(Press-News.org) In experiments in mouse tissues and human cells, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have found that removing a membrane that lines the back of the eye may improve the success rate for regrowing nerve cells damaged by blinding diseases. The findings are specifically aimed at discovering new ways to reverse vision loss caused by glaucoma and other diseases that affect the optic nerve, the information highway from the eye to the brain.
"The idea of restoring vision to someone who has lost it from optic nerve disease has been considered science fiction for decades. But in the last five years, stem cell biology has reached a point where it's feasible," says Thomas Johnson, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor of ophthalmology at the Wilmer Eye Institute at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
The research was published Jan. 12 in the journal Stem Cell Reports.
A human eye has more than 1 million small nerve cells, called retinal ganglion cells, that transmit signals from light-collecting cells called photoreceptors in the back of the eye to the brain. Retinal ganglion cells send out long arms, or axons, that bundle together with other retinal ganglion cell projections, forming the optic nerve that leads to the brain.
When the eye is subjected to high pressure, as occurs in glaucoma, it damages and eventually kills retinal ganglion cells. In other conditions, inflammation, blocked blood vessels, or tumors can kill retinal ganglion cells. Once they die, retinal ganglion cells don't regenerate.
"That's why it is so important to detect glaucoma early," says Johnson. "We know a lot about how to treat glaucoma and help nerve cells survive an injury, but once the cells die off, the damage to someone's vision becomes permanent."
Johnson is a member of a team of researchers at the Johns Hopkins Wilmer Eye Institute looking for ways scientists can repair or replace lost optic neurons by growing new cells.
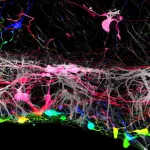
In the current study, Johnson and his team grew mouse retinas in a laboratory dish and tracked what happens when they added human retinal ganglion cells, derived from human embryonic stem cells, to the surface of the mouse retinas. They found that most of the transplanted human cells were unable to integrate into the retinal tissue, which contains several layers of cells.
"The transplanted cells clumped together rather than dispersing from one another like on a living retina," says Johnson.
However, the researchers found that a small number of transplanted retinal cells were able to settle uniformly into certain areas of the mouse retina. Looking more closely, the areas where the transplanted cells integrated well aligned with locations where the researchers had to make incisions into the mouse retinas to get them to lie flat in the culture dish. At these incision points, some of the transplanted cells were able to crawl into the retina and integrate themselves in the proper place within the tissue.
"This suggested that there was some type of barrier that had been broken by these incisions," Johnson says. "If we could find a way to remove it, we may have more success with transplantation."
It turns out that the barrier is a well-known anatomical structure of the retina, called the internal limiting membrane. It's a translucent connective tissue created by the retina's cells to separate the fluid of the eye from the retina.
After using an enzyme to loosen the connective fibers of the internal limiting membrane, the researchers removed the membrane and applied the transplanted human cells to the retinas. They found that most of the transplanted retinal ganglion cells grew in a more normal pattern, integrating themselves more fully. The transplanted cells also showed signs of establishing new nerve connections to the rest of the retinal structure when compared with retinas that had intact membranes.
"These findings suggest that altering the internal limiting membrane may be a necessary step in our aim to regrow new cells in damaged retinas," says Johnson.
The researchers plan to continue investigating the development of transplanted retinal ganglion cells to determine the factors they need to function once integrated into the retina.
INFORMATION:
Other researchers involved in the study include Kevin Zhang, Caitlyn Tuffy, Joseph Mertz, Sarah Quillen, Laurence Wechsler, Harry Quigley and Donald Zack of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
This work was funded by the National Eye Institute (K12EY015025, K08EY031801, R01EY002120, P30EY001765), the ARVO Dr. David L. Epstein Award, Research to Prevent Blindness, the American Glaucoma Society, the Johns Hopkins Physician Scientist Training Program, and generous gifts from the Guerrieri Family Foundation, the Gilbert Family Foundation, and the Marion & Robert Rosenthal Family Foundation.
The authors declare no competing interests.
DALLAS - Jan. 13, 2021 - A new treatment that combines two existing medications may provide long-sought relief for many battling debilitating methamphetamine use disorder, according to a study to be published tomorrow in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The article, based on a multisite study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), describes how combining an injectable drug currently used to treat alcohol and opioid addictions (naltrexone), and a commonly prescribed antidepressant (bupropion) produced positive results in 13.6 percent of the 403 patients treated, significantly higher than the 2.5 percent response in placebo ...
