NIH-funded study examines mono, chronic fatigue syndrome in college students
Researchers in Chicago conduct longitudinal study of 4,500 undergraduates
2021-01-22
(Press-News.org) Many college students fully recover from infectious mononucleosis (which is almost always caused by Epstein-Barr virus) within 1-6 weeks, but some go on to develop chronic fatigue syndrome, also called myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME/CFS). A longitudinal study from DePaul University and Northwestern University followed 4,501 college students to examine risk factors that may trigger longer illness. The research appears in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases and was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Previous retrospective studies found that risk factors for developing ME/CFS after catching mono included preexisting physical symptoms and the number of days spent in bed, according to co-principal investigators Leonard A. Jason, professor of psychology at DePaul University; and Dr. Ben Z. Katz, a professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago.
"We are the only study to collect comprehensive biological and behavioral data prior to illness onset, which for the first time allowed us to identify some of the predisposing circumstances or conditions that make certain individuals more likely to get ill due to mono and stay ill," says Jason, director of the Center for Community Research at DePaul.
Of the 4,501 college students in the study, 238 or 5.3% developed mononucleosis; and 55 of those (23%) met criteria for ME/CFS six months later, 20 of whom (8%) met criteria for severe ME/CFS. Researchers found that those who developed ME/CFS had more physical symptoms and immune irregularities at baseline, but they did not start out with statistically significantly more psychological symptoms such as stress, depression, anxiety or abnormal coping.
"Some people who are attacked by a virus stay sick. What we've found is that their emotional functioning and psychological states are not statistically different from those who get attacked by the same virus and recover. This becomes important validating information for those people who have this illness," says Jason.
Participants in the study each completed seven different surveys to assess potential symptoms of ME/CFS. They also received a comprehensive psychiatric exam, and provided samples of serum, plasma and white blood cells. In future publications, researchers aim to analyze cytokine networks in participants' blood and other risk factors. Deficiencies in certain cytokines "might suggest predisposing irregularities in immune response," write the researchers. Vicky Whittemore, the Program Director at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), stated that NINDS is supporting follow-up research to continue to study this cohort, and to examine possible predictors of COVID-19 as well.
"Since we have baseline data on nearly all of the 4500 students, we can use our same database to tease out risk factors for COVID infection as well as prolonged recovery from that illness," says Katz.
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors on the study are Joseph Colter, Mohammed F. Islam and Madison Sunnquist of DePaul's Center for Community Research.
The study, "Risks for Developing ME/CFS in College Students Following Infectious Mononucleosis: A Prospective Cohort Study" was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, grant number AI 105781.
Research at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago is conducted through the Stanley Manne Children's Research Institute. The Manne Research Institute is focused on improving child health, transforming pediatric medicine and ensuring healthier futures through the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Lurie Children's is ranked as one of the nation's top children's hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. It is the pediatric training ground for Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. Last year, the hospital served more than 220,000 children from 48 states and 49 countries.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-22
By 2050, most people on Earth will live downstream of tens of thousands of large dams built in the 20th century, many of them already operating at or beyond their design life, according to a UN University analysis.
The report, "Ageing water infrastructure: An emerging global risk," by UNU's Canadian-based Institute for Water, Environment and Health, says most of the 58,700 large dams worldwide were constructed between 1930 and 1970 with a design life of 50 to 100 years, adding that at 50 years a large concrete dam "would most probably begin to express signs of aging."
Ageing ...
2021-01-22
The tracking of eye movement is one of the key elements of virtual and amplified reality technologies (VR/AR). A team from MSU together with a professor from RUDN University developed a mathematical model that helps accurately predict the next gaze fixation point and reduces the inaccuracy caused by blinking. The model would make VR/AR systems more realistic and sensitive to user actions. The results of the study were published in the SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers.
Foveated rendering is a basic technology of VR systems. When a person looks at something, their gaze is focused on the so-called foveated region, and everything else is covered by peripheral vision. Therefore, a computer has to render the images in the ...
2021-01-22
Becoming a parent often brings great joy, but not always. Parenthood also entails challenges, stress and, for some people, it can trigger depression. A new study from Lund University in Sweden shows that male postnatal depression is more common in men who are insecure in their relationship with their partner.
