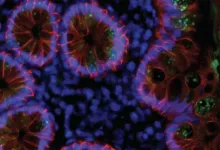
(Press-News.org) As the number of people who have fought off SARS-CoV-2 climbs ever higher, a critical question has grown in importance: How long will their immunity to the novel coronavirus last? A new Rockefeller study offers an encouraging answer, suggesting that those who recover from COVID-19 are protected against the virus for at least six months, and likely much longer.
The findings, published in Nature, provide the strongest evidence yet that the immune system "remembers" the virus and, remarkably, continues to improve the quality of antibodies even after the infection has waned. Antibodies produced months after the infection showed increased ability to block SARS-CoV-2, as well as its mutated versions such as the South African variant.
The researchers found that these improved antibodies are produced by immune cells that have kept evolving, apparently due to a continued exposure to the remnants of the virus hidden in the gut tissue.
Based on these findings, researchers suspect that when the recovered patient next encounters the virus, the response would be both faster and more effective, preventing re-infection.
"This is really exciting news. The type of immune response we see here could potentially provide protection for quite some time, by enabling the body to mount a rapid and effective response to the virus upon re-exposure," says Michel C. Nussenzweig, the Zanvil A. Cohn and Ralph M. Steinman Professor and head of the Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, whose team has been tracking and characterizing antibody response in Covid-19 patients since the early days of the pandemic in New York.
Long-lasting memory
Antibodies, which the body creates in response to infection, linger in the blood plasma for several weeks or months, but their levels significantly drop with time. The immune system has a more efficient way of dealing with pathogens: instead of producing antibodies all the time, it creates memory B cells that recognize the pathogen, and can quickly unleash a new round of antibodies when they encounter it a second time.
But how well this memory works depends on the pathogen. To understand the case with SARS-CoV-2, Nussenzweig and his colleagues studied the antibody responses of 87 individuals at two timepoints: one month after infection, and then again six months later. As expected, they found that although antibodies were still detectable by the six-month point, their numbers had markedly decreased. Lab experiments showed that the ability of the participants' plasma samples to neutralize the virus was reduced by five-fold.
In contrast, the patients' memory B cells, specifically those that produce antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, did not decline in number, and even slightly increased in some cases. "The overall numbers of memory B cells that produced antibodies attacking the Achilles' heel of the virus, known as the receptor-binding domain, stayed the same," says Christian Gaebler, a physician and immunologist in Nussenzweig's lab. "That's good news because those are the ones that you need if you encounter the virus again."
Viral stowaways
A closer look at the memory B cells revealed something surprising: these cells had gone through numerous rounds of mutation even after the infection resolved, and as a result the antibodies they produced were much more effective than the originals. Subsequent lab experiments showed this new set of antibodies were better able to latch on tightly to the virus and could recognize even mutated versions of it.
"We were surprised to see the memory B cells had kept evolving during this time," Nussenzweig says. "That often happens in chronic infections, like HIV or herpes, where the virus lingers in the body. But we weren't expecting to see it with SARS-CoV-2, which is thought to leave the body after infection has resolved."
SARS-CoV-2 replicates in certain cells in the lungs, upper throat, and small intestine, and residual viral particles hiding within these tissues could be driving the evolution of memory cells. To look into this hypothesis, the researchers have teamed up with Saurabh Mehandru, a former Rockefeller scientist and currently a physician at Mount Sinai Hospital, who has been examining biopsies of intestinal tissue from people who had recovered from COVID-19 on average three months earlier.
In seven of the 14 individuals studied, tests showed the presence of SARS-CoV-2's genetic material and its proteins in the cells that line the intestines. The researchers don't know whether these viral left-overs are still infectious or are simply the remains of dead viruses.
The team plans to study more people to better understand what role the viral stowaways may play in both the progression of the disease and in immunity.
INFORMATION:
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - University of Alabama at Birmingham polymer and radionuclide chemists report what they say "may represent a major step forward in microcapsule drug delivery systems."
The UAB microcapsules -- labeled with radioactive zirconium-89 -- are the first example of hollow polymer capsules capable of long-term, multiday positron emission tomography, or PET, imaging in vivo. In previous work, UAB researchers showed that the hollow capsules could be filled with a potent dose of the cancer drug doxorubicin, which could then be released by therapeutic ultrasound that ruptures the microcapsules.
PET imaging with zirconium-89 -- which has a half-life of 3.3 days -- allowed the capsules to be traced in test mice up to seven days. The major ...
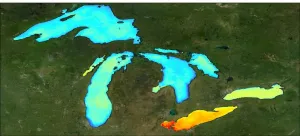
NASA-funded research on the 11 largest freshwater lakes in the world coupled field and satellite observations to provide a new understanding of how large bodies of water fix carbon, as well as how a changing climate and lakes interact.
