Using ancient fossils and gravitational-wave science to predict earth's future
A group of international scientists, including an Australian astrophysicist, has used knowhow from gravitational wave astronomy (used to find black holes in space) to study ancient marine fossils as a predictor of climate change.
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) A group of international scientists, including an Australian astrophysicist, has used knowhow from gravitational wave astronomy (used to find black holes in space) to study ancient marine fossils as a predictor of climate change.
The research, published in the journal Climate of the Past, is a unique collaboration between palaeontologists, astrophysicists and mathematicians - to improve the accuracy of a palaeo-thermometer, which can use fossil evidence of climate change to predict what is likely to happen to the Earth in coming decades.
Professor Ilya Mandel, from the ARC Centre of Excellence in Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav), and colleagues, studied biomarkers left behind by tiny single-cell organisms called archaea in the distant past, including the Cretaceous period and the Eocene.
Marine archaea in our modern oceans produce compounds called Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers (GDGTs). The ratios of different types of GDGTs they produce depend on the local sea temperature at the site of formation.
When preserved in ancient marine sediments, the measured abundances of GDGTs have the potential to provide a geological record of long-term planetary surface temperatures.
To date, scientists have combined GDGT concentrations into a single parameter called TEX86, which can be used to roughly estimate the surface temperature. However, this estimate is not very accurate when the values of TEX86 from recent sediments are compared to modern sea surface temperatures.
"After several decades of study, the best available models are only able to measure temperature from GDGT concentrations with an accuracy of around 6 degrees Celsius," Professor Mandel said. Therefore, this approach cannot be relied on for high-precision measurements of ancient climates.
Professor Mandel and his colleagues at the University of Birmingham in the UK have applied modern machine-learning tools -- originally used in the context of gravitational-wave astrophysics to create predictive models of merging black holes and neutron stars -- to improve temperature estimation based on GDGT measurements. This enabled them to take all observations into account for the first time rather than relying on one particular combination, TEX86. This produced a far more accurate palaeo-thermometer. Using these tools, the team extracted temperature from GDGT concentrations with an accuracy of just 3.6 degrees - a significant improvement, nearly twice the accuracy of previous models.
According to Professor Mandel, determining how much the Earth will warm in coming decades relies on modelling, "so it is critically important to calibrate those models by utilising literally hundreds of millions of years of climate history to predict what might happen to the Earth in the future," he said.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
In the strawberry nursery industry, a nursery's reputation relies on their ability to produce disease- and insect-free plants. The best way to produce clean plants is to start with clean planting stock. Many nurseries struggle with angular leaf spot of strawberry, a serious disease that can result in severe losses either by directly damaging the plant or indirectly through a violation of quarantine standards within the industry.
Angular leaf spot is caused by the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas fragariae. Current management strategies rely primarily ...
2021-01-19
Chemotherapy and radiation treatments are known to cause harsh side effects that patients can see or feel throughout their bodies. Yet there are additional, unseen and often undiscussed consequences of these important therapies: the impacts on their future pregnancies and hopes for healthy children.
Extensive evidence shows that chemotherapy and radiation treatments are genotoxic, meaning they can mutate the DNA and damage chromosomes in patients' cancerous and noncancerous cells alike. When this occurs in a germline cell - which are egg cells in women and sperm in men - it can lead to serious fetal and birth ...
2021-01-19
A new type of ultra-efficient, nano-thin material could advance self-powered electronics, wearable technologies and even deliver pacemakers powered by heart beats.
The flexible and printable piezoelectric material, which can convert mechanical pressure into electrical energy, has been developed by an Australian research team led by RMIT University.
It is 100,000 times thinner than a human hair and 800% more efficient than other piezoelectrics based on similar non-toxic materials.
Importantly, researchers say it can be easily fabricated through a cost-effective and commercially scalable method, using ...
