(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. - Researchers at Oregon State University have found that the blue orchard bee, an important native pollinator, produces female offspring at higher rates in the aftermath of wildfire in forests.
The more severe the fire had been, the greater percentage of females - more than 10% greater in the most badly burned areas relative to areas that burned the least severely.
"This is one of the first studies that has looked at how forest fire severity influences bee demography," said Jim Rivers, an animal ecologist with the OSU College of Forestry. "Sex ratio varied under different fire conditions but the number of young produced did not, which indicates bees altered the sex of their offspring depending on the degree of fire severity."
Female bees control the sex of their offspring, laying eggs fertilized with sperm that become females, or non-fertilized eggs that become males.
Bees pollinate many of the flowering plants that make up native ecosystems and food chains Understanding how fire - expected to increase in frequency and severity - influences their reproductive outputs is an important part of knowing how post-fire management actions could help or harm bees.
"We placed bees on different sites within recently burned mixed-conifer forest in southwestern Oregon and used them as a measuring stick to tell us how good the bee habitat was," said Sara Galbraith, a postdoctoral researcher in the College of Forestry. "Adjusting offspring production toward the more expensive offspring sex shows a functional response to changes in habitat quality via an increased density of flowering plants."
In general, pollinators benefit from canopy-reducing fires in dense conifer forest ecosystems; flowering plant abundance usually increases for several years following a fire, resulting in food resources that enhance wild bee diversity and abundance.
Bees are the most important among the Earth's pollinators, which combine for an estimated $100 billion in global economic impact each year. Oregon is home to more than 600 species of native bees.
Animal pollinators enhance the reproduction of nearly 90% of the Earth's flowering plants, including many food crops.
Pollinators are an essential component of insect and plant biodiversity. Bees are the standard bearer because they're usually present in the greatest numbers and because they're the only pollinator group that feeds exclusively on nectar and pollen their entire life.
For this study involving the blue orchard bee, known scientifically as Osmia lignaria, Galbraith, Rivers and James Cane of the U.S. Department of Agriculture set up nest blocks containing a standardized number and sex ratio of pre-emergent adult bees.
They then looked at the relationship between fire severity and reproductive output, sex ratio and offspring mass at the local (within 100 meters of the blocks) and landscape (750 meters) scales. Female bees forage across both scales when caring for offspring.
"In fire-prone landscapes, there is variation in species-level response to wildfire that serves to maintain ecosystem structure and function," Rivers said. "With the blue orchard bee and similar species, foraging females invest in larger progeny and more females when more resources are available."
The findings showed that burned mixed-conifer forest provides forage for the blue orchard bee along a gradient of severity, and that the rise in floral resources that comes after high-severity fire causes females to reallocate resources to the larger and more costly sex - females - when nesting.
"Our study revealed more female progeny than is typically observed with blue orchard bees," Galbraith said. "The greater proportion of females in areas surrounded by a more severely burned landscape indicates an investment in more female offspring because of greater resource availability."
INFORMATION:
Findings were published in Oecologia. The Bureau of Land Management and the OSU College of Forestry supported this research.
A first-of-its-kind, international study of 107,000 children finds that higher temperatures are an equal or even greater contributor to child malnutrition and low quality diets than the traditional culprits of poverty, inadequate sanitation, and poor education.
The 19-nation study is the largest investigation of the relationship between our changing climate and children's diet diversity to date. It is believed to be the first study across multiple nations and continents of how both higher temperatures and rainfall--two key results of climate change--have impacted children's diet diversity.
"Certainly, future climate changes have been predicted to affect malnutrition, but it surprised ...
DALLAS, Jan. 14, 2021 -- The longer the time between when heart attack symptoms start and a patient has an artery-clearing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), the more damage to the heart muscle, according to new research published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions, an American Heart Association journal.
A heart attack happens about every 40 seconds in the U.S., and the most common heart attack is caused by a complete blockage in a coronary artery, called ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). STEMI patients are most often treated with PCI, also known as angioplasty with stent, in which a catheter with a deflated balloon is inserted into the narrowed heart artery. Subsequently, the balloon is inflated, which clears the obstruction and restores ...
