Electrons caught in the act
Scientists at the University of Tsukuba combine scanning tunneling microscopy with ultrafast spectroscopy to image the motion of electrons with unprecedented resolution, which may lead to advances in semiconductors and optoelectronics
2021-01-21
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan - A team of researchers from the Faculty of Pure and Applied Sciences at the University of Tsukuba filmed the ultrafast motion of electrons with sub-nanoscale spatial resolution. This work provides a powerful tool for studying the operation of semiconductor devices, which can lead to more efficient electronic devices.
The ability to construct ever smaller and faster smartphones and computer chips depends on the ability of semiconductor manufacturers to understand how the electrons that carry information are affected by defects. However, these motions occur on the scale of trillionths of a second, and they can only be seen with a microscope that can image individual atoms. It may seem like an impossible task, but this is exactly what a team of scientists at the University of Tsukuba was able to accomplish.
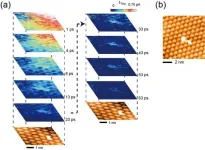
The experimental system consisted of Buckminsterfullerene carbon molecules--which bear an uncanny resemblance to stitched soccer balls--arranged in a multilayer structure on a gold substrate. First, a scanning tunneling microscope was set up to capture the movies. To observe the motion of electrons, an infrared electromagnetic pump pulse was applied to inject electrons into the sample. Then, after a set time delay, a single ultrafast terahertz pulse was used to probe the location of the elections. Increasing the time delay allowed the next "frame" of the movie to be captured. This novel combination of scanning tunneling microscopy and ultrafast pulses allowed the team to achieve sub-nanoscale spatial resolution and near picosecond time resolution for the first time. "Using our method, we were able to clearly see the effects of imperfections, such as a molecular vacancy or orientational disorder," explains first author Professor Shoji Yoshida. Capturing each frame took only about two minutes, which allows the results to be reproducible. This also makes the approach more practical as a tool for the semiconductor industry.
"We expect that this technology will help lead the way towards the next generation of organic electronics" senior author Professor Hidemi Shigekawa says. By understanding the effects of imperfections, some vacancies, impurities, or structural defects can be purposely introduced into devices to control their function.
INFORMATION:
The work is published in ACS Photonics as "Terahertz Scanning Tunneling Microscopy for Visualizing Ultrafast Electron Motion in Nanoscale Potential Variations" (DOI:10.1021/acsphotonics.0c01572).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-21
The results of a study led by Northern Arizona University and the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope, suggest the immune systems of people infected with COVID-19 may rely on antibodies created during infections from earlier coronaviruses to help fight the disease.
COVID-19 isn't humanity's first encounter with a coronavirus, so named because of the corona, or crown-like, protein spikes on their surface. Before SARS-CoV-2 -- the virus that causes COVID-19 -- humans have navigated at least 6 other types of coronaviruses.
The study sought to understand how coronaviruses (CoVs) ignite the human immune system and conduct a deeper ...
2021-01-21
An adverse upbringing often impairs people's circumstances and health in their adult years, especially for couples who have both had similar experiences. This is shown by a new study, carried out by Uppsala University researchers, in which 818 mothers and their partners filled in a questionnaire one year after having a child together. The study is now published in the scientific journal PLOS ONE.
"When we studied couples where both partners stated they'd had a hard time as children, the connection between negative childhood experience and a relatively ...
2021-01-21
Early Medieval Europe is frequently viewed as a time of cultural stagnation, often given the misnomer of the 'Dark Ages'. However, analysis has revealed new ideas could spread rapidly as communities were interconnected, creating a surprisingly unified culture in Europe.
Dr Emma Brownlee, Department of Archaeology, University of Cambridge, examined how a key change in Western European burial practices spread across the continent faster than previously believed - between the 6th - 8th centuries AD, burying people with regionally specific grave goods was largely abandoned in favour of a more standardised, unfurnished burial.
