Study recommends rugby league invests in young players' diets
Nutrition to power young rugby league players
2021-01-22
(Press-News.org) Young rugby league players could benefit from individualised nutrition plans to maximise performance and optimise recovery throughout their careers, according to QUT researchers.
The new study, published in the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, provides nutritional recommendations and considers potential supplements to improve players' physical capacity, health and recovery during the preparatory and competition phases of a season.
Lead researcher, Associate Professor Vince Kelly from QUT's Faculty of Health's Exercise and Nutrition Sciences, is a committee member of the National Rugby League Research Committee and has more than 20 years' experience in elite sport.
"Young players don't have the same access to dietary support as professional players do but it is just as important to invest in their nutritional needs," Associate Professor Kelly said.
"You don't put diesel into a Ferrari and high-performance players require the right type of fuel."
Key points:-
Professional rugby league is an intense physically-demanding sport, and young male players (aged 16-24) have incredibly high energy requirements.
Players' energy requirements are highly individual, and they may find it hard to meet current nutrition recommendations.
Research provides practical food and drink examples so that sports dietitians and coaches can help players eat and drink enough as part of a healthy diet.
Research shares information on evidence-based supplements via HASTA that could be used to maximise performance.
Associate Professor Kelly said healthy food habits for young players helps aid physical and mental wellbeing to cope with the demands of the game and as they mature.
A review and analysis of studies including players aged 16-24 highlighted the large variability in match and training profiles of rugby league players.
Co-author and PhD researcher Liam Oliver has prepared practical nutrition tables recommending take home packs for players to consume after a match.
The tables provide information for players to better manage their nutrition based on whether they are gaining or maintaining weight.
"For a collision sport like Rugby League, body mass and being heavier provides more momentum for tackling but this also leads to muscle damage so adequate protein may accelerate recovery," Assoc Prof Kelly said.
He said, for example, cherry concentrate taken consistently three days ahead of a match may improve muscle damage recovery while 30ml taken post-match may aid sleep, and blueberries or blackcurrants taken one-hour pre-match could improve sprint performance.
Currently, there are no nutritional recommendations across a complete season of rugby league and the researchers say future studies should apply to similar female-specific rugby league recommendations.
INFORMATION:
The research has been shared with the Brisbane Broncos Sports and Performance Dietitian and the Head of Strength and Conditioning at Stade Francais Rugby Club in Paris.
The study's other co-authors include Professor Johanna Bowtell from University of Exeter, UK, and Professor David Jenkins from the University of the Sunshine Coast.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-22
Nanofiltration (NF) is an advanced technology for treating wastewater containing organic micropollutants (OMPs).
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a stable graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane with uniform pore size to remove OMPs.
The study was published in Chemical Engineering Journal on Jan. 20.
It proposes combining signal amplification strategy and defect chemistry to reduce membrane pore size distribution, thus offering a promising method for preparing highly ...
2021-01-22
The Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and its research collaborators have successfully demonstrated the four-dimensional (4D) printing of shape memory polymers in submicron dimensions which are comparable to the wavelength of visible light. This novel development has allowed researchers to now explore new applications in the field of nanophotonics.
4D printing enables 3D printed structures to change its configurations over time and is used in a wide variety of fields such as soft robotics, flexible electronics, and medical devices.
Different materials such as hydrogels, liquid crystal elastomers and magnetic nanoparticles embedded resists ...
2021-01-22
Scientists at Hokkaido University and Chiba University have developed simultaneous triploid and hexaploid varieties of Haemanthus albiflos by the application of endosperm culture, thus extending the use of this technique.
In plants, the number of chromosome sets in cells (ploidy) affects a large number of desirable characteristics. In general, the greater the number of chromosome sets, the more like the plant is to have larger flowers, larger fruits, be more disease resistant, and so on. Hence, particularly in agriculture and horticulture, the development of polyploid plants continues to receive much attention.
Scientists from Hokkaido University and Chiba University have successfully developed triploid (3 chromosome sets) ...
