(Press-News.org) Marine microalgae-based cellular agriculture is a promising new way to sustainably produce plant-based 'meat' and healthy 'superfoods' for the future.
Researchers at Flinders University's Centre for Marine Bioproducts Development (CMBD) in Australia are responding to growing interest from consumers looking for healthier, more environmentally friendly, sustainable and ethical alternatives to animal proteins.
Marine microalgae, single-cell photosynthetic organisms from the ocean could be the solution to the world's meat protein shortage, says CMBD director Flinders University Professor Wei Zhang, who is also co-leading a bid to establish a national Marine Bioproducts Cooperative Research Centre (MB-CRC) in Australia.
The CRC's mission is to find ways to develop the third-generation of Australian high-value marine bioindustry (as opposed to the first-generation of fisheries and the second-generation of aquaculture) and transform Australia's emerging marine bioproducts sector into a globally competitive industry.
The Centre's focus will be on industry and market-driven innovations to improve both the supply chain and value chain to deliver costs savings, improved production and competitive capacity for Australia to access high value marine bioproducts markets across the globe.
"Our research spans the entire value chain, from microalgae cultivation and circular advanced biomanufacturing to the development of high-value functional food," Professor Zhang says.
"Microalgae come in a diverse range of nutritional profiles and advanced cultivation strategies can be developed for tuning microalgae to produce protein-, oil- and carbohydrate-dominant types that can be processed into a broad range of functional foods, including healthy cell patties, chips, pastes, jams and even caviar."
Two freshwater microalgal products currently on the market are the high protein Chlorella and Spirulina varieties used in the production of foods such as green pasta, drinks and beverages.
Marine species are of significant interest as they do not require scarce freshwater and crop land. Their unique nutritional profiles such as their high DHA and EPA content (long chain omega 3 fatty acids) are essential for infant and brain development and cardiac health.
Bioreactors for upscaling upscaled aquatic production of photosynthetic microalgae can also help to combat greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. One 90 x 90 x 210 cm (3 x 3 x 7 ft) bioreactor unit can absorb up to 400 times more carbon dioxide than the same footprint of trees.
Using sunlight, certain varieties of microalgae create oxygen and convert carbon dioxide into organic carbon (protein, carbohydrates, pigments, fats and fibres), just like plants, but do not require valuable arable land for their production.
"They are therefore often called the rainforests of the oceans," says Associate Professor Kirsten Heimann, senior lecturer in biotechnology at Flinders University.
"Using sunlight, photosynthetic microalgae create oxygen and convert carbon dioxide into organic carbon (protein, carbohydrates, pigments, fats, fibres, and micronutrients), just like plants, but do not require valuable arable land for their production.
This means microalgae can be sustainably harvested and converted into eco-friendly superfoods," she says. "Putting one and one together, microalgae and innovative production and processing could help to service the world's booming population and growing demand for sustainable protein production," she says.
Along with research into processing techniques, the CMBD team is also investigating the use of waste or harvested seaweed for biodegradable plastics production, another sustainable solution to non-degradable petroleum-based plastics.
INFORMATION:
For the latest paper on microalgae processing development see, 'Release of encapsulated bioactives influenced by alginate viscosity under in-vitro gastrointestinal model' by RE Abraham, P Su, M Puri and CL Raston and W Zhang in International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (Elsevier) Vol 170, 15 February 2021, Pages 540-548, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.143.
The results demonstrate the use of both microalgae and macroalgae for development of controlled release of health and nutritional bioactives from marine sources.
Young rugby league players could benefit from individualised nutrition plans to maximise performance and optimise recovery throughout their careers, according to QUT researchers.
The new study, published in the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, provides nutritional recommendations and considers potential supplements to improve players' physical capacity, health and recovery during the preparatory and competition phases of a season.
Lead researcher, Associate Professor Vince Kelly from QUT's Faculty of Health's Exercise and Nutrition Sciences, is a committee member of the National Rugby League Research Committee and has more than 20 years' experience in elite sport.
"Young players don't have the same access to dietary support as professional ...
Nanofiltration (NF) is an advanced technology for treating wastewater containing organic micropollutants (OMPs).
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a stable graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane with uniform pore size to remove OMPs.
The study was published in Chemical Engineering Journal on Jan. 20.
It proposes combining signal amplification strategy and defect chemistry to reduce membrane pore size distribution, thus offering a promising method for preparing highly ...
The Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and its research collaborators have successfully demonstrated the four-dimensional (4D) printing of shape memory polymers in submicron dimensions which are comparable to the wavelength of visible light. This novel development has allowed researchers to now explore new applications in the field of nanophotonics.
4D printing enables 3D printed structures to change its configurations over time and is used in a wide variety of fields such as soft robotics, flexible electronics, and medical devices.
Different materials such as hydrogels, liquid crystal elastomers and magnetic nanoparticles embedded resists ...
Scientists at Hokkaido University and Chiba University have developed simultaneous triploid and hexaploid varieties of Haemanthus albiflos by the application of endosperm culture, thus extending the use of this technique.
In plants, the number of chromosome sets in cells (ploidy) affects a large number of desirable characteristics. In general, the greater the number of chromosome sets, the more like the plant is to have larger flowers, larger fruits, be more disease resistant, and so on. Hence, particularly in agriculture and horticulture, the development of polyploid plants continues to receive much attention.
Scientists from Hokkaido University and Chiba University have successfully developed triploid (3 chromosome sets) ...
It's mid-January 2021, and the first gray whales from the eastern North Pacific population have started to arrive in the breeding lagoons in Baja California, Mexico. Since the start of their southbound migration from their high latitude feeding grounds, several sightings of emaciated gray whales have already been reported along their migration route.
This has raised concern among scientists that the unusual mortality event (UME, an unexpected phenomenon during which a significant number of a marine mammal population dies), that started in January 2019, and which so far has resulted in 378 confirmed ...
Kanazawa, Japan - Liver injury is a rare side effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which are frequently used for daily pain control. This toxicity has been regarded as a "black box" and is mainly managed by an empirical approach, but there is not a clear understanding of the mechanism. Now, researchers from Japan have found that a bit of attention to the types and frequencies of NSAIDs could help people avoid liver injury.
In a study published recently in Biochemical Pharmacology, researchers from Kanazawa University have revealed that specific NSAIDs, including ibuprofen, are metabolized by one of the acyl-CoA synthetases, ACSL1, in a manner that can have toxic effects.
NSAIDs containing a specific chemical group, carboxylic acid, can form "conjugates" with ...
In a new study published in Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, Chen-Yu Zhang's group at Nanjing University, School of Life Sciences, and Antonio Vidal-Puig's group at University of Cambridge report that pancreatic β cells secrete miR-29 family members (miR-29s) via exosomes in response to high levels of free fatty acids (FFAs). Theses β cell-derived exosomal miR-29s regulate glucose homeostasis through their manipulations on glucose output in liver.
Previously, Chen-Yu Zhang's group identified extracellular miRNA as a new form of cell-to-cell communication. They are among the first that reported the selective secretion of miRNAs under different physiological or pathological states; also, the uptake and function of secreted miRNAs in recipient cells. In the past decade, intensive ...
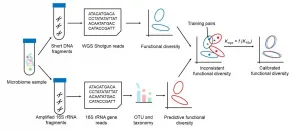
A new algorithm may reduce the need for expensive, time-consuming whole-genome sequencing computations to understand how a microbiome functions. A team led by JING Gongchao of the Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and SU Xiaoquan of Qingdao University, published their approach, called Meta-Apo, on Jan. 6 in BMC Genomics.
Researchers routinely sequence samples of microbial communities found on human skin, in human guts, and in the environment to understand what genes they contain with the ultimate goal of understanding ...
Degradable, bio-based polymers offer options for chemical recycling, and they can be a tool to store and release useful molecules. Scientists have developed a class of sugar-based polymers that are degradable through acid hydrolysis. The researchers also integrated "cargo" molecules in the polymer, which are designed to split off after polymer degradation. Degradable, cargo-bearing polymers are important for medical and sensor applications, says the study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Most plastics resist natural degradation processes. Consequently, increasing contamination of the environment with plastics has led to a call for degradable plastics. Such materials can be subjected to chemical recycling processes, in which chemical reactions break up polymer bonds. ...
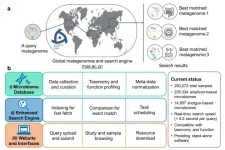
Metagenomics - the study of genetic material from an environmental sample - is growing as species evolve or are discovered across the globe. To correlate the newly developed microbiomes with existing data sets, a team of researchers based in China has developed the Microbiome Search Engine 2 (MSE 2). It was published on Jan. 19 in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Here, we introduce MSE 2, a microbiome database platform for searching query microbiomes in the global metagenome data space based on taxonomic or functional similarity of the whole microbiome," ...