It's a walk in the park
Study from the University of Tsukuba finds that taking regular walks in forests and greenspaces may be connected with workers' stress-coping abilities
2021-01-13
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan - Work causes so much stress that it's become a global public health issue. Stress's impact on mental and physical health can also hurt productivity and result in economic loss. A new study now finds that working people who regularly take walks in forests or greenspaces may have higher stress-coping abilities.
In a study published in Public Health in Practice, researchers led by Professor Shinichiro Sasahara at the University of Tsukuba analyzed workers' "sense of coherence" (SOC) scores, demographic attributes, and their forest/greenspace walking habits. SOC comprises the triad of meaningfulness (finding a sense of meaning in life), comprehensibility (recognizing and understanding stress), and manageability (feeling equipped to deal with stress). Studies have found factors such as higher education and being married can strengthen SOC, while smoking and not exercising can weaken it. People with strong SOC also have greater resilience to stress.
The study used survey data on more than 6,000 Japanese workers between 20 and 60 years old. It found stronger SOC among people who regularly took walks in forests or greenspaces.
"SOC indicates mental capacities for realizing and dealing with stress," Professor Sasahara says. "With workplace stress as a focal issue, there's a clear benefit in identifying everyday activities that raise SOC. It seems we may have found one."
People find comfort in nature, and in countries like Japan urban greenspaces are increasing in popularity where nature isn't readily accessible. This means many workers in cities can easily take a walk among the trees.
The researchers divided the survey respondents into four groups based on their frequency of forest/greenspace walking. Then, they compared their walking activity against attributes such as age, income, and marital status, and with the respondents' SOC scores, which were grouped as weak, middle, and strong.
Those with strong SOC showed a significant correlation with both forest and greenspace walking at least once a week. This key finding implies the greater benefits of urban greening--not just environmental, but also socioeconomic.
"Our study suggests that taking a walk at least once a week in a forest or greenspace can help people have stronger SOC," explains Professor Sasahara. "Forest/greenspace walking is a simple activity that needs no special equipment or training. It could be a very good habit for improving mental health and managing stress."
INFORMATION:
The article, "Association between forest and greenspace walking and stress-coping skills among workers of Tsukuba Science City, Japan: A cross-sectional study," was published in Public Health in Practice at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhip.2020.100074
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-13
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Jan. 13, 2021)--If you're a bit more forgetful or having more difficulty processing complex concepts than in the past, the problem may be your menopause stage. A new study claims that menopause stage is a key determinant of cognition and, contrary to previous studies, shows that certain cognitive declines may continue into the postmenopause period. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
It's commonly assumed that people's memories decline with age, as does their ability to learn new things and grasp challenging concepts. ...
2021-01-13
The ability of our skin to protect us from chemicals is something we inherit. Some people are less well-protected which could imply an increased risk of being afflicted by skin disease or cancer. A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden that has been published in Environmental Health Perspectives shows how the rate of uptake of common chemicals is faster in people with a genetically weakened skin barrier.
We are continually exposed to chemicals from many different sources, for example, food, hygiene products, cosmetics and textiles. Many people are also exposed to chemicals at their place of work which can constitute a work environment problem.
The protein filaggrin is important for the structure and moisture balance of the skin, properties that affect ...
2021-01-13
January 13, 2021 - The element nitrogen is a double-edged sword. It is essential for growing plants and feeding people, but it is also a leading cause of pollution across the world. Only by using nitrogen more sustainably can the positive and harmful effects of nitrogen be balanced.
Xia (Emma) Liang, a member of the American Society of Agronomy, studies nitrogen loss during food production.
Liang and her team created a framework that accurately measures nitrogen loss across a wide variety of crops and food products. She recently presented their research at the virtual 2020 ASA-CSSA-SSSA Annual Meeting.
"This framework can capture the environmental impacts and societal costs of nitrogen ...
