Altering mealtimes could prevent development of Type 2 diabetes
2021-01-15
(Press-News.org) An innovative new study is set to examine if changing our mealtimes to earlier or later in the day could reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Led by Dr Denise Robertson, Professor Jonathan Johnston and post graduate researcher Shantel Lynch from the University of Surrey, the study, outlined in the journal Nutrition Bulletin, will investigate if changing the time we eat during the day could reduce risk factors such as obesity and cholesterol levels that are typically associated with the development of Type 2 diabetes. The team of researchers will also for the first time investigate, via a series of interviews with participants and their friends and family, the impact of such changes on home life, work/social commitments and whether co-habitants of those who make such modifications are influenced to alter their own meal timings/eating habits as a result.
During the unique 10-week study, 51 participants aged between 18- 65 years old who have been identified as having an increased/moderate/high risk of developing Type 2 diabetes will be split into three groups. The first, a control group, will be asked to make no changes to their eating habits; the second group will be required to restrict their eating times during the day to between 7am- 3pm; and the third group will limit their eating time to between 12-8pm.
Participants will regularly attend the Surrey Clinical Investigations Unit to monitor their blood pressure, waist and hip circumferences and provide blood and urine samples. A registered dietitian will also use specialist eye-tracking equipment to analyse participants' eye gaze direction to identify and monitor any changes to food preferences over the course of the intervention. Previous research has shown that eye gaze direction is a strong signal of attention and preference behaviours.
Researchers will examine in detail results gathered from such visits to determine if changing the time meals are consumed to earlier or later in the day could reduce risk factors associated with Type 2 diabetes.
Senior scientist of the study Dr Denise Robertson, Reader in Nutritional Physiology at the University of Surrey, said: "Type 2 diabetes is a growing problem in the UK, with over three million people diagnosed and 12.3 million people at potential risk of developing the condition, which can increase the likelihood of developing serious problems with our eyes, heart and nervous system.
"Public health initiatives are often rolled out with a focus on prevention, but these have had limited success. We need to adopt different approaches in preventing this condition. A simple solution to this could be altering when we eat our meals, lessening the risk factors associated with the development of Type 2 diabetes."
PGR student and registered dietitian Shantel Lynch said: "Treating Type 2 diabetes and its associated complications places a tremendous strain on the NHS. To ease such strain there needs to be more of a focus on prevention and tackling the areas, which are often lifestyle choices, that lead to the development of the condition.
"The possible benefits of altering mealtimes, such as weight loss, have become increasingly topical in nutrition-related research. However, there are still many unanswered questions and we hope to contribute to this field of research while finding out whether time-restricted feeding may help to reduce the risk of developing long-term illnesses like Type 2 diabetes, and how feasible it is to follow this diet in real life."
Jonathan Johnston, Professor of Chronobiology and Integrative Physiology at the University of Surrey, said: "Changing our mealtimes limits our energy intake to a set number of hours in the day, which leads to an extension of the daily fast that generally happens overnight. This study will help us understand what time of day is optimal to eat to reduce our chances of developing Type 2 diabetes.
"We will also for the first time be investigating the impact of time-restricted feeding on individuals' work, social and home life to understand the obstacles people encounter in adapting to new mealtimes, which may affect their ability to stick to the schedule."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-15
Having genitals of a certain shape and size gives male flies a major reproductive advantage, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists examined the reproductive success of male Drosophila simulans flies both alone with a female and in various states of competition with other males.
Certain genital shapes were consistently better in terms of number of offspring sired.
However - surprisingly, given how fast genital form evolves - the selection documented was rather weak.
"Male genitals generally, and in Drosophila specifically, evolve very quickly, so we were really surprised to find this weak selection," said Professor David Hosken, of the University of Exeter.
"Selection is the major mechanism of evolution and hence where we see rapid evolution, ...
2021-01-15
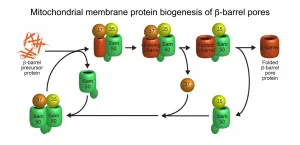
Mitochondria are vital for the human body as cellular powerhouses: They possess more than 1,000 different proteins, required for many central metabolic pathways. Disfunction of these lead to severe diseases, especially of the nervous system and the heart. In order to transport proteins and metabolites, mitochondria contain a special group of so-called beta-barrel membrane proteins, which form transport pores in the outer mitochondrial membrane. So far, scientists have not been able to explain the operating mode of the sorting and assembly machinery (SAM) for the biogenesis of these beta-barrel proteins. A team led by Prof. Dr. Toshiya Endo from Kyoto University/Japan, Prof. Dr. Nils Wiedemann and ...
