(Press-News.org) Data analysis is revealing a second sharp drop in the number of people admitted to hospital in England with acute heart failure or a heart attack.
The decline began in October as the numbers of COVID-19 infections began to surge ahead of the second lockdown, which came into force in early November.
The findings, from a research group led by the University of Leeds, have been revealed in a letter to the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
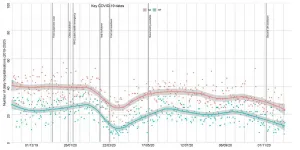
The decline - 41 percent fewer people attending with heart failure and 34 percent with a heart attack compared to pre-pandemic levels - is approaching the size of that observed during the first wave of the pandemic. The researchers believe the drop in people seeking emergency medical help for cardiovascular emergences in the first wave of the pandemic may have contributed to more than 2,000 excess deaths in England and Wales.
In the letter to the journal, the scientists note: "The second dip appears of similar magnitude to that of the first, and signals that the public are fearful of attending hospital despite having medical emergencies..."
Chris Gale, Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine at Leeds, who supervised the data analysis, said: "I am afraid that we are seeing a re-run of one of the preventable tragedies of the first wave - people were either too afraid to go to hospital for fear of contracting COVID-19 or were not referred for treatment.
"The message to patients needs to be clear. If they experience symptoms of a heart attack or acute heart failure, they need to attend hospital. These are unforgiving medical emergencies. With the right help, people can recover from them. But if patients delay or avoid treatment, their will suffer life-limiting complications - or they will die."
Dr Jianhua Wu, Associate Professor at the University of Leeds, led the analysis. He said: "One of the worrying aspects of our research is that the decline we have seen since October may not have yet bottomed out. Inevitably there is a fear that will result in deaths that perhaps could have been avoided."?
Professor Simon Ray, President of the British Cardiovascular Society, added: "This research illustrates again the importance of the message that other medical problems don't stop because of COVID and that people with serious problems like heart attack and acute heart failure still need to be seen and treated urgently to prevent death or long-term ill health."
The data analysis
Data on the daily admission to hospital of people suffering acute heart failure or a heart attack is recorded on a national research database, the National Institute for Cardiovascular Outcomes Research. The researchers compared daily admission rates before the pandemic with what happened during the first wave of the pandemic and then at the start of the second lockdown in England. The data was drawn from 66 hospitals.
Please see the attached time series graph.
The second lockdown
From the beginning of October to 17 November 2020, the daily number of people attending hospital emergency units with heart failure dropped 41 percent - and for heart attack, the decline was 34 percent.
Since submitting their data analysis to the journal, the research team have received more up to date figures, which includes patient data for the whole of November, and it reveals a continuing drop in patient attendances.
The first lockdown
Patient attendances began to drop ahead of the first lockdown, from 23 March 2020, and reached their lowest point in early April, with 54 percent fewer people attending hospital emergency units with heat failure, and 32 percent with a heart attack. Patient numbers did rebound towards the latter half of June but did not return fully to pre-pandemic levels.
INFORMATION:
Notes to editors
For further information and for requests to talk to Professor Gale, please contact David Lewis in the media office at the University of Leeds - d.lewis@leeds.ac.uk or +44 (0)7710 013287
University of Leeds
The University of Leeds is one of the largest higher education institutions in the UK, with more than 38,000 students from more than 150 different countries, and a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive universities. The University plays a significant role in the Turing, Rosalind Franklin and Royce Institutes.
We are a top ten university for research and impact power in the UK, according to the 2014 Research Excellence Framework, and are in the top 100 of the QS World University Rankings 2020.
The University was awarded a Gold rating by the Government's Teaching Excellence Framework in 2017, recognising its 'consistently outstanding' teaching and learning provision. Twenty-six of our academics have been awarded National Teaching Fellowships - more than any other institution in England, Northern Ireland and Wales - reflecting the excellence of our teaching. http://www.leeds.ac.uk
The human brain has about as many neurons as glial cells. These are divided into four major groups: the microglia, the astrocytes, the NG2 glial cells, and the oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocytes function primarily as a type of cellular insulating tape: They form long tendrils, which consist largely of fat-like substances and do not conduct electricity. These wrap around the axons, which are the extensions through which the nerve cells send their electrical impulses. This prevents short circuits and accelerates signal forwarding.
