(Press-News.org) Nearly 38 million people around the world are living with HIV, which, with access to treatment, has become a lifelong chronic condition. Understanding how infection changes the brain, especially in the context of aging, is increasingly important for improving both treatment and quality of life.
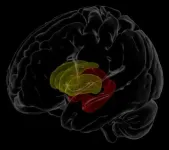
In January, researchers at the Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute (USC Stevens INI), part of the Keck School of Medicine of USC, and other international NeuroHIV researchers, published one of the largest-ever neuroimaging studies of HIV. The researchers pooled magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data from 1,203 HIV-positive individuals across Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe and North America. Their findings were published in JAMA Network Open, an open-access journal from the American Medical Association.
"Brain injury caused by HIV can lead to cognitive challenges, even in those receiving treatment," says Talia Nir, PhD, a postdoctoral scholar at the USC Stevens INI's Laboratory of Brain eScience (LoBeS) and first author of the study. "Establishing a common pattern of effects on the brain across different populations is a key step toward addressing those issues. The strength of this large dataset is that it is more representative of an era where treatment for HIV infection is widely available."
The researchers looked at the link between blood plasma, which is routinely collected to monitor immune function and treatment response, and the volume of various structures in the brain. Lower white blood cell counts generally indicate that the immune system is being suppressed. Here, they found, for example, that participants with lower white blood cell counts also had less brain volume in the hippocampus and thalamus, parts of the brain's limbic system involved in regulating memory, emotion and behavior.
These findings are important because they were largely derived from brain scans of individuals undergoing antiretroviral therapy--and they indicate that people receiving such treatment may exhibit a different brain injury signature compared to untreated individuals, which earlier studies tended to focus on. They highlight deficits in brain areas that are also vulnerable to age-related neurodegenerative diseases.
Accelerated atrophy of the hippocampus, the region that showed the most consistent effects in the study, is a hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Common age and HIV-related pathological processes, such as inflammation and blood brain barrier impairment, may accelerate age-related neurodegenerative processes.
"There are many factors that contribute to brain tissue loss and subsequent cognitive impairments as we age, and a person's immune function is no exception," says Neda Jahanshad, PhD, associate professor of neurology at the INI and one of the senior authors of the study. "Through these large-scale efforts, we're beginning to understand the link between immune function and brain alterations in individuals living, and aging, with HIV."
The analysis was a product of the Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA) consortium's HIV Working Group, established by Jahanshad and colleagues in 2013 to pool harmonized data across neuroimaging studies. The ENIGMA network at large, led by the institute's associate director, Paul M. Thompson, PhD, unites neuroimaging researchers in 45 countries to study psychiatric disorders, neurodegenerative diseases and other aspects of brain function. In addition to housing ENIGMA, the USC Stevens INI is a powerhouse of neuroimaging and related science, known for large cohort analyses of imaging, genetics, behavioral, clinical and other data. Investigators from 13 existing HIV studies in the United States, France, Serbia, Australia, Thailand and South Africa collaborated on the JAMA Network Open paper.
Next, the team will analyze imaging data over time, including diffusion imaging data, another type of MRI data that maps the brain's white matter pathways, to further understand how clinical markers of HIV infection affect the brain and the rate of neurodegeneration. As part of that ongoing work, they are inviting researchers around the world to join the ENIGMA-HIV Working Group.
"With a greater collaborative effort, we hope to be able to assess how genetic, environmental, lifestyle and treatment-related factors may further impact neurological outcomes," Nir says.
INFORMATION:
The White-lipped peccary Tayassu pecari is a boar-like hoofed mammal found throughout Central and South America. These animals roam the forest in bands of 50 to 100 individuals, eating a wide variety of foods. In Brazil's Atlantic Rainforest, they prefer the fruit of the jussara palm Euterpe edulis.
The jussara is very abundant in this biome, probably thanks to vast amounts of dung, urine, and soil trampling by peccaries as well as tapirs (Tapirus terrestris) and other fruit-eating animals, or frugivores. This behavior releases forms of nitrogen, a key element in plant growth.
A study supported ...
Boston - A national group of pediatric addiction medicine experts have released newly-established principles of care for young adults with substance use disorder. Led by the Grayken Center for Addiction at Boston Medical Center, the collection of peer-reviewed papers was developed to guide providers on how to treat young adults with substance use disorder given their age-specific needs, as well as elevate national discussions on addressing these challenges more systematically.
