INFORMATION:
Paper co-authors also include Mohammadhadi Heidari Baladehi and JI Yuetong, all of whom are affiliated with the Single-Cell Center at QIBEBT and the University of CAS.
Single-cell test can reveal precisely how drugs kill cancer cells
2021-01-19
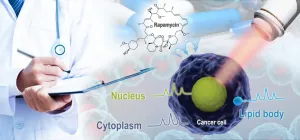
(Press-News.org) Cancer cells are smart when it comes to anti-cancer drugs, evolving and becoming resistant to even the strongest chemotherapies over time. To combat this evasive behavior, researchers have developed a method named D2O-probed CANcer Susceptibility Test Ramanometry (D2O-CANST-R) to see, at single-cell/organelle level, how pharmaceuticals induce cancer cell death and how cancer cells adapt.
The research, conducted by the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), was published on Jan. 12 in Analytical Chemistry, a journal of the American Chemical Society.
"Understanding the mechanism of cellular response to drugs and pharmaceutical therapies is crucial to improving cancer treatment," said paper author XU Jian, director of the Single-Cell Center at QIBEBT. He explained that cancer cells can resist chemotherapy by changing metabolic activity for adaptation to drug stress, but exactly how this happens is poorly understood. "Approaches are needed to rapidly illuminate the particular effects of a drug on metabolic activity of cancer cells. This is clinically important as precise and personal administration of cancer chemotherapy is crucial for saving cancer patients' lives."
Maryam Hekmatara, a PhD student of XU, and her workmates paired a powerful algorithm with Raman spectroscopy, which involves using a laser to excite photons in a sample to reveal structural information, including interactions. They examined how rapamycin, an anti-cancer drug, changed the metabolic activity in a human cancer cell line and in yeast.
Their method revealed the changes small organelles inside the cells made in energy use and consumption. With a resolution capability of less than one micrometer - the width of a human hair is typically 80 to 100 micrometers, for comparison - the approach has the potential to reveal the metabolism in a cancer cell with very fine details.
"The method is able to rapidly and precisely track and distinguish changes in lipid and protein metabolic-inhibitory effect of rapamycin," Hekmatara said, noting the method takes just days compared to traditional tests that can take much longer to see if an individual patient's cells will respond favorably to a drug. "It is also very precise, as it can distinguish cancer cell responses to drugs at the single cell and single organelle resolution, which is crucial for understanding why the drug is - or is not - effective."
The researchers plan to further study how cells become resistant, as well as further develop their method as a personalized approach to determine the most effective anti-cancer drug for a patient.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
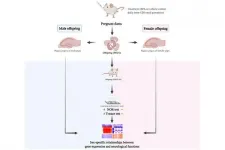
Prenatal BPA exposure may contribute to the male bias of autism spectrum disorder
2021-01-19
A new study by researchers from Chulalongkorn University, Tohoku University, and The George Washington University is the first to identify autism candidate genes that may be responsible for the sex-specific effects of bisphenol A (BPA) on the brain. It suggests BPA may serve as an environmental factor that contributes to the prevalence of male bias in autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
The research was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
BPA is widely used in many products in our daily life and abundant in micro/nanoplastics found in the environment, ...
Ultra-small nanomedicines which stably deliver oligonucleotides to refractory cancers
2021-01-19
Summary
Ultra-small nanomedicines of approximately 18 nm were fabricated by dynamic ion-pairing between Y-shaped block copolymers and nucleic acid drugs, such as siRNA and antisense drugs.
Chemically modified and double-stranded oligonucleotides dramatically enhanced the stability of the ultra-small nanomedicines in the blood circulation.
The ultra-small size allows for high permeability in cancer tissues by slipping through the cracks in tumor vasculatures and stromal tissues.
Clinical trials and preclinical studies using the developed ultra-small nanomedicines are proceeding for cancer therapy.
Published in the website of Journal of Controlled Release on January 6.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.01.001
Main body
January 19, 2021 - Kawasaki in ...
How drain flies dodge a washout
2021-01-19
The survival of pesky little flies in showers and other wet areas around the house, impervious to water droplets that may be larger than they are, comes down to more than quick reflexes. The insects have evolved a unique coating of hairs that allows them to shrug off water droplets of almost any size, KAUST researchers have shown.
