Getting shapes into numbers
A mathematical framework enables accurate characterization of shapes
2021-01-21
(Press-News.org) In nature, many things have evolved that differ in size, color and, above all, in shape. While the color or size of an object can be easily described, the description of a shape is more complicated. In a study now published in Nature Communications, Jacqueline Nowak of the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology and her colleagues have outlined a new and improved way to describe shapes based on a network representation that can also be used to reassemble and compare shapes.
Jacqueline Nowak designed a novel approach that relies on a network-based shape representation, named visibility graph, along with a tool for analyzing shapes, termed GraVis. The visibility graph represents the shape of an object that is defined by its surrounding contour and the mathematical structure behind GraVis is specified by a set of nodes equidistantly placed around the contour. The nodes are then connected with each other by edges, that do not cross or align with the shape boundary.As a result, testing the connection between all pairs of nodes specifies the visibility graph for the analyzed shape.
In this study, Jacqueline Nowak used the visibility graphs and the GraVis tool to compare different shapes. To test the power of the new approach, visibility graphs of simple triangular, rectangular and circular shapes, but also complex shapes of sand grains, fish shapes and leaf shapes were compared with each other.
By using different machine learning approaches, they demonstrated that the approach can be used to distinguish shapes according to their complexity. Furthermore, visibility graphs enable to distinguish the complexity of shapes as it was shown for epidermal pavement cells in plants, which have a similar shape to pieces of jigsaw puzzle. For these cells, distinct shape parameters like lobe length, neck width or cell area can be accurately quantified with GraVis. "The quantification of the lobe number of epidermal cells with GraVis outperforms existing tools, showing that it is a powerful tool to address particular questions relevant to shape analysis", says Zoran Nikoloski, GraVis project leader, head of the research group "Systems biology and Mathematical Modelling" at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology and Professor of Bioinformatics at University of Potsdam.
In future, the scientists want to apply visibility graphs of epidermal cells and entire leaves to gain biological insights of key cellular processes that impact shape. In addition, shape features of different plant cells quantified by GraVis can facilitate genetic screens to determine the genetic basis of morphogenesis. Finally, the application of GraVis will help to gain deeper understanding of the interrelation between cells and organ shapes in nature.
INFORMATION:
Original publication
Jacqueline Nowak, Ryan Christopher Eng, Timon Matz, Matti Waack, Staffan Persson, Arun Sampathkumar, Zoran Nikoloski
A network-based framework for shape analysis enables accurate characterization and classification of leaf epidermal cells
Nature Communications, Published: 19 January 2021
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-21
The study explains the benefits of both the wing shape and the flexibility of their wings.
The Lund researchers studied the wingbeats of freely flying butterflies during take-off in a wind tunnel. During the upward stroke, the wings cup, creating an air-filled pocket between them. When the wings then collide, the air is forced out, resulting in a backward jet that propels the butterflies forward. The downward wingbeat has another function: the butterflies stay in the air and do not fall to the ground.
The wings colliding was described by researchers almost 50 years ago, but it is only in this study that the theory has been tested on real butterflies in free ...
2021-01-21
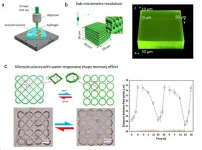
Three-dimensional (3D) direct laser writing (DLW) based on two-photon polymerisation (TPP) is an advanced technology for fabricating precise 3D hydrogel micro- and nanostructures for applications in biomedical engineering. Particularly, the use of visible lasers for the 3D DLW of hydrogels is advantageous because it enables high fabrication resolution and promotes wound healing. Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGda) has been widely used in TPP fabrication owing to its high biocompatibility. However, the high laser power required in the 3D DLW of PEGda microstructures using a visible laser in a high-water-content environment limits its applications to only those below the biological laser power safety level.
In a new paper ...
2021-01-21
Rather like David versus Goliath, it appears that Saturn's tilt may in fact be caused by its moons. This is the conclusion of recent work carried out by scientists from the CNRS, Sorbonne University and the University of Pisa, which shows that the current tilt of Saturn's rotation axis is caused by the migration of its satellites, and especially by that of its largest moon, Titan.
Recent observations have shown that Titan and the other moons are gradually moving away from Saturn much faster than astronomers had previously estimated. By incorporating this increased migration rate into their calculations, the researchers concluded that ...