DALLAS, Jan. 14, 2021 -- Adults who smoke or who are genetically predisposed to smoking behaviors are more likely to experience a serious type of stroke called subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), according to new research published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association. The results of this study provide important evidence that there is a causal link between smoking and the risk of SAH.
SAH is a type of stroke that occurs when a blood vessel on the surface of the brain ruptures and bleeds into the space between the brain and the skull. It mainly affects middle-aged adults and has high rates of complications ...
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE (January 14, 2021) - A team of researchers led by engineers at Tufts University's School of Engineering and Stanford University's Program on Water, Health and Development have developed a novel and inexpensive chlorine dispensing device that can improve the safety of drinking water in regions of the world that lack financial resources and adequate infrastructure. With no moving parts, no need for electricity, and little need for maintenance, the device releases measured quantities of chlorine into the water just before it exits the tap. It provides a quick and ...
There is a growing consensus among scientists as well as national and local governments representing hundreds of millions of people, that humanity faces a climate crisis that demands a crisis response. New research from the University of California San Diego explores one possible mode of response: a massively funded program to deploy direct air capture (DAC) systems that remove CO2 directly from the ambient air and sequester it safely underground.
The findings reveal such a program could reverse the rise in global temperature well before 2100, but only with immediate and sustained investments from governments and firms to scale up the new technology.
Despite the enormous undertaking explored in the study, the research ...
Honeybee historians might seem like a flight of fancy but these tiny pollinators have been helping researchers from the National Botanic Garden of Wales track how the UK's fields, hedgerows, wild spaces and gardens have changed since the 1950s.Using cutting-edge DNA barcoding techniques, scientists at the Botanic Garden identified which plants modern-day honeybees visited most often by looking at the pollen grains trapped within honey.
They compared this to a 1952 survey of honey plants where a microscope had been used to painstakingly identify pollen grains in honey sent from hives across the country. The differences were clear. White clover had been the most important plant for honeybees but, with fewer pastures today and increased use of herbicides and inorganic ...
New research has unlocked the mystery of how the Galápagos Islands, a rocky, volcanic outcrop, with only modest rainfall and vegetation, is able to sustain its unique wildlife habitats.
The Galápagos archipelago, rising from the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean some 900 kilometres off the South American mainland, is an iconic and globally significant biological hotspot. The islands are renowned for their unique wealth of endemic species, which inspired Charles Darwin's theory of evolution and today underpins one of the largest UNESCO World Heritage Sites and Marine Reserves on Earth.
Scientists have known ...
Water isn't just crucial for life, it's fundamental to increasing opportunities for women and girls in rural areas across the globe. A new Stanford study reveals how bringing piped water closer to remote households in Zambia dramatically improves the lives of women and girls, while also improving economic opportunities, food security and well-being for entire households. The research, recently published in Social Science & Medicine, could spur governments and NGOs to more carefully evaluate the costs and benefits of piped water as an alternative to less accessible communal water sources.
"Switching from the village borehole to piped supply saved almost 200 hours of fetching time per year for a typical household," said study senior ...
A new paper in Q Open finds that the availability of fast food restaurants on the route between children's houses and their schools does not affect children's weight.
Reducing the rate of childhood obesity is a top public health priority in the United States where obesity rates are 18.4% for those ages 6-11 and 20.6% for those ages 12-19. Childhood obesity is a documented risk-factor for negative physical and mental health outcomes. Obese children are also more likely to become obese adults and suffer associated health problems.
Researchers have proposed that the accessibility ...
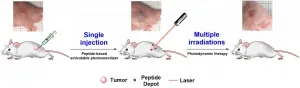
Researchers in South Korea have developed a phototherapy technology that can significantly increase efficiency while reducing the pain of chemotherapy and minimizing side effects after treatment. The President of Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), Seok-Jin Yoon announced that a research team led by Dr. Se-hoon Kim at the Theragnosis Research Center (KU-KIST Graduate School of Converging Science and Technology) has developed a cancer-targeted phototherapeutic agent that promises complete elimination of cancer cells without side effects. It involves only one injection and repeated phototherapy. This development ...