Published in Pediatrics, the 11-paper supplement is the result of a convening of national experts in the treatment of young adults to determine the most important principles to address when caring for this unique population of patients with substance use disorder. ...
Liquids are ubiquitous in Nature: from the water that we consume daily to superfluid helium which is a quantum liquid appearing at temperatures as low as only a few degrees above the absolute zero. A common feature of these vastly different liquids is being self-bound in free space in the form of droplets. Understanding from a microscopic perspective how a liquid is formed by adding particles one by one is a significant challenge.
Recently, a new type of quantum droplets has been experimentally observed in ultracold atomic systems. These ones ...
Researchers from Skoltech and the University of Texas Medical Branch (US) have shown how optoacoustics can be used for monitoring skin water content, a technique which is promising for medical applications such as tissue trauma management and in cosmetology. The paper outlining these results was published in the Journal of Biophotonics.
(swelling caused by fluid accumulation) or dehydration, which can also have cosmetic impacts. Right now, electrical, mechanical and spectroscopic methods can be used to monitor water content in tissues, but there is no accurate and noninvasive technique that would also provide a high resolution and significant probing depth required for potential clinical applications.
Sergei Perkov of the Skoltech Center for Photonics ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - "Buy low and sell high" says the old adage about investing in the stock market.
But a relatively new type of investment fund is luring unsophisticated investors into buying when values are at their highest, resulting in losses almost immediately, a new study has found.
The lure? Buying into trendy investment areas like cannabis, cybersecurity and work-from-home businesses.
"As soon as people buy them, these securities underperform as the hype around them vanishes," said Itzhak Ben-David, co-author of the study and professor of finance at The Ohio State University's Fisher College of Business.
"They appeal to people who are not sophisticated ...
New Rochelle, NY, January 15, 2021--The biodistribution of adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene transfer vectors can be measured in nonhuman primates using a new method. The method quantifies whole-body and organ-specific AAV capsids from 1 to 72 hours after administration. Study design and results are presented in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the full-text article free on the Human Gene Therapy website through February 15, 2021.
AAV capsids were labeled with I-124 and delivered using two routes of administration: intravenous and directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Biodistribution was measured by quantitative positron emission tomography (PET) at 1, 24, 48, and 72 hours after AAV administration. Two AAV vectors - AAVrsh.10 and AAV9 - were compared.
"Following ...
HAMILTON, ON, Jan. 15, 2021 -- A team of neuroscientists and engineers at McMaster University has created a nasal spray to deliver antipsychotic medication directly to the brain instead of having it pass through the body.
The leap in efficiency means patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and other conditions could see their doses of powerful antipsychotic medications cut by as much as three quarters, which is expected to spare them from sometimes-debilitating side effects while also significantly reducing the frequency of required treatment.
The new method delivers medication in a spray that reaches the brain directly through ...
Pediatric laryngotracheal stenosis (LTS), a narrowing of the airway in children, is a complex medical condition. While it can be something a child is born with or caused by injury, the condition can result in a life-threatening emergency if untreated.
Treatment, however, is challenging. Depending on the severity, doctors will use a combination of endoscopic techniques, surgical repair, tracheostomy, or deployment of stents to hold the airway open and enable breathing.
While stents are great at holding the airway open and simultaneously allowing the trachea to continue growing, they can move around, ...
There is currently no cure for osteoarthritis, but a group of scientists believe they've discovered a method through which a simple knee injection could potentially stop the disease's effects. These researchers showed that they could target a specific protein pathway in mice, put it into overdrive and halt cartilage degeneration over time. Building on that finding, they were able to show that treating mice with surgery-inducedknee cartilage degeneration through the same pathway via the state of the art of nanomedicine could dramatically reduce the cartilage degeneration and knee pain. These findings were published in Science Translational Medicine.
"Our lab is one of the few in the world studying epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ...
The Gulf of Mexico holds huge untapped offshore oil deposits that could help power the U.S. for decades.
The energy super basin's longevity, whose giant offshore fields have reliably supplied consumers with oil and gas since the 1960s, is the result of a remarkable geologic past - a story that began 200 million years ago among the fragments of Pangea, when a narrow, shallow seaway grew into an ocean basin, while around it mountains rose then eroded away.
The processes that shaped the basin also deposited and preserved vast reserves of oil and gas, of which only a fraction has been extracted. Much of the remaining oil lies buried beneath ancient salt layers, just recently illuminated ...