(Press-News.org) The ability of our skin to protect us from chemicals is something we inherit. Some people are less well-protected which could imply an increased risk of being afflicted by skin disease or cancer. A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden that has been published in Environmental Health Perspectives shows how the rate of uptake of common chemicals is faster in people with a genetically weakened skin barrier.
We are continually exposed to chemicals from many different sources, for example, food, hygiene products, cosmetics and textiles. Many people are also exposed to chemicals at their place of work which can constitute a work environment problem.
The protein filaggrin is important for the structure and moisture balance of the skin, properties that affect the skin's ability to function as a barrier against chemicals.
Earlier research has indicated that inherited variations of DNA sequences for filaggrin mean some people have less good "barrier protection" which leads to an increased uptake of chemicals. That could imply a greater risk of being afflicted by cancer or various skin diseases such as contact dermatitis.
This genetic variation is relatively common in northern Europe and occurs in a person when one of the parents has the genetic predisposition in question. About ten percent of Swedes have this variation.
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet and Lund University have shown in a new study that this genetic variation leads to a considerably faster uptake of three common chemicals through the skin.
The researchers screened 500 people in Sweden. The results are based on 23 people with the mutation that causes a deficit of filaggrin, and 31 people who do not have it. The participants in the study were exposed to a harmless dose of three chemicals on their skin for four hours.
The chemicals used for the study were a pesticide used in Sweden, a UV filter used in sunscreen, and a hydrocarbon found in, for example, smoke from firewood.
The researchers were able to calculate the speed of uptake and the dose in the body with the help of urine samples taken from the participants during a period of 48 hours.
"We found, for example, twice as high a dose of the pesticide in the people with a mutation compared with those without. The fact that the skin takes up a greater amount of certain chemicals as a result of a genetic variation could mean that people with this mutation get a higher internal dose and, in the long run, could be at greater risk of disease such as cancer or a hormonal disorder," says Karin Broberg, Professor at the Department of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, and the study's last author. She continues:
"For the next step, we are planning to investigate whether the mutation affects the uptake of other chemicals in the skin. We also want to find out whether these mutations lead to disease caused by chemicals in the body and in the skin."
INFORMATION:
The research has been funded by Forte, Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, Formas, Karolinska Institutet, Region Skane and the Faculty of Medicine at Lund University. There are no reported conflicts of interests.
Publication: "Filaggrin polymorphisms and the uptake of chemicals through the skin - a human experimental study". Emelie Rietz Liljedahl, Gunnar Johanson, Helena Korres de Paula, Moosa Faniband, Eva Assarsson, Margareta Littorin, Malin Engfeldt, Carola Liden, Anneli Julander, Karin Wahlberg, Christian Lindh, and Karin Broberg. Environmental Health Perspectives, online 13 January 2021, doi:10.1289/EHP7310.
January 13, 2021 - The element nitrogen is a double-edged sword. It is essential for growing plants and feeding people, but it is also a leading cause of pollution across the world. Only by using nitrogen more sustainably can the positive and harmful effects of nitrogen be balanced.
Xia (Emma) Liang, a member of the American Society of Agronomy, studies nitrogen loss during food production.
Liang and her team created a framework that accurately measures nitrogen loss across a wide variety of crops and food products. She recently presented their research at the virtual 2020 ASA-CSSA-SSSA Annual Meeting.
"This framework can capture the environmental impacts and societal costs of nitrogen ...
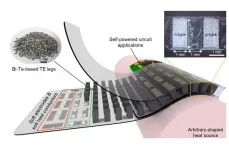
A thermoelectric device is an energy conversion device that utilizes the voltage generated by the temperature difference between both ends of a material; it is capable of converting heat energy, such as waste heat from industrial sites, into electricity that can be used in daily life. Existing thermoelectric devices are rigid because they are composed of hard metal-based electrodes and semiconductors, hindering the full absorption of heat sources from uneven surfaces. Therefore, recent studies were actively conducted on the development of flexible thermoelectric devices capable of generating energy in close contact with various heat sources such as human skins and hot water pipes.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced ...
