Semiconductor chip that detects exhaled gas with high sensitivity at room temperature
For use in IoT chemical sensors that can diagnose diseases through breath tests
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) Overview:
Third-year doctoral student Toshiaki Takahashi, associate professor Kazuhiro Takahashi, and their research team from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology developed a testing chip using semiconductor micro-machining that can detect volatile gasses in exhaled breath in ppm concentrations at room temperature. A polymer that expands and contracts when gas is absorbed is formed on a flexibly deformable nanosheet, and the amount of deformation that occurs when a target gas is absorbed is measured, allowing gas to be detected at high sensitivity. The testing chip, which is formed in the size of a few square millimeters with semiconductor micro-machining technology, is expected to contribute to telehealth as an IoT gas sensor that can easily be used in the home for breath tests.
Details:
There are testing methods that measure specific molecules in the breath and blood that are an index for identifying the existence and degree of progression of various diseases. Among them is non-invasive measuring through breath testing, which is a promising testing method for diseases with low patient burden that has attracted attention in recent years. It is reported that volatile organic compounds included in exhaled breath increase in concentration in cases of diabetes, renal failure, lung cancer, etc., and it can be expected that these laboratory markers will be measured for use in patient screenings. Previously developed semiconductor gas sensors have a film formed on a sensor whose electrical resistance and capacitance change in reaction to a gas, and measurements are made by heating the film to several hundred degree Celsius. However, in order to reduce temperature increases in peripheral circuits due to heating, the separate forming of a structure that separates the heating parts from the periphery is required, and the increased complexity of manufacturing processes and the decrease of the integration per unit area due to the isolation of elements are issues. Also, the increase in power consumption caused by heating poses a problem for applications in IoT devices.
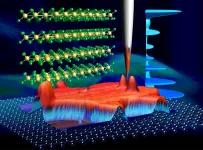
Therefore, the research team developed a sensor that forms a polymer material that expands and contracts when gas molecules are absorbed on a thin, flexibly deformable nanosheet, and it measures the amount of the target gas absorbed in terms of the amount of deformation of the sheet. The proposed sensor uses the interferometric property of light intensification through a narrow gap to determine gas adsorption in terms of color change. With this technology, a testing chip was realized that can measure gas at room temperature without a heating mechanism. Also, this sensor can increase the sensitivity without increasing the area because of the formation of a narrow, sub-micron air gap of up to a few hundred nanometers between the thin nanosheet that changes shape and the semiconductor substrate. However, it was very difficult to merge the thin nanosheet above the sub-micron air gap while forming the gap, and it was necessary to develop a new manufacturing process to achieve the structure. Therefore, the team focused on the strong adhesive properties of the thin nanosheet when heat and pressure are applied. A new manufacturing process was introduced where two different silicon substrates are adhered, and then the substrate on one side is removed to create a sensor structure with a sub-micron air gap of about 400 nanometers. In comparison to traditional sensor structures formed with a gap of a few micrometers, the sensor response was demonstrated to have improved by 11 times, and it was possible to determine the deformation of the thin nanosheet due to gas adsorption in terms of color change.
Additionally, it was demonstrated that the testing chip that was developed can detect ethanol gas, a typical volatile organic compound, in ppm concentrations. The lower concentration detection limit is equivalent in performance to the most sensitive semiconductor sensors that can measure at room temperature, and compared to sensors that use the same detection method, the detection performance improved by 40 times, while the area per single element was reduced to 1/150. The sensor can be expected to be used as a small, portable breath testing device.
Future Outlook:
The research team plans to demonstrate the possibility of using the semiconductor sensor they developed to detect various volatile gasses related to diseases. Also, they aim to construct a small, portable sensor system for breath monitoring that consumes less power than traditional IoT gas sensors.
INFORMATION:
Reference:
Toshiaki Takahashi, Yong-Joon Choi, Kazuaki Sawada, and Kazuhiro Takahashi, A ppm Ethanol Sensor Based on Fabry-Perot Interferometric Surface Stress Transducer at Room Temperature, Sensors, DOI: 10.3390/s20236868.
This research was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP19J12825 and JST, PRESTO Grant Number JPMJPR1526.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
New research shows that patterns inspired by lobster shells can make 3D printed concrete stronger, to support more complex and creative architectural structures.
Digital manufacturing technologies like 3D concrete printing (3DCP) have immense potential to save time, effort and material in construction.
They also promise to push the boundaries of architectural innovation, yet technical challenges remain in making 3D printed concrete strong enough for use in more free-form structures.
WATCH AND EMBED THE VIDEO: https://youtu.be/mpPAPlst42o
In a new experimental study, researchers at RMIT University ...