Depression affects around 10-12 per cent of new mothers, and at least 8 per cent of new fathers. The figures are even higher when looking at depressive symptoms; as many as one in five new fathers experience troublesome symptoms, according to the new study conducted by Elia Psouni, registered psychologist and associate professor of ...
2021-01-22
Most lung cancers are of a type called non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). This type of cancer is relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, so NSCLC therapies are usually based on drug treatment. Alectinib is a drug commonly used for treating patients with NSCLC. It addresses a gene rearrangement known as ALK that occurs in 3 to 5% of NSCLC patients (alectinib belongs to a class of drugs called ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors). It has been unclear, however, whether there is a correlation between the use of alectinib and the poorer prognosis in ALK-NSCLC patients in which secondary cancer mutations ...
2021-01-22
Metals such as gold or platinum are often used as catalysts. In the catalytic converters of vehicles, for example, platinum nanoparticles convert poisonous carbon monoxide into non-toxic CO2. Because platinum and other catalytically active metals are expensive and rare, the nanoparticles involved have been made smaller and smaller over time.
"Single-atom" catalysts are the logical end point of this downsizing: The metal is no longer present as particles, but as individual atoms that are anchored on the surface of a cheaper support material. Individual atoms can no longer be described using the rules developed from larger pieces of metal, so the rules used to predict which metals will ...
2021-01-22
Normal ageing causes disruptions in the brain that can lead to cognitive decline. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging studies have found significant age-related alterations in functional connectivity across various networks. However, most of the studies have focused primarily on static functional connectivity.
The authors of a recent study published in Cerebral Cortex based their research on the idea that studying the dynamics of resting-state brain activity across the whole-brain functional network can provide a better characterization of age-related changes.
The study was led by Gustavo Deco, director of the Center for Brain and Cognition (CBC) and ICREA research professor at the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), and Anira ...
2021-01-22
Chimpanzees, one of the closest relatives of humans, cooperate on a group level - in combative disputes, they even cooperate with group members to whom they are not related. Those involved in fights with neighbouring groups put themselves at risk of serious injury or even death.
Within the context of the Tai Chimpanzee Project researchers observed three chimpanzee communities in Tai National Park in Cote d'Ivoire documenting social relationships, territory range and intergroup encounters amongst others. "We have been able to analyze almost 500 vocal and physical battles from the last 25 years with participation of at least one ...
2021-01-22
Good news for the green transition: Flowery diets help predatory insects help farmers keep pests in check
Predatory insects have been shown to live longer when they have access to nectar and pollen, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Copenhagen. Thus, flowers don't just benefit insects, they help farmers farm sustainably. Predatory insects are skilled pest controllers whose hunting reduces the need for agricultural pesticides.
Until now, it was believed that predatory insects needed prey to survive. But in a systematic review conducted at the University ...
2021-01-22
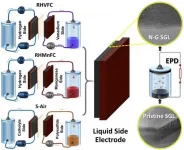
Researchers in WMG at the University of Warwick, in collaboration with Imperial College London, have found a way to enhance hybrid flow batteries and their commercial use. The new approach can store electricity in these batteries for very long durations for about a fifth the price of current technologies, with minimal location restraints and zero emissions.
The researchers enhanced three hybrid flow cells using nitrogen doped graphene (exposed to nitrogen plasma) in a binder-free electrophoresis technique (EPD).
Wind and solar power are increasingly popular sources for renewable energy. Unfortunately, intermittency issues keep them ...
2021-01-22
GREEN TRANSITION Researchers at the University of Copenhagen have demonstrated that unique fungi strengthen the "immune systems" of wheat and bean plants against aphids. Fungi enter and influence the amount of a plant's own defences, resulting in fewer aphids. The results could serve to reduce agricultural insecticide use and bring Denmark a step further along the path towards its green transition.
Wheat field
Certain fungi are able to establish a close rapport with plants that results in fewer insect infestations and thereby less damage to crops. Until now, it was unclear how these fungi could be used to reduce insect infestations.
"In order for us to really use fungi ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NIH-funded study examines mono, chronic fatigue syndrome in college students
Researchers in Chicago conduct longitudinal study of 4,500 undergraduates