2021-01-13
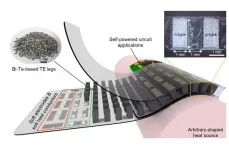
A thermoelectric device is an energy conversion device that utilizes the voltage generated by the temperature difference between both ends of a material; it is capable of converting heat energy, such as waste heat from industrial sites, into electricity that can be used in daily life. Existing thermoelectric devices are rigid because they are composed of hard metal-based electrodes and semiconductors, hindering the full absorption of heat sources from uneven surfaces. Therefore, recent studies were actively conducted on the development of flexible thermoelectric devices capable of generating energy in close contact with various heat sources such as human skins and hot water pipes.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced ...
2021-01-13
A rare mineral that has allowed Roman concrete marine barriers to survive for more than 2,000 years has been found in the thick concrete walls of a decommissioned nuclear power plant in Japan. The formation of aluminous tobermorite increased the strength of the walls more than three times their design strength, Nagoya University researchers and colleagues report in the journal Materials and Design. The finding could help scientists develop stronger and more eco-friendly concrete.
"We found that cement hydrates and rock-forming minerals reacted in a way similar to what ...
2021-01-13
Researchers from University of Hawaii and University of Florida published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that argues that a biological account of human behavior, especially undesirable behavior, will benefit human welfare. This biological perspective can complement traditional psychological, anthropological, and economic perspectives on consumption, particularly with respect to the vital topic of self-control.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Consumer Self-Control and the Biological Sciences: Implications for Marketing Stakeholders" and is authored by Yanmei Zheng and Joe Alba.
Society's understanding of human ills is constantly evolving. Many ill-advised consumer behaviors are conventionally viewed through a non-biological ...
2021-01-13
CLEVELAND--The combined effectiveness of three COVID-prevention strategies on college campuses--mask-wearing, social distancing, and routine testing--are as effective in preventing coronavirus infections as the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), according to a new study co-authored by a Case Western Reserve University researcher.
The research, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, has immediate significance as college semesters are poised to start again--and as the distribution of approved vaccines lags behind goals.
The study found that a combination of just two common measures--distancing and mandatory masks--prevents 87% of campus COVID-19 infections and costs only $170 per infection prevented. ...
2021-01-13
New research from King's College London shows nearly half of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) staff are likely to meet the threshold for PTSD, severe anxiety or problem drinking during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Results from a study of ICU healthcare workers, published today in Occupational Medicine, shows the stark impact of working in critical care during the COVID-10 pandemic. The researchers found poor mental health was common in many ICU clinicians although they were more pronounced in nurses than in doctors or other healthcare professionals.
Lead author, Professor Neil Greenberg, from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN), King's College London said:
'Our results show a substantial burden of mental health symptoms being reported by ICU staff towards the end ...
2021-01-13
As schools prepare to re-open to all pupils in February, experts warn that UK government plans for mass testing risks spreading covid-19 more widely.
Writing in The BMJ, Professor Jon Deeks and colleagues at the Royal Statistical Society argue that using the INNOVA rapid lateral flow tests to manage classroom outbreaks, without isolating close contacts, risks increasing disease spread and causing further disruption to children's education.
Before Christmas, schools limited pupil mixing and activities, and isolated pupil groups at home once a covid-19 case was identified, they explain. This year the government is relying on the INNOVA rapid lateral flow tests to mass screen staff and pupils, and test close contacts ...
2021-01-12
Crowdsourced Responses from Dermatologists on Twitter Found to be as Effective as Formal Telemedicine
At the start of the pandemic, many doctors on the front lines turned to Twitter and other social media platforms to find guidance and solace directly from their peers. In early 2020, information on COVID-19 had yet to be studied and published in peer-reviewed journals or printed in medical textbooks. Since then, social media has been characterized as both a boon to medical communities seeking real time information and a major driver of misinformation on the virus and its spread. A new study from researchers at the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Need to reduce work-related stress? It's a walk in the park
Study from the University of Tsukuba finds that taking regular walks in forests and greenspaces may be connected with workers' stress-coping abilities