2021-01-21
To process information in our brains, nerve cells produce brief electrical impulses, called action potentials, triggered from one highly specialized region. Research from the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, together with researchers from Heidelberg University and the University of Göttingen in Germany, now show that the electrical trigger sites surprisingly change with experience; they are either becoming smaller with increasing number of experiences and, vice versa, they grow larger when less input arrives in the brain. The results were published in Nature Communications.
Exploring the environment
Rodents learn about their environment by moving their highly sensitive whiskers, with which they touch ...
2021-01-21
Researchers from the Sonia and Marco Nadler Institute of Archaeology at Tel Aviv University unraveled the function of flint tools known as 'chopping tools', found at the prehistoric site of Revadim, east of Ashdod. Applying advanced research methods, they examined use-wear traces on 53 chopping tools, as well as organic residues found on some of the tools. They also made and used replicas of the tools, with methods of experimental archaeology. The researchers concluded that tools of this type, found at numerous sites in Africa, Europe and Asia, were used by prehistoric humans at Revadim to neatly break open bones of medium-size animals such as fallow deer, gazelles and ...
2021-01-21
UV-radiation can affect hormone levels of postmenopausal women negatively and this may contribute to several health issues.
The concentration of oestrogens in the blood affects a woman's health in many ways. For example, oestrogens contribute to a strong bone structure and help wounds heal more quickly:
"When a woman reaches menopause, we see the levels of oestrogens decline and an increase of other hormones, called gonadotropins", says Kai Triebner at the University of Bergen.
For several years, he has studied the hormonal balance of women in relation to menopause: What effects changing hormone levels ...
2021-01-21
With Japan's society rapidly aging, there has been a sharp increase in patients who experience motor dysfunctions. Rehabilitation is key to overcoming such ailments.
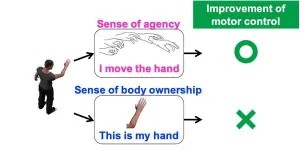
A researcher from Tohoku University has developed a new virtual reality (VR) based method that can benefit rehabilitation and sports training by increasing bodily awareness and?improving motor control.
His research was published in the Journal Scientific Report.
Not only can we see and touch our body, but we can sense it too. Our body is constantly firing off information to our brains that tell us where our limbs are in real-time. This process makes us aware of our body and gives us ownership over it. Meanwhile, our ability to control ...
2021-01-21
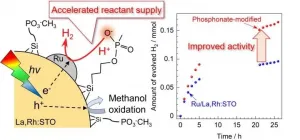
Water splitting research for solar hydrogen production has focused on physical processes inside the semiconductor, such as light absorption, charge separation, and chemical processes on the surface that are highly complex and rely on the development of new materials. However, processes inside the solution had yet to be thoroughly explored.
One recent approach to improve photocatalytic hydrogen production was proposed by loading phosphonate groups on the surface of the visible-light-responsive photocatalyst lanthanum and rhodium-doped strontium titanate (La,Rh:STO) with a silane coupling agent. The phosphonate functional group functions as a mediator of proton supply (i.e., promotes the supply of reactants) and improves hydrogen production activity.
There have been ...
2021-01-21
Just a few millimetres thick, articular cartilage plays a crucial role in our musculoskeletal system, since it is responsible for smooth (in the truest sense of the word) movement. However, the downside of its particular structure is that even minor injuries do not regenerate. Timely treatment of cartilage damage is therefore essential. Biomaterials are often used to support the cells, their distribution and protection. In most cases, this treatment significantly improves the patient's clinical symptoms but fails to fully restore the cartilage to its original state. The working group led by Sylvia Nürnberger (MedUni Vienna's Department of Orthopedics and Trauma Surgery) ...
2021-01-21
One of Brazil's worst environmental disasters - a dam collapse that also killed more than 200 people - could have been foreseen with the right monitoring technology, according to a new study by the University of Nottingham and Durham University.
The high-profile catastrophe took place on 25 January 2019 at a tailings dam near the Córrego do Feijão iron ore mine, close to the town of Brumadinho, in Minas Gerais state, south-east Brazil.
When the dam collapsed, it caused a torrent of sludge to cover surrounding land; taking lives, destroying homes and livelihoods and polluting rivers with toxic material.
Owned by Vale, Brazil's largest mining company, the tailings dam was ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Getting shapes into numbers
A mathematical framework enables accurate characterization of shapes