Human-induced climate change caused the northwestern Pacific warming record in August 2020
A once-in-1000-year warming event has been already altered to occur once per 15 years because of past human activities
2021-01-14
(Press-News.org) August 2020 set new record high sea surface temperatures (SSTs) in the northwestern Pacific Ocean and around the Japan coasts. A new study led by National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES) researchers revealed that this warming record could not happen without human-induced climate changes.
The northwestern Pacific sea surface becomes warm seasonally around August every year. However, it was unprecedentedly high in August 2020, according to the Japan Meteorological Agency and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The extremely high SSTs exceeding 30°C, which lasted until mid-September, may have intensified tropical cyclones such as Typhoon Haisheng, causing severe damages to the East Asian countries. Although human-induced greenhouse gas emissions such as carbon dioxide have gradually warmed the northwestern Pacific Ocean since the mid-20th century, it remains unclear yet how much past human activities may increase the occurrence likelihood of such regional record-warm SSTs.
"Understanding the tropical warm water expansion in the Indo-Pacific and Atlantic Oceans is essential for projecting changes in the characteristics of tropical cyclones and other weather events in the future," said Hideo Shiogama, a co-author and the head of Climate Risk Assessment Section at the Center for Global Environmental Research, NIES. "A quantitative evaluation of what drives regional extreme temperatures happening recently is necessary to take appropriate measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and the impacts of global warming."
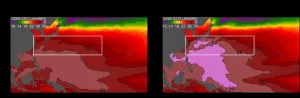
The paper published in Geophysical Research Letters illustrates the quantitative impact of greenhouse gases emitted by human activities on the unprecedentedly high SSTs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean in August 2020. By analyzing multiple observational datasets from 1901 to 2020 and a large number of experimental outputs from the state-of-the-art numerical climate models, a climate research group at NIES statistically estimated changes in the occurrence probability of the northwestern Pacific Ocean (120°E-180° and 20°N-35°N) condition exceeding the record-warm SST in August 2020 from the past to future. The scientists revealed that its probability in the present climate was increased from once-in-1000 years to once-in-15 years because of human-induced climate changes.
Detecting human-induced climate changes
"The numerical climate model ensembles are powerful tools to quantitatively distinguish between natural variability of the Earth system and climate changes caused by human activities," said corresponding lead author Michiya Hayashi, a research associate at NIES. The ensemble of 31 climate models participating in the sixth phase of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP6) consists of a series of historical experiments and future scenario experiments forced by greenhouse gas- and aerosol emissions from human activities and natural volcanic and solar variations from 1850 to 2100. "We can compare the historical and future experiments with a sub-ensemble of the CMIP6 climate models forced only by the natural volcanic and solar activities to estimate to what extent human-caused climate changes have altered the northwestern Pacific Ocean condition until today."
"The northwestern Pacific warming has proceeded clearly since the 1980s," stated Shiogama. "The warming speed has been accelerated in the last four decades as the reduced aerosol emissions do not cancel the warming signal forced by increasing greenhouse gas concentration anymore." The results show that the CMIP6 ensemble well reproduces the observed long-term change in the northwestern Pacific August SST within the range of 'once-in-20-year' events in the historical simulations. "The SSTs that exceed the pre-industrial range are rarely observed during the 20th century but have occurred frequently since 2010, indicating that human influences on the northwestern Pacific Ocean are already detectable in observations," noted a co-author Seita Emori, deputy director of the Center for Global Environmental Research at NIES.
This new study estimates that the occurrence frequency of high northwestern Pacific SSTs exceeding the August 2020 level has been increased from once-in-600 years in the 20th century (1901-2000) to once-in-15 years in the present climate (2001-2020) using the CMIP6 ensemble. On the other hand, in the sub-ensemble forced only by natural volcanic and solar activities, the frequency for 2001-2020 is estimated to be once-in-1000 years or less. "The record high level of the northwestern Pacific SST in August could have occurred approximately once per 15 years in 2001-2020, as observed, but it never likely occurred without human-induced greenhouse gases or in the 20th century," said Hayashi.
Importantly, the scientists also imply from the future scenario experiments that the 2020 record high SST is becoming a new normal climate condition in August at the northwestern Pacific region by 2031-2050 when the globally averaged air temperature relative to pre-industrial levels would exceed 1.5°C. In this case, the tropical warm sea surface water, exceeding 28°C, may reach Japan, the Korean Peninsula, the west coast of India, the east coast of the U.S. mainland, and the west of the Hawaiian Islands. "We might need to prepare for living with such warm ocean conditions even if we humans could achieve the 1.5°C goal of the Paris Agreement," said Hayashi.
"The human-induced ocean warming may have impacted tropical cyclones, heavy rainfall, and marine life from the past to present and will continue in the future unless tremendous mitigation measures would be implemented," added Emori. "It is time to take prompt actions to transform our society for reducing the greenhouse gas emissions and for adapting to a changing climate."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-14
At cruising altitude, airplanes emit a steady stream of nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, where the chemicals can linger to produce ozone and fine particulates. Nitrogen oxides, or NOx, are a major source of air pollution and have been associated with asthma, respiratory disease, and cardiovascular disorders. Previous research has shown that the generation of these chemicals due to global aviation results in 16,000 premature deaths each year.
