Nonsurgical treatment for cerebral infarction using wearable wireless ultrasound devices
Preclinical efficacy validation of a light-weight wearable wireless ultrasound brain stimulator for stroke rehabilitation. Establishing the grounds for the development of wearable ultrasound stimulation technology applicable in everyday life
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) Cerebral infarction, commonly known as ischemic stroke, has a high mortality rate and causes severe damage to nervous cells in the brain owing to the loss of oxygen, which results in limiting body movements. Several technologies, including physiotherapy and brain stimulation techniques, are being developed and tested for the rehabilitation of brain nervous cells damaged by a stroke. In particular, low-intensity focused ultrasound is expected to be effective for rehabilitating neurological diseases such as stroke, as it can excite or inhibit nerve cells by delivering mechanical energy with high precision at the desired position, while ultrasound is penetrating the cranium without requiring a surgical operation.
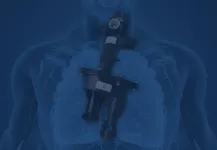
Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the research team at the Center for Bionics, led by Dr. Kim Hyungmin, developed a wireless rehabilitation treatment technology for brain nervous system damaged by a stroke by fabricating a wearable, wireless low-intensity focused ultrasound brain stimulator. Additionally, to verify its effectiveness, this brain stimulator was applied to animal models of stroke.
In 2018, the research team developed a treatment method in which a low-intensity focused ultrasound was applied to the cerebellar core to recover motor functions that deteriorated owing to hemiplegia, and in 2020, they proved that the low-intensity focused ultrasound applied to the cerebellar core after a stroke is closely related to the changes in a delta wave in the brain.
To harness this technology efficiently in rehabilitating stroke patients in various environments, the ultrasound device should be easy to be used in everyday life. However, the existing brain stimulator is heavy and fixed, and is therefore only applicable to experiments involving anesthetized or restrained animals, thereby making it difficult to be commercialized.
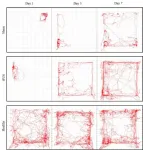
Based on the findings of previous studies, the research team at KIST developed a wearable light-weight brain stimulator, which weighs approximately 20 g, that can be wirelessly controlled. In addition, they verified the rehabilitation effectiveness after assessing the motor ability of a rat stroke model with the device. When ultrasound was applied with a pressure of approximately 426 kPa to the part of the brain that controls motor functions in a rat stroke model, the motor functions were significantly improved after three days compared to the rat stroke model to which ultrasound was not applied; the motor functions were improved to a level similar to that of normal rats after seven days of rehabilitation.
The brain stimulator developed by Dr. Kim's research team is light in weight and operates wirelessly, which does not limit the physical movements of a body as it continues stimulating the part of the brain that controls motor functions via ultrasound, thereby restoring the nervous system damaged by a stroke. The results obtained from the study are expected to soon contribute to the development of a wearable ultrasound brain stimulation technology at a clinical level.
According to Dr. Kim Hyungmin at KIST, "Recently, the wearable brain stimulation technology is advancing rapidly, and the significance of this study is in verifying the possibility of non-invasive neurorehabilitation therapy using a wearable ultrasound device," and he added that "In order to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatement, further research is required to optimize stimulation protocol by determining the molecular and cellular mechanisms of ultrasonic neuromodulation."
INFORMATION:
This study was conducted as a Creative Allied Project (CAP) of the National Research Council of Science and Technology and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). The findings of this study have been published in the latest edition of a prestigious international journal "IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering" of medical engineering.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
Why is studying spin properties of one-dimensional quantum nanowires important?
Quantum nanowires-which have length but no width or height-provide a unique environment for the formation and detection of a quasiparticle known as a Majorana zero mode.
A new UNSW-led study overcomes previous difficulty detecting the Majorana zero mode, and produces a significant improvement in device reproducibility.
Potential applications for Majorana zero modes include fault-resistant topological quantum computers, and topological superconductivity.
MAJORANA FERMIONS IN 1D WIRES
A Majorana fermion is a composite particle that is its own antiparticle.
Antimatter explainer: Every fundamental particle has a corresponding antimatter particle, with ...
2021-01-19
A KAIST team's mathematical modelling shows that the topographic tiling of cortical maps originates from bottom-up projections from the periphery.
Researchers have explained how the regularly structured topographic maps in the visual cortex of the brain could arise spontaneously to efficiently process visual information. This research provides a new framework for understanding functional architectures in the visual cortex during early developmental stages.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has demonstrated that the orthogonal organization of retinal mosaics in the periphery is mirrored onto the primary visual cortex and initiates ...