2021-01-22
It's mid-January 2021, and the first gray whales from the eastern North Pacific population have started to arrive in the breeding lagoons in Baja California, Mexico. Since the start of their southbound migration from their high latitude feeding grounds, several sightings of emaciated gray whales have already been reported along their migration route.
This has raised concern among scientists that the unusual mortality event (UME, an unexpected phenomenon during which a significant number of a marine mammal population dies), that started in January 2019, and which so far has resulted in 378 confirmed ...
2021-01-22
Kanazawa, Japan - Liver injury is a rare side effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which are frequently used for daily pain control. This toxicity has been regarded as a "black box" and is mainly managed by an empirical approach, but there is not a clear understanding of the mechanism. Now, researchers from Japan have found that a bit of attention to the types and frequencies of NSAIDs could help people avoid liver injury.
In a study published recently in Biochemical Pharmacology, researchers from Kanazawa University have revealed that specific NSAIDs, including ibuprofen, are metabolized by one of the acyl-CoA synthetases, ACSL1, in a manner that can have toxic effects.
NSAIDs containing a specific chemical group, carboxylic acid, can form "conjugates" with ...
2021-01-22
In a new study published in Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, Chen-Yu Zhang's group at Nanjing University, School of Life Sciences, and Antonio Vidal-Puig's group at University of Cambridge report that pancreatic β cells secrete miR-29 family members (miR-29s) via exosomes in response to high levels of free fatty acids (FFAs). Theses β cell-derived exosomal miR-29s regulate glucose homeostasis through their manipulations on glucose output in liver.
Previously, Chen-Yu Zhang's group identified extracellular miRNA as a new form of cell-to-cell communication. They are among the first that reported the selective secretion of miRNAs under different physiological or pathological states; also, the uptake and function of secreted miRNAs in recipient cells. In the past decade, intensive ...
2021-01-22
A new algorithm may reduce the need for expensive, time-consuming whole-genome sequencing computations to understand how a microbiome functions. A team led by JING Gongchao of the Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and SU Xiaoquan of Qingdao University, published their approach, called Meta-Apo, on Jan. 6 in BMC Genomics.
Researchers routinely sequence samples of microbial communities found on human skin, in human guts, and in the environment to understand what genes they contain with the ultimate goal of understanding ...
2021-01-22
Degradable, bio-based polymers offer options for chemical recycling, and they can be a tool to store and release useful molecules. Scientists have developed a class of sugar-based polymers that are degradable through acid hydrolysis. The researchers also integrated "cargo" molecules in the polymer, which are designed to split off after polymer degradation. Degradable, cargo-bearing polymers are important for medical and sensor applications, says the study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Most plastics resist natural degradation processes. Consequently, increasing contamination of the environment with plastics has led to a call for degradable plastics. Such materials can be subjected to chemical recycling processes, in which chemical reactions break up polymer bonds. ...
2021-01-22
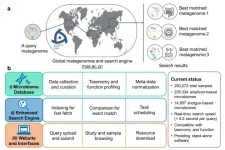
Metagenomics - the study of genetic material from an environmental sample - is growing as species evolve or are discovered across the globe. To correlate the newly developed microbiomes with existing data sets, a team of researchers based in China has developed the Microbiome Search Engine 2 (MSE 2). It was published on Jan. 19 in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Here, we introduce MSE 2, a microbiome database platform for searching query microbiomes in the global metagenome data space based on taxonomic or functional similarity of the whole microbiome," ...
2021-01-22
Research from the University of Kent has demonstrated a decline in 'son preference' by women of childbearing age in Bangladesh. However, the study also shows that fertility decisions are still influenced according to son preference.
The paper, 'Is son preference disappearing from Bangladesh?', surveyed a nationally representative sample of Bangladeshi women of childbearing age, born between 1975 and 1994, to assess how son preference is evolving.
The term 'son preference' refers to any situation where parents value sons over daughters and make resulting choices accordingly, which can have a strong economic and demographic impact.
The study finds that among women of childbearing age in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study recommends rugby league invests in young players' diets
Nutrition to power young rugby league players