Depression in new fathers connected to relationship insecurities
2021-01-22
(Press-News.org) Becoming a parent often brings great joy, but not always. Parenthood also entails challenges, stress and, for some people, it can trigger depression. A new study from Lund University in Sweden shows that male postnatal depression is more common in men who are insecure in their relationship with their partner.
Depression affects around 10-12 per cent of new mothers, and at least 8 per cent of new fathers. The figures are even higher when looking at depressive symptoms; as many as one in five new fathers experience troublesome symptoms, according to the new study conducted by Elia Psouni, registered psychologist and associate professor of psychology at Lund University in Sweden, and Anna Eichbichler, clinical psychologist.
The study focused on reasons behind the fathers' depressive symptoms. Affected men often have a negative view of themselves and are worried about being inadequate in their intimate relationships; a concern that may be based on childhood experiences with their own parents.
"Having a negative view of oneself, one's own characteristics and abilities, while valuing other people highly often leads to a constant worry about not being good enough, about disappointing others and - potentially - losing them", says Elia Psouni.
The study also attempted to determine what specific aspect of low self-esteem in intimate relationships triggered the depression. Is it a question of relationship difficulties in general, or stress about not being good enough as a parent? The answers showed it was the latter.
"Low self-confidence in close relationships seems to trigger parental stress, which in turn triggers the symptoms of depression", says Psouni.
This is the second study in which Psouni and her colleagues show that over one in five fathers of children aged 1-18 months experience debilitating symptoms of depression. The study also revealed that men whose female partners suffered from postpartum depression were over-represented, and that very few of them were in contact with a professional to get help.
"The study shows beyond doubt that parents affect one another and reveals the importance of monitoring how parents in various relationships and family constellations manage and fare over a long period", says Psouni.
She and her colleagues are now conducting a longitudinal project that will monitor families over time to generate knowledge about the wellbeing and development of children and parents in various family constellations.
INFORMATION:
About the study:
530 fathers took part. 143 had symptoms of depression that would justify a referral for further assessment. Of these, 43 fathers described very debilitating symptoms and 22 described very serious symptoms.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-22
Most lung cancers are of a type called non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). This type of cancer is relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, so NSCLC therapies are usually based on drug treatment. Alectinib is a drug commonly used for treating patients with NSCLC. It addresses a gene rearrangement known as ALK that occurs in 3 to 5% of NSCLC patients (alectinib belongs to a class of drugs called ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors). It has been unclear, however, whether there is a correlation between the use of alectinib and the poorer prognosis in ALK-NSCLC patients in which secondary cancer mutations ...
2021-01-22
Metals such as gold or platinum are often used as catalysts. In the catalytic converters of vehicles, for example, platinum nanoparticles convert poisonous carbon monoxide into non-toxic CO2. Because platinum and other catalytically active metals are expensive and rare, the nanoparticles involved have been made smaller and smaller over time.
"Single-atom" catalysts are the logical end point of this downsizing: The metal is no longer present as particles, but as individual atoms that are anchored on the surface of a cheaper support material. Individual atoms can no longer be described using the rules developed from larger pieces of metal, so the rules used to predict which metals will ...
2021-01-22
Normal ageing causes disruptions in the brain that can lead to cognitive decline. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging studies have found significant age-related alterations in functional connectivity across various networks. However, most of the studies have focused primarily on static functional connectivity.
The authors of a recent study published in Cerebral Cortex based their research on the idea that studying the dynamics of resting-state brain activity across the whole-brain functional network can provide a better characterization of age-related changes.
The study was led by Gustavo Deco, director of the Center for Brain and Cognition (CBC) and ICREA research professor at the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), and Anira ...
2021-01-22
Chimpanzees, one of the closest relatives of humans, cooperate on a group level - in combative disputes, they even cooperate with group members to whom they are not related. Those involved in fights with neighbouring groups put themselves at risk of serious injury or even death.
Within the context of the Tai Chimpanzee Project researchers observed three chimpanzee communities in Tai National Park in Cote d'Ivoire documenting social relationships, territory range and intergroup encounters amongst others. "We have been able to analyze almost 500 vocal and physical battles from the last 25 years with participation of at least one ...
2021-01-22
Good news for the green transition: Flowery diets help predatory insects help farmers keep pests in check
Predatory insects have been shown to live longer when they have access to nectar and pollen, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Copenhagen. Thus, flowers don't just benefit insects, they help farmers farm sustainably. Predatory insects are skilled pest controllers whose hunting reduces the need for agricultural pesticides.
Until now, it was believed that predatory insects needed prey to survive. But in a systematic review conducted at the University ...
2021-01-22
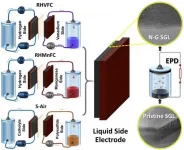
Researchers in WMG at the University of Warwick, in collaboration with Imperial College London, have found a way to enhance hybrid flow batteries and their commercial use. The new approach can store electricity in these batteries for very long durations for about a fifth the price of current technologies, with minimal location restraints and zero emissions.
The researchers enhanced three hybrid flow cells using nitrogen doped graphene (exposed to nitrogen plasma) in a binder-free electrophoresis technique (EPD).
Wind and solar power are increasingly popular sources for renewable energy. Unfortunately, intermittency issues keep them ...
2021-01-22
GREEN TRANSITION Researchers at the University of Copenhagen have demonstrated that unique fungi strengthen the "immune systems" of wheat and bean plants against aphids. Fungi enter and influence the amount of a plant's own defences, resulting in fewer aphids. The results could serve to reduce agricultural insecticide use and bring Denmark a step further along the path towards its green transition.
Wheat field
Certain fungi are able to establish a close rapport with plants that results in fewer insect infestations and thereby less damage to crops. Until now, it was unclear how these fungi could be used to reduce insect infestations.
"In order for us to really use fungi ...
2021-01-22
PHILADELPHIA, PA (January 22, 2021) - Advancements in diabetes technology have improved quality of life and glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes. However, data show that a subset of children is being left behind. Those from low-income families and non-Hispanic Black (NHB) children are not experiencing benefits associated with technological advances, and are at higher risk for diabetes complications and adverse outcomes through ongoing poor glycemic control.
In an invited commentary to be published in the journal Diabetes Care, researchers describe how socioeconomic disparities ...
2021-01-22
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London, have identified a protein that may represent a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Using this protein as a target, the team successfully created a CAR T cell therapy - a type of immunotherapy - that killed pancreatic cancer cells in a pre-clinical model.
CAR T cell therapy is an immunotherapy that has shown great promise for the treatment of some blood cancers; however, the treatment of solid tumours using this therapy has proved very difficult. One barrier to success is toxicity in tissues other than the cancer because most of the proteins currently used to target CAR T cells to pancreatic cancer cells and other solid tumours are present in low levels on other normal tissues, ...
2021-01-22
Organic photodetectors (OPDs) have a huge potential for applications in low-cost imaging, health monitoring and near infrared sensing. Yet, before industrially realizing these applications, the performance of these devices still needs to be improved.
Recent research on organic photodetectors based on donor-acceptor systems has resulted in narrow-band, flexible and biocompatible devices, of which the best reach external photovoltaic quantum efficiencies of close to 100%. However, the high noise in the off state produced by these devices limits their specific detectivity, severely reducing the performance, for example ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Depression in new fathers connected to relationship insecurities