"Almost everyone from the eighth century onwards ...
2021-01-21
As scientists increasingly rely on eyewitness accounts of earthquake shaking reported through online systems, they should consider whether those accounts are societally and spatially representative for an event, according to a new paper published in Seismological Research Letters.
Socioeconomic factors can play a significant if complex role in limiting who uses systems such as the U.S. Geological Survey's "Did You Feel It?" (DYFI) to report earthquake shaking. In California, for instance, researchers concluded that DYFI appears to gather data across a wide socioeconomic range, albeit with some intriguing differences related to neighborhood income levels during earthquakes such as the ...
2021-01-21
The neocortex is the part of the brain that humans use to process sensory impressions, store memories, give instructions to the muscles, and plan for the future. These computational processes are possible because each nerve cell is a highly complex miniature computer that communicates with around 10,000 other neurons. This communication happens via special connections called synapses.
The bigger the synapse, the stronger its signal
Researchers in Kevan Martin's laboratory at the Institute of Neuroinformatics at the University of Zurich (UZH) and ETH Zurich have now shown for the first time that the size of synapses determines the strength of their ...
2021-01-21
TAMPA, Fla. -- Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are rare hematologic malignancies of the bone marrow. They can occur spontaneously or secondary to treatment for other cancers, so called therapy related disease, which is frequently associated with a mutation of the tumor suppressor gene TP53. Standard treatment for these patients includes hypomethylating agents such as azacitidine or decitabine but unfortunately outcomes are very poor.
"Patients with TP53-mutant disease, which is roughly 10% to 20% of AML and de novo MDS cases, don't have many options ...
2021-01-21
Growing perennial grasses on abandoned cropland has the potential to counteract some of the negative impacts of climate change by switching to more biofuels, according to a research group from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
Researchers consider increased use of biofuels to be an important part of the solution to reduce CO2 emissions. But the production of plants for biofuels can have some unfortunate trade-offs.
Now, the NTNU researchers have come up with a scenario that would put less pressure on food production and plant and animal life.
"We can grow perennial grasses in areas that until recently were used for growing food but that are no longer used for that purpose," explains Jan Sandstad ...
2021-01-21
DURHAM, N.C. - Researchers at Duke and Mt. Sinai have identified a molecular mechanism that prevents a viral infection during a mother's pregnancy from harming her unborn baby.
When a person becomes infected by a virus, their immune system sends out a chemical signal called type I interferon, which tells surrounding cells to increase their anti-viral defenses, including making more inflammation.
This response helps to prevent the virus from copying itself and gives the adaptive immune system more time to learn about the new invader and begin to hunt it down.
A pregnant woman ...
2021-01-21
Initially earmarked for covert military operations, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones have since gained tremendous popularity, which has broadened the scope of their use. In fact, "remote pilot" drones have been largely replaced by "autonomous" drones for applications in various fields. One such application is their usage in rescue missions following a natural or man-made disaster. However, this often requires the drones to be able to land safely on uneven terrain--which can be very difficult to execute.
"While it is desirable to automate the landing using a depth camera that can gauge terrain unevenness and find suitable landing spots, a framework serving as a useful base needs to be developed first," ...
2021-01-21
A neurosurgeon from RUDN University studied the mental activity of developers at work. In his novel method, he combined mobile EEG devices and software that analyzes neurophysiological data. The results of the study were published in the materials of the 23rd Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD).
To collect data about the activity of specific areas of the brain, one can use functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). However, this method involves massive equipment and is only available at clinics or laboratories. Therefore, it is quite difficult to register human mental activity in a natural environment. Even if usual conditions are reproduced in a lab, the very fact that it is an experiment would still affect the behavior of the participants. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Electrons caught in the act
Scientists at the University of Tsukuba combine scanning tunneling microscopy with ultrafast spectroscopy to image the motion of electrons with unprecedented resolution, which may lead to advances in semiconductors and optoelectronics