2021-01-19
Overview:
Third-year doctoral student Toshiaki Takahashi, associate professor Kazuhiro Takahashi, and their research team from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology developed a testing chip using semiconductor micro-machining that can detect volatile gasses in exhaled breath in ppm concentrations at room temperature. A polymer that expands and contracts when gas is absorbed is formed on a flexibly deformable nanosheet, and the amount of deformation that occurs when a target gas is absorbed is measured, allowing gas to be detected at high sensitivity. ...
2021-01-19
New research shows that patterns inspired by lobster shells can make 3D printed concrete stronger, to support more complex and creative architectural structures.
Digital manufacturing technologies like 3D concrete printing (3DCP) have immense potential to save time, effort and material in construction.
They also promise to push the boundaries of architectural innovation, yet technical challenges remain in making 3D printed concrete strong enough for use in more free-form structures.
WATCH AND EMBED THE VIDEO: https://youtu.be/mpPAPlst42o
In a new experimental study, researchers at RMIT University ...
2021-01-19
Pulsed lasers repeatedly emit light for a short period of time as if blinking. They have the advantage of focusing more energy than a continuous wave laser, whose intensity is kept unchanged over time. If digital signals are loaded in a pulsed laser, each pulse can encode one bit of data. In this respect, the higher the repetition rate, the more the amount of data that can be transmitted. However, conventional optical-fiber-based pulsed lasers have typically had a limitation in increasing the number of pulses per second above the MHz level.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the research ...
2021-01-19
Synthetic cannabidiol, better known as CBD, has been shown for the first time to kill the bacteria responsible for gonorrhoea, meningitis and legionnaires disease.
The research collaboration between The University of Queensland and Botanix Pharmaceuticals Limited could lead to the first new class of antibiotics for resistant bacteria in 60 years.
The UQ Institute for Molecular Bioscience's Associate Professor Mark Blaskovich said CBD - the main nonpsychoactive component of cannabis - can penetrate and kill a wide range of bacteria including Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which causes ...
2021-01-19
'A journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step' is a popular adage that talks about the initial thrust required to embark on a task. However, once begun, how do we persevere on the job and not let it fall apart like a New Year resolution? How do we stay motivated?
Well, these are not just philosophical deliberations, but compelling science projects for neuroscience aficionados. Scientists have in fact been on the lookout for the neuronal and molecular players which are at the root of governing motivation.
Here is a research story from the generous fruit fly that identifies the machinery behind the fly's relentless flying pursuits.
Prof. Gaiti Hasan's group, in a recent study, has discovered that the ability of flies to sustain ...
2021-01-19
Your food intake patterns are partly under genetic control, according to the latest research from researchers at King's College London, published today in the journal Twin Research and Human Genetics.
Researchers can study the quality of an individual's typical diet by using a type of analysis called 'dietary indices'. Researchers use dietary indices to understand what foods someone eats and the nutrients provided, compared with recommended guidelines.
The team analysed food questionnaire responses from 2,590 twins, using nine commonly used dietary indices. The researchers studied the degree of similarity among identical twins - who share 100% of their genes - compared with non-identical twins, who share 50% of their genes.
The team found that identical twin pairs ...
2021-01-19
The design, testing, and validation of the Illinois RapidVent emergency ventilator has been published in the journal Plos One. The article, "Emergency Ventilator for COVID-19," by University of Illinois Urbana researchers, is the first of its kind to report such details about an emergency ventilator that was designed, prototyped, and tested at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
"This article reports the development and testing of the RapidVent emergency ventilator," said William King, professor at The Grainger College of Engineering and Carle Illinois College of Medicine, and leader of the RapidVent ...
2021-01-19
Previously controversial values of the energy gap of a van der Waals material -- chromium tribromide -- were reported based on various optical measurements. A University of Wyoming faculty member and his research team used scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy measurements that clearly reveal a much smaller energy gap value and resolved the controversy.
"Our results settled a long controversy on one important material property -- the energy gap of the material," says TeYu Chien, an associate professor in the UW Department of Physics and Astronomy. "Our scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy measurements clearly revealed that the energy gap is around 0.3 electron volt (eV), which is much smaller than those measured by optical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nonsurgical treatment for cerebral infarction using wearable wireless ultrasound devices
Preclinical efficacy validation of a light-weight wearable wireless ultrasound brain stimulator for stroke rehabilitation. Establishing the grounds for the development of wearable ultrasound stimulation technology applicable in everyday life