Personalizing cancer care with improved tumor models
2021-01-21
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, January 21, 2021 -- Cancer is a major, worldwide challenge, and its impact is projected to escalate due to aging and growth of the population. Researchers recognize that new approaches to diagnose and treat deadly cancers, including identifying new drugs to treat cancer, will be essential to curbing the growing impact of the disease.
While decades of investment in research have resulted in substantial improvements in surviving cancer, a key challenge remains in identifying new drugs that improve outcomes for cancer patients, particularly for cancers when tumors have spread throughout the body.
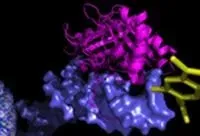
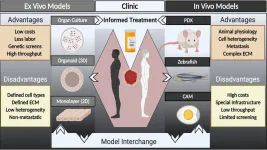
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers suggest a major hurdle to identifying new drugs is the paucity of models -- organisms mimicking human cancers in a lab setting -- for cancer research that accurately represent patient tumors. They provide a perspective on strategies for developing models to inform cancer treatment using models from individual patients and where the field needs to go in terms of research in animal systems and in culture systems.
"In addition to having better models for cancer research, we are trying to evolve patient-derived models to the point where we can have speedy and reliable drug testing on patient specimens to help personalize cancer care," said author Alana Welm. "This is the concept of functional precision oncology."
In functional precision oncology, tumor samples from individual patients are tested for susceptibility to various drugs in the context of a patient-derived xenograft or culture system in order to guide patient therapy during the course of their disease.
The researchers suggest an even more powerful approach to accelerating the pace of cancer research would be to couple patient-derived model development with the plethora of clinical trials being run every day.
If clinical data and models were collated and shared along with drug response information, machine learning could facilitate analysis of this big data to discover complex patterns of drug response or resistance across individuals, which could then be further tested in the patient-derived models.
The researchers envision that patients' tumors may be bioinformatically profiled to identify a complex set of features that can be used to predict response to various therapies and informed by functional drug response data collected from previous studies. The researchers believe this would facilitate selection of more effective drugs earlier in treatment, while preventing administration of toxic drugs that offer no benefit.
These types of data could even be integrated with germline DNA sequence variants that predict aberrant drug metabolism and toxicity for an even more personalized approach to reduce mortality from cancer while simultaneously reducing toxicity as much as possible.
INFORMATION:
The article "Towards improved models of human cancer" is authored by Bryan E. Welm, Christos Vaklavas, and Alana L. Welm. The article appears in APL Bioengineering (DOI: 10.1063/5.0030534) and can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0030534.
See also: Combining best of both worlds for cancer modeling at https://publishing.aip.org/publications/latest-content/combining-best-of-both-worlds-for-cancer-modeling/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.scitation.org/journal/apb.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-21
EUGENE, Ore. -- Jan. 21, 2021 -- Developing economies suffer from a paradox: they don't receive investment flows from developed economies because they lack stability and high-quality financial and lawmaking institutions, but they can't develop those institutions without foreign funds.
A study co-authored by Brandon Julio, a professor in the Department of Finance at the University of Oregon's Lundquist College of Business, found that bilateral investment treaties, commonly known as BITs, can help developing economies overcome this paradox, but only as long as those ...
2021-01-21
Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and colleagues have identified genetic factors that increase the risk for developing pneumonia and its severe, life-threatening consequences.
Their findings, published recently in the American Journal of Human Genetics, may aid efforts to identify patients with COVID-19 at greatest risk for pneumonia, and enable earlier interventions to prevent severe illness and death.
Despite the increasing availability of COVID-19 vaccines, it will take months to inoculate enough people to bring the pandemic under control, experts predict. In the meantime, thousands of Americans are hospitalized and die from COVID-19 each ...
2021-01-21
A new study from researchers at MIT uncovers the kinds of infrastructure improvements that would make the biggest difference in increasing the number of electric cars on the road, a key step toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions from transportation.