2021-01-19
Pulsed lasers repeatedly emit light for a short period of time as if blinking. They have the advantage of focusing more energy than a continuous wave laser, whose intensity is kept unchanged over time. If digital signals are loaded in a pulsed laser, each pulse can encode one bit of data. In this respect, the higher the repetition rate, the more the amount of data that can be transmitted. However, conventional optical-fiber-based pulsed lasers have typically had a limitation in increasing the number of pulses per second above the MHz level.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the research ...
2021-01-19
Synthetic cannabidiol, better known as CBD, has been shown for the first time to kill the bacteria responsible for gonorrhoea, meningitis and legionnaires disease.
The research collaboration between The University of Queensland and Botanix Pharmaceuticals Limited could lead to the first new class of antibiotics for resistant bacteria in 60 years.
The UQ Institute for Molecular Bioscience's Associate Professor Mark Blaskovich said CBD - the main nonpsychoactive component of cannabis - can penetrate and kill a wide range of bacteria including Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which causes ...
2021-01-19
'A journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step' is a popular adage that talks about the initial thrust required to embark on a task. However, once begun, how do we persevere on the job and not let it fall apart like a New Year resolution? How do we stay motivated?
Well, these are not just philosophical deliberations, but compelling science projects for neuroscience aficionados. Scientists have in fact been on the lookout for the neuronal and molecular players which are at the root of governing motivation.
Here is a research story from the generous fruit fly that identifies the machinery behind the fly's relentless flying pursuits.
Prof. Gaiti Hasan's group, in a recent study, has discovered that the ability of flies to sustain ...
2021-01-19
Your food intake patterns are partly under genetic control, according to the latest research from researchers at King's College London, published today in the journal Twin Research and Human Genetics.
Researchers can study the quality of an individual's typical diet by using a type of analysis called 'dietary indices'. Researchers use dietary indices to understand what foods someone eats and the nutrients provided, compared with recommended guidelines.
The team analysed food questionnaire responses from 2,590 twins, using nine commonly used dietary indices. The researchers studied the degree of similarity among identical twins - who share 100% of their genes - compared with non-identical twins, who share 50% of their genes.
The team found that identical twin pairs ...
2021-01-19
The design, testing, and validation of the Illinois RapidVent emergency ventilator has been published in the journal Plos One. The article, "Emergency Ventilator for COVID-19," by University of Illinois Urbana researchers, is the first of its kind to report such details about an emergency ventilator that was designed, prototyped, and tested at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
"This article reports the development and testing of the RapidVent emergency ventilator," said William King, professor at The Grainger College of Engineering and Carle Illinois College of Medicine, and leader of the RapidVent ...
2021-01-19
Previously controversial values of the energy gap of a van der Waals material -- chromium tribromide -- were reported based on various optical measurements. A University of Wyoming faculty member and his research team used scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy measurements that clearly reveal a much smaller energy gap value and resolved the controversy.
"Our results settled a long controversy on one important material property -- the energy gap of the material," says TeYu Chien, an associate professor in the UW Department of Physics and Astronomy. "Our scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy measurements clearly revealed that the energy gap is around 0.3 electron volt (eV), which is much smaller than those measured by optical ...
2021-01-19
Nearly every galaxy hosts a monster at its center -- a supermassive black hole millions to billions times the size of the Sun. While there's still much to learn about these objects, many scientists believe they are crucial to the formation and structure of galaxies. What's more, some of these black holes are particularly active, whipping up stars, dust and gas into glowing accretion disks emitting powerful radiation into the cosmos as they consume matter around them. These quasars are some of the most distant objects that astronomers can see, and there is now a new record for the farthest one ever observed.
A team of scientists, led by former UC Santa Barbara ...
2021-01-19
What's the relationship between money and well-being? "It's one of the most studied questions in my field," says Matthew Killingsworth, a senior fellow at Penn's Wharton School who studies human happiness. "I'm very curious about it. Other scientists are curious about it. Laypeople are curious about it. It's something everyone is navigating all the time."
To answer this question, Killingsworth collected 1.7 million data points from more than 33,000 participants who provided in-the-moment snapshots of their feelings during daily life. In a paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Killingsworth confirms that money does influence happiness and, contrary to previous influential research on the subject suggesting that this plateaus above ...
2021-01-19
'What goes in, must come out' is a familiar refrain. It is especially pertinent to the challenges facing UBC researchers who are investigating methods to remove chemicals and pharmaceuticals from public water systems.
Cleaning products, organic dyes and pharmaceuticals are finding their ways into water bodies with wide-ranging negative implications to health and the environment, explains Dr. Mohammad Arjmand, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at UBC Okanagan.
And while pharmaceuticals like a chemotherapy drug called methotrexate can be highly effective ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Semiconductor chip that detects exhaled gas with high sensitivity at room temperature
For use in IoT chemical sensors that can diagnose diseases through breath tests