A rare mineral that has allowed Roman concrete marine barriers to survive for more than 2,000 years has been found in the thick concrete walls of a decommissioned nuclear power plant in Japan. The formation of aluminous tobermorite increased the strength of the walls more than three times their design strength, Nagoya University researchers and colleagues report in the journal Materials and Design. The finding could help scientists develop stronger and more eco-friendly concrete.
"We found that cement hydrates and rock-forming minerals reacted in a way similar to what ...
Researchers from University of Hawaii and University of Florida published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that argues that a biological account of human behavior, especially undesirable behavior, will benefit human welfare. This biological perspective can complement traditional psychological, anthropological, and economic perspectives on consumption, particularly with respect to the vital topic of self-control.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Consumer Self-Control and the Biological Sciences: Implications for Marketing Stakeholders" and is authored by Yanmei Zheng and Joe Alba.
Society's understanding of human ills is constantly evolving. Many ill-advised consumer behaviors are conventionally viewed through a non-biological ...
CLEVELAND--The combined effectiveness of three COVID-prevention strategies on college campuses--mask-wearing, social distancing, and routine testing--are as effective in preventing coronavirus infections as the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), according to a new study co-authored by a Case Western Reserve University researcher.
The research, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, has immediate significance as college semesters are poised to start again--and as the distribution of approved vaccines lags behind goals.
The study found that a combination of just two common measures--distancing and mandatory masks--prevents 87% of campus COVID-19 infections and costs only $170 per infection prevented. ...
New research from King's College London shows nearly half of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) staff are likely to meet the threshold for PTSD, severe anxiety or problem drinking during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Results from a study of ICU healthcare workers, published today in Occupational Medicine, shows the stark impact of working in critical care during the COVID-10 pandemic. The researchers found poor mental health was common in many ICU clinicians although they were more pronounced in nurses than in doctors or other healthcare professionals.
Lead author, Professor Neil Greenberg, from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN), King's College London said:
'Our results show a substantial burden of mental health symptoms being reported by ICU staff towards the end ...
As schools prepare to re-open to all pupils in February, experts warn that UK government plans for mass testing risks spreading covid-19 more widely.
Writing in The BMJ, Professor Jon Deeks and colleagues at the Royal Statistical Society argue that using the INNOVA rapid lateral flow tests to manage classroom outbreaks, without isolating close contacts, risks increasing disease spread and causing further disruption to children's education.
Before Christmas, schools limited pupil mixing and activities, and isolated pupil groups at home once a covid-19 case was identified, they explain. This year the government is relying on the INNOVA rapid lateral flow tests to mass screen staff and pupils, and test close contacts ...
Crowdsourced Responses from Dermatologists on Twitter Found to be as Effective as Formal Telemedicine
At the start of the pandemic, many doctors on the front lines turned to Twitter and other social media platforms to find guidance and solace directly from their peers. In early 2020, information on COVID-19 had yet to be studied and published in peer-reviewed journals or printed in medical textbooks. Since then, social media has been characterized as both a boon to medical communities seeking real time information and a major driver of misinformation on the virus and its spread. A new study from researchers at the ...
Mothers with multiple children report more fragmented sleep than mothers of a single child, but the number of children in a family doesn't seem to affect the quality of sleep for fathers, according to a study from McGill University.
A total of 111 parents (54 couples and 3 mothers of single-parent families) participated in the study published in the Journal of Sleep Research led by McGill doctoral student Samantha Kenny under the supervision of Marie-Hélène Pennestri, Assistant Professor in the Department of Educational and Counselling Psychology.
Participants' ...
At the start of the pandemic, many doctors on the front lines turned to Twitter and other social media platforms to find guidance and solace directly from their peers. In early 2020, information on COVID-19 had yet to be studied and published in peer-reviewed journals or printed in medical textbooks. Since then, social media has been characterized as both a boon to medical communities seeking real time information and a major driver of misinformation on the virus and its spread. A new study from researchers at the University of Paris provides support for social media as a potentially useful ...