The researchers found that installing charging stations on residential streets, rather than just in central locations such as shopping malls, could have an outsized benefit. They also found that adding on high-speed charging stations along highways and making supplementary vehicles more easily available to people who need to travel beyond the single-charge range of their electric vehicles could greatly increase the vehicle electrification potential.
The findings are reported today in the journal Nature Energy, in a paper by MIT associate ...
2021-01-21
DAVIS, Calif., January 21, 2020 - A new peer-reviewed study reveals that the vast majority of U.S. infants may be suffering from a substantial deficiency in an important bacterium key to breast milk utilization and immune system development, as well as protection against gut pathogens linked to common newborn conditions such as colic and diaper rash.
According to the study published today in END ...
2021-01-21
Sex-specific chromosomes are a dangerous place to be, if you're a gene. Because these chromosomes -- Y chromosomes, in humans -- do not have a matching chromosome with which to exchange genetic information, they are prone to losing non-essential genes left and right in a process called genetic decay.
Now, a new study from research scientist Daniel Winston Bellott in the lab of Whitehead Institute Member David Page broadens our understanding of what makes a gene able to survive on a sex-specific chromosome by looking at one especially slithery branch of the evolutionary tree: snakes.
Comparing surviving genes on snake ...
2021-01-21
PHILADELPHIA -- (Jan. 21, 2021) -- Researchers at The Wistar Institute have discovered a new enzymatic function of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) protein EBNA1, a critical factor in EBV's ability to transform human cells and cause cancer. Published in Cell, this study provides new indications for inhibiting EBNA1 function, opening up fresh avenues for development of therapies to treat EBV-associated cancers.
EBV establishes life-long, latent infection in B lymphocytes, which can contribute to development of different cancer types, including Burkitt's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 (EBNA1) serves as an attractive therapeutic ...
2021-01-21
Two out of five individuals delayed or missed medical care in the early phase of the pandemic--from March through mid-July 2020--according to a new survey from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The survey of 1,337 U.S. adults found that 544, or 41 percent, delayed or missed medical care during the survey period. Among the 1,055 individuals who reported needing medical care, 29 percent (307 respondents), indicated fear of transmission of COVID-19 as the main reason. Seven percent (75 respondents) reported financial concerns as the main reason for delaying ...
2021-01-21
Researchers from the University Hospitals in Zurich and Basel, ETH Zurich, University of Zurich and the pharmaceutical company Roche have set out to improve cancer diagnostics by developing a platform of state-of-the-art molecular biology methods. The "Tumor Profiler" project aims to derive the comprehensive molecular profile of tumours in cancer patients, which has the potential to predict the efficacy of a host of new cancer medications. It will therefore make it possible to offer treating physicians personalised and improved therapy recommendations.
Three years ago, the researchers began a large-scale clinical study involving ...
2021-01-21
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- When sheets of two-dimensional nanomaterials like graphene are stacked on top of each other, tiny gaps form between the sheets that have a wide variety of potential uses. In research published in the journal Nature Communications, a team of Brown University researchers has found a way to orient those gaps, called nanochannels, in a way that makes them more useful for filtering water and other liquids of nanoscale contaminants.
"In the last decade, a whole field has sprung up to study these spaces that form between 2-D nanomaterials," said Robert Hurt, a professor in Brown's School of Engineering and coauthor of the ...
2021-01-21
TROY, N.Y. -- Warnings about misinformation are now regularly posted on Twitter, Facebook, and other social media platforms, but not all of these cautions are created equal. New research from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute shows that artificial intelligence can help form accurate news assessments -- but only when a news story is first emerging.
These findings were recently published in Computers in Human Behavior Reports by an interdisciplinary team of Rensselaer researchers. They found that AI-driven interventions are generally ineffective when used to flag issues with stories on frequently covered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Personalizing cancer care with improved tumor models