2021-01-15
Guangzhou, January 15, 2021: New journal BIO Integration (BIOI) publishes its fourth issue, volume 1, issue 4. BIOI is a peer-reviewed, open access, international journal, which is dedicated to spreading multidisciplinary views driving the advancement of modern medicine. Aimed at bridging the gap between the laboratory, clinic, and biotechnology industries, it will offer a cross-disciplinary platform devoted to communicating advances in the biomedical research field and offering insights into different areas of life science, in order to encourage cooperation and exchange among scientists, clinical researchers, and health care providers.
The issue contains an original article, three review ...
2021-01-15
A clinical trial involving COVID-19 patients hospitalized at UT Health San Antonio and University Health, among roughly 100 sites globally, found that a combination of the drugs baricitinib and remdesivir reduced time to recovery, according to results published Dec. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine. Six researchers from UT Health San Antonio and University Health are coauthors of the publication because of the San Antonio site's sizable patient enrollment in the trial.
The Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial 2 (ACTT-2), which compared the combination therapy versus remdesivir paired with an inactive placebo in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), ...
2021-01-15
Certain snakes have evolved a unique genetic trick to avoid being eaten by venomous snakes, according to University of Queensland research.
Associate Professor Bryan Fry from UQ's Toxin Evolution Lab said the technique worked in a manner similar to the way two sides of a magnet repel each other.
"The target of snake venom neurotoxins is a strongly negatively charged nerve receptor," Dr Fry said.
"This has caused neurotoxins to evolve with positively charged surfaces, thereby guiding them to the neurological target to produce paralysis.
"But some snakes have evolved to replace a negatively charged amino acid on their receptor with a positively charged one, meaning the neurotoxin is repelled.
"It's an inventive genetic mutation and it's been completely missed until now.
"We've ...
2021-01-15
PHILADELPHIA - Our biological or circadian clock synchronizes all our bodily processes to the natural rhythms of light and dark. It's no wonder then that disrupting the clock can wreak havoc on our body. In fact, studies have shown that when circadian rhythms are disturbed through sleep deprivation, jet lag, or shift work, there is an increased incidence of some cancers including prostate cancer, which is the second leading cause of cancer death for men in the U.S. With an urgent need to develop novel therapeutic targets for prostate cancer, researchers at the Sidney Kimmel Cancer - ...
2021-01-15
Oxygen levels in the ancient oceans were surprisingly resilient to climate change, new research suggests.
Scientists used geological samples to estimate ocean oxygen during a period of global warming 56 million years ago - and found "limited expansion" of seafloor anoxia (absence of oxygen).
Global warming - both past and present - depletes ocean oxygen, but the new study suggests warming of 5°C in the Paleocene Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) led to anoxia covering no more than 2% of the global seafloor.
However, conditions are different today to the PETM - today's rate of carbon emissions is much faster, and we are adding nutrient pollution to the oceans - both of which could drive more rapid and expansive oxygen loss.
The study was carried out by an international ...
2021-01-15
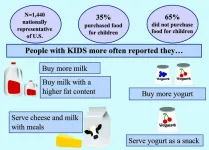
Champaign, IL, January 15, 2021 - American dairy consumers are often influenced by a variety of factors that can affect their buying habits. These factors include taste, preference, government information, cultural background, social media, and the news. In an article appearing in JDS Communications, researchers found that households that frequently bought food for children are interested in dairy as part of their diet and purchased larger quantities of fluid milk and more fluid milk with a higher fat content.
To assess the purchasing habits of households that purchase food for children versus those ...
2021-01-15
Families are complicated. For members of the Alligatoridae family, which includes living caimans and alligators - this is especially true. They are closely related, but because of their similarity, their identification can even stump paleontologists.
But after the recent discovery of a partial skull, the caimans of years past may provide some clarity into the complex, and incomplete, history of its relatives and their movements across time and space.
Michelle Stocker, an assistant professor of vertebrate paleontology in Virginia Tech's Department of Geosciences in the College of Science; Chris Kirk, of the University of Texas at Austin; and Christopher Brochu, of the University of Iowa, have ...
2021-01-15
Researchers from University of Stavanger, University of Melbourne, and University of Wisconsin-Madison published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how major projects undertaken by temporary organizations can be better managed so that cost overruns are minimized.
The study forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing is titled "Mobilizing the Temporary Organization: The Governance Roles of Selection and Pricing" and is authored by Elham Ghazimatin, Erik Mooi, and Jan Heide.
When consumers return to the skies again, they may do so in Boeing's 787 Dreamliner. But the project, or "temporary organization," created to make this plane ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Altering mealtimes could prevent development of Type 2 diabetes