Eastern and central China become brighter due to clean air action
2021-01-14
(Press-News.org) Since 2013, China has implemented the strictest ever air pollution control policies, which resulted in substantial reductions in aerosol concentrations.
However, extreme and persistent haze events frequently occur during wintertime in China. In winter haze events, aerosol-related reductions of surface solar radiation (SSR) have comparable impacts on clouds over eastern provinces.
Recently, researchers from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory of the United States (PNNL) and their collaborators conducted a study to further understand the underlying chemical mechanisms driving winter haze events and how the recent stringent control measures affect SSR.
Observational analysis unexpectedly showed a much weaker decrease in particle matters, known as PM, during winter compared with other seasons. "State-of-the-art model simulations suggest that the weakened wintertime PM decline is mainly attributed to the increase in wintertime atmospheric oxidation capacity and the enhanced conversion of nitric acid to nitrate by ammonia, which are induced by anthropogenic emission reductions," said Dr. Bin Zhao from PNNL, one of the corresponding authors of the studies published in Geophysical Research Letters.
"We find a dramatic increasing trend in SSR during 2014-2019 over the eastern and central China, which is among the world's fastest brightening in the last few decades," said Dr. Hongrong Shi from IAP. "Further, we use a novel method to elucidate the relative contributions of the aerosol and cloud radiative effects to the SSR trends."
The results showed that the strongly declining aerosol radiative effect due to the strict control policies played a dominant role in producing the upward SSR trends.
According to their studies, previous pollution control policies did not effectively mitigate severe wintertime PM pollution due to these unfavored chemical processes. Stricter control policies targeting oxidants and wintertime emission sources are imperative to counteract the buffering chemical mechanisms over China.
"Our findings indicate that the air pollution control actions can lead to not only considerable environmental and health improvements, but also increases in solar photovoltaic energy production." said Dr. Shi. "This is potentially an important co-benefit of air pollution controls in China which deserves more attention in future decision making."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-14
A new type of stem cell - that is, a cell with regenerative abilities - could be closer on the horizon, a new study led by UNSW Sydney shows.
The stem cells (called induced multipotent stem cells, or iMS) can be made from easily accessible human cells - in this case, fat - and reprogrammed to act as stem cells.
The results of the animal study, which created human stem cells and tested their effectiveness in mice, was published online in Science Advances today - and while the results are encouraging, more research and tests are needed before any potential translation ...
2021-01-14
Males are more likely to test positive for COVID-19, more likely to have complications and more likely to die from the virus than females, independent of age, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Farhaan Vahidy of Houston Methodist Research Institute, US, and colleagues.
As the COVID-19 pandemic unfolds and evolves across the globe, researchers have identified population sub-groups with higher levels of disease vulnerability, such as those with advanced age or certain pre-existing conditions. Small studies from China and Europe have indicated that males tend to experience higher disease ...
2021-01-14
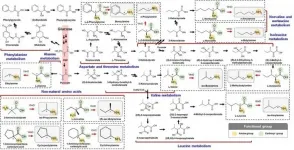
KAIST metabolic engineers presented the bio-based production of multiple short-chain primary amines that have a wide range of applications in chemical industries for the first time. The research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering designed the novel biosynthetic pathways for short-chain primary amines by combining retrobiosynthesis and a precursor selection step.
The research team verified the newly designed pathways by confirming the in vivo production of 10 short-chain primary amines by supplying the precursors. Furthermore, the platform Escherichia ...
2021-01-14
Women who are young, "conventionally attractive" and appear and act feminine are more likely to be believed when making accusations of sexual harassment, a new University of Washington-led study finds.
That leaves women who don't fit the prototype potentially facing greater hurdles when trying to convince a workplace or court that they have been harassed.
The study, involving more than 4,000 participants, reveals perceptions that primarily "prototypical" women are likely to be harassed. The research also showed that women outside of those socially determined norms ...
2021-01-14
WASHINGTON -- Women who do not fit female stereotypes are less likely to be seen as victims of sexual harassment, and if they claim they were harassed, they are less likely to be believed, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
"Sexual harassment is pervasive and causes significant harm, yet far too many women cannot access fairness, justice and legal protection, leaving them susceptible to further victimization and harm within the legal system," said Cheryl Kaiser, PhD, of the University of Washington and a co-author of the study published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. "Our research found that a claim was deemed less ...
2021-01-14
In experiments in mouse tissues and human cells, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have found that removing a membrane that lines the back of the eye may improve the success rate for regrowing nerve cells damaged by blinding diseases. The findings are specifically aimed at discovering new ways to reverse vision loss caused by glaucoma and other diseases that affect the optic nerve, the information highway from the eye to the brain.
"The idea of restoring vision to someone who has lost it from optic nerve disease has been considered science fiction for decades. ...
2021-01-14
DALLAS - Jan. 13, 2021 - A new treatment that combines two existing medications may provide long-sought relief for many battling debilitating methamphetamine use disorder, according to a study to be published tomorrow in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The article, based on a multisite study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), describes how combining an injectable drug currently used to treat alcohol and opioid addictions (naltrexone), and a commonly prescribed antidepressant (bupropion) produced positive results in 13.6 percent of the 403 patients treated, significantly higher than the 2.5 percent response in placebo ...
2021-01-14
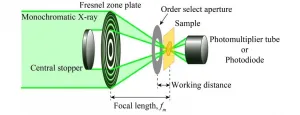
Lithium-ion batteries (LIB) are widely used for daily products in our life, such as hybrid cars, cell phone, etc. but their charge/discharge process is not fully understood yet. To understand the process, behaviors of lithium ion, distribution and chemical composition and state, should be revealed. A research group in Institute for Molecular Science noticed on a scanning transmission X-ray microscope (STXM, shown in Fig. 1) as a powerful technique to perform X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) with high spatial resolution. By using absorption edge of a specific ...
2021-01-14
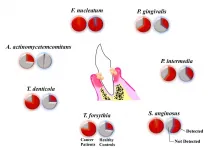
Researchers led by Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that certain oral pathogens are more prevalent in esophageal cancer patients, and could be used as a novel diagnostic tool
Tokyo, Japan - It is increasingly clear that the trillions of bacteria that make themselves at home in and on the human body are more than just casual observers along for the ride. Gut bacteria in particular have been shown to have an enormous influence on human health, with studies suggesting they play a role in illnesses ranging from autoimmune disorders to anxiety and depression.
The oral cavity is another rich source of microbial diversity, ...
2021-01-14
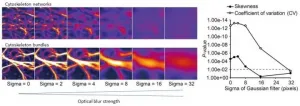
A research group from Kumamoto University, Japan has developed a highly sensitive technique to quantitatively evaluate the extent of cytoskeleton bundling from microscopic images. Until now, analysis of cytoskeleton organization was generally made by manually checking microscopic images. The new method uses microscopic image analysis techniques to automatically measure cytoskeleton organization. The researchers expect it to dramatically improve our understanding of various cellular phenomena related to cytoskeleton bundling.
The cytoskeleton is a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Eastern and central China become brighter due to clean air action