Astrocytes, on the other hand, supply the nerve cells with energy: Through their appendages they come into contact with blood vessels and absorb glucose from these. ...
AMES, Iowa - Even if you weren't a physics major, you've probably heard something about the Higgs boson.
There was the title of a 1993 book by Nobel laureate Leon Lederman that dubbed the Higgs "The God Particle." There was the search for the Higgs particle that launched after 2009's first collisions inside the Large Hadron Collider in Europe. There was the 2013 announcement that Peter Higgs and Francois Englert won the Nobel Prize in Physics for independently theorizing in 1964 that a fundamental particle - the Higgs - is the source of mass in subatomic ...
BROOKLYN, New York, Tuesday, January 19, 2021 - The World Health Organization END ...
WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- A Velcro-like fastener with a microscopic design that looks like tiny mushrooms could mean advances for everyday consumers and scientific fields like robotics.
In Biointerphases, published by AIP Publishing, researchers from Wageningen University in the Netherlands show how the design can use softer materials and still be strong enough to work.
Probabilistic fasteners work, because they are designed with a tiny pattern on one surface that interlocks with features on the other surface. Currently available fasteners, like Velcro and 3M, are called hook and loop fasteners. That design requires harder, stiff material, which ...
Even prior to the pandemic, burnout among health care professionals was a pervasive public health concern, with END ...
Large-scale land acquisitions by foreign investors, intended to improve global food security, had little to no benefit, increasing crop production in some areas while simultaneously threatening local food security in others, according to researchers who studied their effects.
The END ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Tiny amounts of gender bias in employee hiring decisions contribute to concerning rates of discrimination and productivity losses that together represent significant costs, financial and otherwise, for employers, a new study from Oregon State University has found.
Gender bias is a subtle, unintentional preference for one gender over the other. Despite significant efforts to reduce bias in hiring over the last several decades, it continues to persist and pose potential problems for companies, said Jay Hardy, an assistant professor of management in OSU's College ...
BOZEMAN, Montana (January 19, 2021) - A four-year study recently published in Ecology and Evolution concludes that the fungal disease, white-nose syndrome, poses a severe threat to many western North American bats.
Since it was first detected in 2006, white-nose syndrome has killed millions of bats in eastern and central North America. The spread of the fungal pathogen that causes white-nose syndrome in hibernating bats has reached several western U.S. states, mostly likely through bat-to-bat spread, and is presently threatening western species.
Bats with white-nose syndrome have fungus growing on their nose and wings, as the name implies, but the fungal infection also triggers a higher frequency of arousals from hibernation. ...
Anyone who has tried and failed to meditate knows that our minds are rarely still. But where do they roam? New research led by UC Berkeley has come up with a way to track the flow of our internal thought processes and signal whether our minds are focused, fixated or wandering.
Using an electroencephalogram (EEG) to measure brain activity while people performed mundane attention tasks, researchers identified brain signals that reveal when the mind is not focused on the task at hand or aimlessly wandering, especially after concentrating on an assignment.
Specifically, increased alpha brain waves were detected in the prefrontal cortex of ...
For the first time, scientists have successfully used satellite cameras coupled with deep learning to count animals in complex geographical landscapes, taking conservationists an important step forward in monitoring populations of endangered species.
For this research, the satellite Worldview 3 used high-resolution imagery to capture African elephants moving through forests and grasslands. The automated system detected animals with the same accuracy as humans are able to achieve.
The algorithm that enabled the detection process was created by Dr Olga Isupova, a computer scientist at the University of Bath in the UK. The project was a collaboration with the UK's University of Oxford and the University of Twente in the Netherlands.
Dr ...