2021-01-19
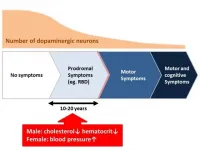
A research team led by Nagoya University in Japan has found that blood pressure, the hematocrit (the percentage of red blood cells in blood), and serum cholesterol levels change in patients with Parkinson's disease long before the onset of motor symptoms. This finding, which was recently published online in Scientific Reports, may pave the way for early diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Parkinson's disease, the second most common disease affecting the nervous system after Alzheimer's disease, is caused by a deficiency in a neurotransmitter called dopamine. It is known that more than half of all dopaminergic neurons are already lost in patients with Parkinson's disease in the stage wherein they ...
2021-01-19
India has an energy problem. It currently relies heavily on coal and consumer demand is expected to double by 2040, making its green energy targets look out of reach. Part of the solution could come from harvesting energy from footsteps, say Hari Anand and Binod Kumar Singh from the University of Petroleum and Energy Studies in Dehradun, India. Their new study, published in the De Gruyter journal Energy Harvesting and Systems, shows that Indian attitudes towards power generated through piezoelectric tiles are overwhelmingly positive.
Cities like Delhi and Mumbai are famously crowded, especially at railway stations, temples and big commercial buildings. This led researchers to wonder whether piezoelectric tiles, which produce ...
2021-01-19
Researchers have used the world's smallest, smartphone-sized DNA sequencing device to monitor hundreds of different bacteria in a river ecosystem.
Writing in the journal eLife, the interdisciplinary team from the University of Cambridge, UK, provide practical and analytical guidelines for using the device, called the MinION (from Oxford Nanopore Technologies), to monitor freshwater health. Their guidelines promise a significantly more cost-effective and simple approach to this work outside the lab, compared to existing methods.
Rowers and swimmers in Cambridge are regularly affected by waterborne infections such as Weil's disease, sometimes leading to public closures of the city's iconic waterways. Monitoring the microbial species in freshwater ...
2021-01-19
Whether consciously or unconsciously, automotive firms time their product recalls to minimize stock price penalties, resulting in unnecessary delays and clusters of subsequent recalls by other companies, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
An initial recall by one firm prompts clusters of additional recalls in close proximity by competitor firms, according to "Hiding in the Herd: The Product Recall Clustering Phenomenon," forthcoming in Manufacturing and Service Operations Management from Kaitlin Wowak, assistant professor of IT, analytics, and operations at Notre Dame's Mendoza College of Business.
According to the study, "Automobile recalls seem to be announced after inexplicable delays. Toyota's unintended acceleration recall and General ...
2021-01-19
Nearly 78 per cent of children with autism have at least one mental health condition and nearly half have two mental health conditions or more, according to a new U.S. study from the University of British Columbia's department of psychology and the AJ Drexel Autism Institute at Drexel University (Pennsylvania).
The study also found mental health conditions present in 44.8 per cent of pre-school age children with autism. The scope of the issue among that age group had not previously been established using a large, population-based sample.
By contrast, the study found that only 14.1 per cent of youth without autism (ages 3-17) had mental health conditions.
It is the first research since 2008 to examine the prevalence of mental health conditions among children with autism at a population ...
2021-01-19
Malta, a sovereign microstate in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, has no shortage of sunny beaches, honey-bricked villages and rugged countryside. Beyond its Mediterranean charm, Malta is home to a geographically and culturally isolated population whose unique genetic makeup, makes this island nation a goldmine for genetics research.
Four years ago, the University of Malta set up a national ALS Registry and Biobank to identify patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and collect data on their residence, occupation, lifestyle and environmental exposures. Blood samples ...
2021-01-19
With the global student community taking online courses as a result of the anti-Covid-19 measures, a study led by the University of Geneva (UNIGE) reveals that online courses deepen inequalities between gifted and less gifted students by 5%. The results of the study, which was based on data collected in 2016-2017 prior to the anti-Covid lockdown initiatives, are published in the Journal of the European Economic Association. They indicate that this learning gap between different student profiles is mainly due to their behaviour and motivation. The study gives higher education establishments worldwide practical ways to deal with lockdown or the chronic lack of space in lecture theatres, including via co-educational ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Using ancient fossils and gravitational-wave science to predict earth's future
A group of international scientists, including an Australian astrophysicist, has used knowhow from gravitational wave astronomy (used to find black holes in space) to study ancient marine fossils as a predictor of climate change.