Sigurdur Thoroddsen, who leads the high-speed fluids imaging laboratory at KAUST, couldn't help but take a professional interest in the small drain flies that made a home in his shower and never seemed to wash away. Thoroddsen's research focuses on multiphase flow and dynamics at air-liquid interfaces -- an environment where drain flies have found a niche, despite some risky physics.
Insects are so small that the surface tension of ...
Solar activity reconstructed over a millennium
2021-01-19
What goes on in the sun can only be observed indirectly. Sunspots, for instance, reveal the degree of solar activity - the more sunspots are visible on the surface of the sun, the more active is our central star deep inside. Even though sunspots have been known since antiquity, they have only been documented in detail since the invention of the telescope around 400 years ago. Thanks to that, we now know that the number of spots varies in regular eleven-year cycles and that, moreover, there are long-lasting periods of strong and weak solar activity, which is also reflected in the climate on Earth.
However, how solar activity developed before the start of systematic records has so far been ...
New biodegradable polyurethane foams are developed from wheat straw
2021-01-19
Every year around 734 million tons of wheat straw are produced worldwide, a large amount of waste, which is cheap and has had no well-defined use until now. Recently, the RNM-271 Chemical Engineering and FQM-383 NANOVAL Organic Chemistry research groups at the University of Córdoba have been able to give a new use to this agricultural excess material, by using it as the foundation in order to manufacture polyurethane foams.
Also known as foam rubber, this plastic material, often manufactured from petroleum by-products, is extremely versatile within the industry and has multiple uses in the construction and automobile sectors as a sealant as well as ...
Clocking electron movements inside an atom
2021-01-19
An international consortium of scientists, initiated by Reinhard Kienberger, Professor of Laser and X-ray Physics at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), several years ago, has made significant measurements in the femtosecond range at the U.S. Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC).
However, on these miniscule timescales, it is extremely difficult to synchronize the X-ray pulse that sparks a reaction in the sample on the one hand and the laser pulse which 'observes' it on the other. This problem is called timing jitter, and it is a major hurdle in ongoing ...
New method heals skeletal injuries with synthetic bone
2021-01-19
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden, in collaboration with colleagues in Dresden, Germany, have developed a way of combining a bone substitute and drugs to regenerate bone and heal severe fractures in the thigh or shin bone. The study, published in the research journal Science Advances, was conducted on rats, but the researchers think that the method in various combinations will soon be commonplace in clinical settings.
"The drugs and materials we used in the study for the regeneration of bone are already approved. We simply packaged them in a new combination. Therefore, there are no real obstacles to already using the method in clinical studies for certain major bone defects that are difficult to resolve in patients. But we want to ...
A sea of rubbish: ocean floor landfills
2021-01-19
The Messina Strait, a submarine bridge separating the island of Sicily from the Italian Peninsula, is the area with the largest marine litter density worldwide -more than a million objects per square kilometre in some parts-, as reported in a new review paper published in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Also, over the next thirty years, the volume of rubbish in the sea could surpass three billion metric tons (Mt), as cited in the study, whose corresponding authors are the experts Miquel Canals, from the Faculty of Earth Sciences of the University of Barcelona, and Georg Hanke from the European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC), where ...
Rescuers at risk: emergency personnel face trauma and post traumatic stress symptoms
2021-01-19
A new study in Frontiers in Psychiatry has for the first time, demonstrated differences in the prevalence of post-traumatic stress symptoms (PTSS) in different groups of rescue workers and emergency personnel, including firefighters, police officers and psychiatric nurses. The researchers showed that the varying experiences and circumstances these workers encounter, such as handling aggressive people, working with families or dealing with deaths and suicide, are tied to varying levels of PTSS and suicidal thoughts, with emergency department staff and psychiatric nurses showing the highest levels of PTSS and suicidal thoughts out of the emergency professions studied. The findings highlight the urgent need for bespoke training and counselling services ...
Aphids suck: Invasive aphid found on Danish apple trees
2021-01-19
INSECTS The spirea aphid, Aphis spiraecola, an invasive pest, has been discovered for the first time in Denmark by University of Copenhagen researchers. The extent of its current distribution remains unknown, but in time, it could prove to be a troublesome pest for Danish apple growers.
Aphis
Whether the discovery of this aphid in Denmark is an isolated incident, or if the species has made itself at home due to a milder climate, remains unknown to the researchers. Closer investigation is needed. Photo: UCPH/Uni.Budapest
In a collaboration with colleagues at the University of Budapest, University of Copenhagen researchers have analysed and compared a number of samples of green aphids from apples around ...