Reducing traps increases performance of organic photodetectors
2021-01-22
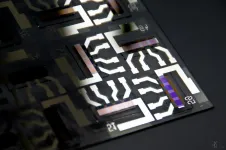
(Press-News.org) Organic photodetectors (OPDs) have a huge potential for applications in low-cost imaging, health monitoring and near infrared sensing. Yet, before industrially realizing these applications, the performance of these devices still needs to be improved.
Recent research on organic photodetectors based on donor-acceptor systems has resulted in narrow-band, flexible and biocompatible devices, of which the best reach external photovoltaic quantum efficiencies of close to 100%. However, the high noise in the off state produced by these devices limits their specific detectivity, severely reducing the performance, for example measuring faint light.
Jonas Kublitski and his colleagues at the Dresden Integrated Center for Applied Physics and Photonic Materials (IAPP) and the Institute of Applied Physics (IAP) at TU Dresden now found out that the high noise in the off state is a consequence of unwanted trap states distributed near the mid-gap of organic semiconductors. By measuring the amount of traps, the physicists draw a direct correlation between the characteristics of the trap states and the off state of OPDs.
Building on these results, Mr. Kublitski was able to draw a model depicting this relation:
"By modelling the dark current of several donor-acceptor systems, we reveal the interplay between traps and charge-transfer states as a source of dark current and show that traps dominate the generation processes, thus being the main limiting factor of OPD detectivity.
The newly discovered relation does only clarify the operation of OPDs but gives guidance for further research in the field. This work is a result of four years of research during my Ph.D. I am very happy to share these results, as they can refocus the attention of our field into understanding the origin of the limited performance of OPDs, which was so far unknown."
INFORMATION:
Original publication:
Kublitski, Jonas; Hofacker, Andreas; K. Boroujeni, Bahman; Benduhn, Johannes; C. Nikolis, Vasileios; Kaiser, Christina; Spoltore, Donato; Kleemann, Hans; Fischer, Axel; Ellinger, Frank; Vandewal, Koen; Leo, Karl. Reverse dark current in organic photodetectors and the major role of traps as source of noise, Nature Communications.
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20856-z
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-22
Popular in aquariums all over the world, the zebrafish is native to South Asia. But here in a Cincinnati Children's laboratory, the freshwater variant plays a vital role in scientific discovery.
The iconic stripes are eye-catching but it's the transparency of zebrafish embryonic tissue which are most prized by researchers like Oriana Zinani, a fifth-year doctoral student in molecular developmental biology in the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine. The patterning of the zebrafish's spine gives the appearance of stripes; it is controlled by ...
2021-01-22
In science, sometimes a new perspective can turn our interpretation of the data upside-down, and necessitate a paradigm shift.
There has been, and continues to be, fierce disagreements in nutrition science as to what constitutes a healthy diet. A key controversy is the role of saturated fats in health and disease. Saturated fats are known to increase blood cholesterol levels, and increased blood cholesterol is often observed in people who develop cardiovascular disease.
It has been thought for more than half a century that saturated fats in the diet promote heart disease by increasing blood cholesterol. However, a new model explains why this so-called "diet-heart hypothesis", which ...
2021-01-22
Professor MATSUYAMA Hideto's research group at Kobe University's Research Center for Membrane and Film Technology has successfully developed a new desalination membrane. They achieved this by laminating a two-dimensional carbon material (*1) on to the surface of a porous polymer membrane (*2).
Desalination (*3) membranes are used to produce freshwater from seawater. In order to solve the worldwide issue of insufficient freshwater resources, researchers are striving to develop desalination membranes that are not only permeated by water faster than those currently in use but also remove salt efficiently, so that more effective, low-energy desalination systems can be implemented.
In this research study, graphene oxide (*4) nanosheets, which ...
2021-01-22
Real-world materials are usually messier than the idealized scenarios found in textbooks. Imperfections can add complications and even limit a material's usefulness. To get around this, scientists routinely strive to remove defects and dirt entirely, pushing materials closer to perfection. Now, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have turned this problem around and shown that for some materials defects could act as a probe for interesting physics, rather than a nuisance.
The team, led by professors Gaurav Bahl and Taylor Hughes, studied artificial materials, or metamaterials, which they engineered to include defects. The team used these customizable circuits as a proxy for studying exotic topological crystals, which are often ...
2021-01-22
Marine microalgae-based cellular agriculture is a promising new way to sustainably produce plant-based 'meat' and healthy 'superfoods' for the future.
Researchers at Flinders University's Centre for Marine Bioproducts Development (CMBD) in Australia are responding to growing interest from consumers looking for healthier, more environmentally friendly, sustainable and ethical alternatives to animal proteins.
Marine microalgae, single-cell photosynthetic organisms from the ocean could be the solution to the world's meat protein shortage, says CMBD director Flinders University Professor Wei Zhang, who is also co-leading a bid to establish a national Marine Bioproducts Cooperative Research Centre ...
2021-01-22
Young rugby league players could benefit from individualised nutrition plans to maximise performance and optimise recovery throughout their careers, according to QUT researchers.
The new study, published in the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, provides nutritional recommendations and considers potential supplements to improve players' physical capacity, health and recovery during the preparatory and competition phases of a season.
Lead researcher, Associate Professor Vince Kelly from QUT's Faculty of Health's Exercise and Nutrition Sciences, is a committee member of the National Rugby League Research Committee and has more than 20 years' experience in elite sport.
"Young players don't have the same access to dietary support as professional ...
2021-01-22
Nanofiltration (NF) is an advanced technology for treating wastewater containing organic micropollutants (OMPs).
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a stable graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane with uniform pore size to remove OMPs.
The study was published in Chemical Engineering Journal on Jan. 20.
It proposes combining signal amplification strategy and defect chemistry to reduce membrane pore size distribution, thus offering a promising method for preparing highly ...
2021-01-22
The Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and its research collaborators have successfully demonstrated the four-dimensional (4D) printing of shape memory polymers in submicron dimensions which are comparable to the wavelength of visible light. This novel development has allowed researchers to now explore new applications in the field of nanophotonics.
4D printing enables 3D printed structures to change its configurations over time and is used in a wide variety of fields such as soft robotics, flexible electronics, and medical devices.
Different materials such as hydrogels, liquid crystal elastomers and magnetic nanoparticles embedded resists ...
2021-01-22
Scientists at Hokkaido University and Chiba University have developed simultaneous triploid and hexaploid varieties of Haemanthus albiflos by the application of endosperm culture, thus extending the use of this technique.
In plants, the number of chromosome sets in cells (ploidy) affects a large number of desirable characteristics. In general, the greater the number of chromosome sets, the more like the plant is to have larger flowers, larger fruits, be more disease resistant, and so on. Hence, particularly in agriculture and horticulture, the development of polyploid plants continues to receive much attention.
Scientists from Hokkaido University and Chiba University have successfully developed triploid (3 chromosome sets) ...
2021-01-22
It's mid-January 2021, and the first gray whales from the eastern North Pacific population have started to arrive in the breeding lagoons in Baja California, Mexico. Since the start of their southbound migration from their high latitude feeding grounds, several sightings of emaciated gray whales have already been reported along their migration route.
This has raised concern among scientists that the unusual mortality event (UME, an unexpected phenomenon during which a significant number of a marine mammal population dies), that started in January 2019, and which so far has resulted in 378 confirmed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Reducing traps increases performance of organic photodetectors