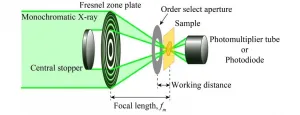
Lithium-ion batteries (LIB) are widely used for daily products in our life, such as hybrid cars, cell phone, etc. but their charge/discharge process is not fully understood yet. To understand the process, behaviors of lithium ion, distribution and chemical composition and state, should be revealed. A research group in Institute for Molecular Science noticed on a scanning transmission X-ray microscope (STXM, shown in Fig. 1) as a powerful technique to perform X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) with high spatial resolution. By using absorption edge of a specific ...
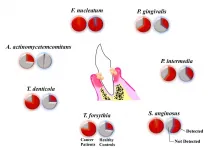
Researchers led by Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that certain oral pathogens are more prevalent in esophageal cancer patients, and could be used as a novel diagnostic tool
Tokyo, Japan - It is increasingly clear that the trillions of bacteria that make themselves at home in and on the human body are more than just casual observers along for the ride. Gut bacteria in particular have been shown to have an enormous influence on human health, with studies suggesting they play a role in illnesses ranging from autoimmune disorders to anxiety and depression.
The oral cavity is another rich source of microbial diversity, ...
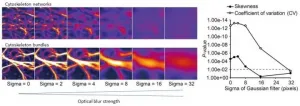
A research group from Kumamoto University, Japan has developed a highly sensitive technique to quantitatively evaluate the extent of cytoskeleton bundling from microscopic images. Until now, analysis of cytoskeleton organization was generally made by manually checking microscopic images. The new method uses microscopic image analysis techniques to automatically measure cytoskeleton organization. The researchers expect it to dramatically improve our understanding of various cellular phenomena related to cytoskeleton bundling.
The cytoskeleton is a ...
Data from the DESI (Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument) Legacy Imaging Surveys have revealed over 1200 new gravitational lenses, approximately doubling the number of known lenses. Discovered using machine learning trained on real data, these warped and stretched images of distant galaxies provide astronomers with a flood of new targets with which to measure fundamental properties of the Universe such as the Hubble constant, which describes the expanding Universe.
Astronomers hunting for gravitational lenses utilized machine learning to inspect the vast dataset known as the DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys, uncovering 1210 new lenses. The data were collected at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) and Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO), ...
URBANA, Ill. ¬- Illinois residents value efforts to reduce watershed pollution, and they are willing to pay for environmental improvements, according to a new study from agricultural economists at the University of Illinois.
Nutrient runoff from agricultural production is a major cause of pollution in the Mississippi River Basin and contributes to hypoxia - limited oxygen to support sea life in the Gulf of Mexico. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) set up action plans to reduce pollution in 12 midwestern states and reduce transmissions of nitrate-nitrogen and phosphorus by 45% in 2040.
Illinois agencies have established the Illinois Nutrient Loss Reduction Strategy (INLRS) to ...
Recently there has been a reemergence of interest in optical computing platforms for artificial intelligence-related applications. Optics/photonics is ideally suited for realizing neural network models because of the high speed, large bandwidth and high interconnectivity of optical information processing. Introduced by UCLA researchers, Diffractive Deep Neural Networks (D2NNs) constitute such an optical computing framework, comprising successive transmissive and/or reflective diffractive surfaces that can process input information through light-matter interaction. These surfaces are designed using standard deep learning techniques ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Researchers at Oregon State University have found that the blue orchard bee, an important native pollinator, produces female offspring at higher rates in the aftermath of wildfire in forests.
The more severe the fire had been, the greater percentage of females - more than 10% greater in the most badly burned areas relative to areas that burned the least severely.
"This is one of the first studies that has looked at how forest fire severity influences bee demography," said Jim Rivers, an animal ecologist with the OSU College of Forestry. "Sex ratio varied under different fire conditions but the number of young produced did not, which indicates bees ...
A first-of-its-kind, international study of 107,000 children finds that higher temperatures are an equal or even greater contributor to child malnutrition and low quality diets than the traditional culprits of poverty, inadequate sanitation, and poor education.
The 19-nation study is the largest investigation of the relationship between our changing climate and children's diet diversity to date. It is believed to be the first study across multiple nations and continents of how both higher temperatures and rainfall--two key results of climate change--have impacted children's diet diversity.
"Certainly, future climate changes have been predicted to affect malnutrition, but it surprised ...
DALLAS, Jan. 14, 2021 -- The longer the time between when heart attack symptoms start and a patient has an artery-clearing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), the more damage to the heart muscle, according to new research published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions, an American Heart Association journal.
A heart attack happens about every 40 seconds in the U.S., and the most common heart attack is caused by a complete blockage in a coronary artery, called ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). STEMI patients are most often treated with PCI, also known as angioplasty with stent, in which a catheter with a deflated balloon is inserted into the narrowed heart artery. Subsequently, the balloon is inflated, which clears the obstruction and restores ...