Scientists at the Michigan Tech Research Institute (MTRI) studied the five Laurentian Great Lakes bordering the U.S. and Canada; the three African Great Lakes, Tanganyika, Victoria and Malawi; Lake Baikal in Russia; and Great Bear and Great Slave lakes in Canada.
These 11 lakes hold more than 50% of the surface freshwater that millions of people and countless other creatures rely on, underscoring the importance of understanding how they are being altered by climate change and other factors.
The two Canadian lakes ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- In the dark waters of Lake Superior, a fish species adapted to regain a genetic trait that may have helped its ancient ancestors see in the ocean, a study finds.
The research focuses on kiyis, which inhabit Lake Superior at depths of about 80 to over 200 meters deep. These fish, known to scientists as "Coregonus kiyi," belong to a group of closely related salmonids known as ciscoes.
In contrast to three other Lake Superior ciscoes that dwell and feed in shallower regions of water, the kiyis are far more likely to carry a version of the rhodopsin gene that probably improves vision in dim "blue-shifted" waters, ...
Curtin University researchers have uncovered a method of making silicon, found commonly in electronics such as phones, cameras and computers, at room temperature.
The new technique works by replacing extreme heat with electrical currents to produce the same chemical reaction that turns silica into silicon at a reduced economic and environmental cost.
Lead researcher, PhD candidate Song Zhang from Curtin's School of Molecular and Life Sciences said that while the team's discovery was made at the nanoscale, it defines a way of replacing thermochemical processes with electrochemical processes, which ...
With the recent explosive demand for data storage, ranging from data centers to various smart and connected devices, the need for higher-capacity and more compact memory devices is constantly increasing. As a result, semiconductor devices are now moving from 2D to 3D. The 3D-NAND flash memory is the most commercially successful 3D semiconductor device today, and its demand for supporting our data-driven world is now growing exponentially.
The scaling law for 3D devices is achieved by stacking more and more semiconductor layers, well above 100 layers, in a more reliable way. As each layer thickness corresponds to the effective channel length, accurate characterization and control of layer-by-layer thickness is critical. To date, ...
Giant ambush-predator worms, possible ancestors of the 'bobbit worm', may have colonized the seafloor of the Eurasian continent around 20 million years ago. The findings, based on the reconstruction of large, L-shaped burrows from layers of seafloor dating back to the Miocene (23 million to 5.3 million years ago) of northeast Taiwan, are reported in Scientific Reports this week.
Ludvig Löwemark and colleagues reconstructed a new trace fossil, which they name Pennichnus formosae, using 319 specimens preserved within layers of seafloor formed during the Miocene era across northeast Taiwan. Trace fossils are geological features such as burrows, track marks and plant root cavities preserved ...
BOSTON - Four years after patients with melanoma were treated with a personalized cancer vaccine, the immune response kindled by the vaccine remains robust and effective in keeping cancer cells under control, researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Brigham and Women's Hospital, and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard report in a new study.
The findings, published online today by the journal Nature Medicine, demonstrate the staying power of the immune response generated by the vaccine, known as NeoVax, which works by targeting specific proteins on each patient's tumor cells. The researchers found that, nearly four ...
While it has been reported that opioid overdose deaths have increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, a new study looking at data in Philadelphia showed that this hardship has been overwhelmingly suffered by Black individuals. Researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania analyzed the period of time after the city's stay-at-home order was announced in 2020 and showed that, compared to the year before, the number of fatal overdoses suffered by Black individuals spiked by more than 50 percent. At the same time, the rate for white individuals actually fell by 31 percent over the same period. This research ...
PORTLAND, OR - A first-of-its-kind randomized clinical trial found that patients with pancreatic cancer didn't live any longer than expected after receiving pre-operative chemotherapy from either of the two standard regimens, according to trial results published in JAMA Oncology.
While the trial findings did not show a direct patient benefit, they do show that it's possible to safely administer chemotherapy prior to pancreatic cancer surgery. They also pave the way for better treatment testing for this notorious killer. With no symptoms in the early stages, and few effective therapies, pancreatic cancer is the fourth-most deadly cancer type in the United ...
What The Study Did: This study monitored suicide-related internet search rates during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States and researchers report searches for suicide decreased during that time. Although this study cannot independently confirm that changes in search rates were caused by changes in population-level suicide rates, it showed that COVID-19 may have been inversely associated with population suicide trends between March and July 2020.
Authors: John W. Ayers, Ph.D., M.A., of theUniversity of California San Diego, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34261)
Editor's ...