Now MIT engineers have come up with a concept for airplane propulsion that they estimate would eliminate 95 percent of aviation's NOx emissions, and thereby reduce the number of associated early deaths by 92 percent.
The concept is inspired ...
2021-01-14
Tsukuba, Japan -- We laugh when we see Homer Simpson falling asleep while driving, while in church, and while even operating the nuclear reactor. In reality though, narcolepsy, cataplexy, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep behavior disorder are all serious sleep-related illnesses. Researchers at the University of Tsukuba led by Professor Takeshi Sakurai have found neurons in the brain that link all three disorders and could provide a target for treatments.
REM sleep correlates when we dream. Our eyes move back and forth, but our bodies remain still. This near-paralysis of muscles while dreaming is called REM-atonia, and is lacking in people with REM sleep behavior disorder. Instead ...
2021-01-14
Non-invasive imaging technique called 31-phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy used to measure mitochondrial function in patients with motor neuron disease (MND)
Evidence shows that mitochondria - often referred to as the cell's battery - are impaired in MND
This technique could be used to measure the effectiveness of future treatments for MND
Researchers from the Sheffield Institute for Translational Neuroscience (SITraN) have used a new imaging technique to measure the function of mitochondria in patients with motor neuron disease (MND).
The research, published today (13 January 2021) ...
2021-01-14
Patients with type 2 diabetes who follow a strict low carbohydrate diet for six months may experience greater rates of remission compared with other recommended diets without adverse effects, suggests a study published by The BMJ today.
The researchers acknowledge that most benefits diminished at 12 months, but say doctors might consider short term strict low carbohydrate diets for managing type 2 diabetes, while actively monitoring and adjusting diabetes medication as needed.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes worldwide and diet is recognised as an essential part of treatment. But uncertainty remains about which diet to choose and previous studies have reported mixed results.
To address this evidence gap, a team of international researchers ...
2021-01-13
The build-up of calcium in a major artery outside of the heart could predict future heart attack or stroke, a new Edith Cowan University led study has demonstrated.
Published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, the research could help doctors identify people at risk of cardiovascular disease years before symptoms arise.
Analysing 52 previous studies, the international team of researchers found that people who have abdominal aortic calcification (AAC) have a two to four times higher risk of a future cardiovascular event.
The study also found the more extensive the calcium in the blood vessel wall, the greater the risk of future cardiovascular events and people with AAC ...
2021-01-13
Decades of research show that depression, stress, loneliness, and poor health behaviors can weaken the body's immune system and lower the effectiveness of certain vaccines. A new report accepted for publication in Perspectives on Psychological Science suggests that the same may be true for the new COVID-19 vaccines that are in development and the early stages of global distribution. Fortunately, it may be possible to reduce these negative effects with simple steps like exercise and sleep.
Vaccines are among the safest and most effective advances in medical history, protecting society from a wide range of otherwise devastating diseases, including smallpox and polio. The key to their success, however, is ensuring that a critical percentage of the population is effectively ...
2021-01-13
Pulsed ultraviolet light can be an effective alternative to some of the antimicrobial technologies now used by the poultry industry to kill pathogens on eggshells, according to Penn State researchers, who simulated production conditions to test the technology.
Researcher Paul Patterson, professor of poultry science, College of Agricultural Sciences, suggests the technology has merit for commercial application in the egg industry.
"This study is unique because it scaled-up and applied components of standard egg processing to a conveyor and sanitizing eggs in a commercial setting," he said. "In the absence of water or other chemical sanitizers, this technology ...
2021-01-13
Honey bee health has been on the decline for two decades, with U.S. and Canadian beekeepers now losing about 25 to 40% of their colonies annually. And queen bees are failing faster than they have in the past in their ability to reproduce. The reason has been a mystery, but researchers at North Carolina State University and the University of British Columbia are finding answers.
Their latest research, published Jan. 8 in the journal Communications Biology, offers clues about what's behind queen bee failure, finding that when sperm viability is low, the expression of a protein known to act against pathogens such as bacteria and viruses is high.
David Tarpy, a University Faculty Scholar and professor in NC State's Department ...
2021-01-13
BOSTON -- Completing cancer screening tests, such as mammograms, can be challenging for low-income people, who may face such challenges as lack of transportation or inability to take time off work. A team at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) explored the possibility of addressing preventive care needs when patients are admitted to the hospital.
The pilot study, published in the Annals of Family Medicine, examined the feasibility of performing mammograms in women insured by Medicaid or both Medicaid and Medicare (dual-eligible patients) while they were hospitalized. "We designed the study to reach the patients who face significant barriers to completing their mammograms in the outpatient setting," says Andrew S. Hwang, MD, MPH, an internist at MGH and first author of ...
2021-01-13
DES PLAINES, IL -- Among children who were not in an independently verified incident, evaluation for child abuse should be done by specialty consultation in children aged less than three-years old presenting with rib fractures and children aged less than 18-months presenting with humeral or femoral fractures. That is the conclusion of a study titled Identifying Maltreatment in Infants and Young Children Presenting with Fractures: Does Age Matter?, to be published in the January 2021 issue of Yersinia pestis (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
The lead author of the study is Ian ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Human-induced climate change caused the northwestern Pacific warming record in August 2020
A once-in-1000-year warming event has been already altered to occur once per 15 years because of past human activities




