(Press-News.org) In a study of local rivers, experts at the University of Nottingham in the UK have discovered more invertebrates - animals without a backbone, such as insects and snails - living on litter than on rocks.
In urban rivers where there are no better alternatives, litter provided the largest, most stable and complex habitat available for invertebrates to live on.
The findings could have important implications for the management of urban rivers, including how river clean-up events are conducted.
The research team, in the School of Geography, studied three local rivers; the River Leen, Black Brook, and Saffron Brook, in Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire by collecting samples of rocks and litter from the riverbeds to compare in their laboratory.
The scientists found that the surfaces of the litter were inhabited by different and more diverse communities of invertebrates than those on rocks. Plastic, metal, fabric, and masonry samples consistently had the highest diversity, meanwhile, glass and rock samples were considerably less diverse than other material samples.
They observed that flexible pieces of plastic, like plastic bags, were inhabited by the most diverse communities and speculated that the types of invertebrates they found on flexible plastic suggests it might mimic the structure of water plants.
The study is the first of its kind to evaluate the role of litter as a riverine habitat and has been published in the journal END
Litter provides habitat for diverse animal communities in rivers, study finds
2021-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New skull of tube-crested dinosaur reveals evolution of bizarre crest
2021-01-25
DISCOVERY BRIEF:
The first new skull of a rare species of the dinosaur Parasaurolophus (recognized by the large hollow tube that grows on its head) discovered in 97 years.
Exquisite preservation of the new skull gives paleontologists their first opportunity to definitively identify how such a bizarre structure grew on this dinosaur.
For the first time, this study found characteristics to link tube-crested dinosaur species found in southern North America (New Mexico, Utah), distinct from the only northern species (Alberta).
The locality, in northwestern New Mexico, is dated to about 75 million years ago, a time when North America was divided by a shallow sea and teemed with duckbilled dinosaurs, horned dinosaurs and early tyrannosaurs.
Fossils from ...
Oncotarget: Improved therapeutic efficacy of unmodified anti-tumor antibodies
2021-01-25
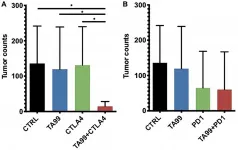
The cover for issue 2 of Oncotarget features Figure 4, "Combination therapy TA99/ICB reduced the lung tumor burden in the B16 model of metastases," published in "Improved therapeutic efficacy of unmodified anti-tumor antibodies by immune checkpoint blockade and kinase targeted therapy in mouse models of melanoma" by Pérez-Lorenzo, et al. which reported that here, the authors showed that removing immune suppression and enhancing stimulatory signals increased the anti-tumor activity of unmodified TA99 antibodies with a significant reduction of ...
Oncotarget: Drug-resistant cells grow exponentially in metastatic prostate cancer
2021-01-25
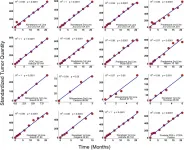
The cover for issue 1 of Oncotarget features Figure 2, "Results in clinical trials," published in "Drug resistant cells with very large proliferative potential grow exponentially in metastatic prostate cancer" by Blagoev, et al. which reported that most metastatic cancers develop drug resistance during treatment and continue to grow, driven by a subpopulation of cancer cells unresponsive to the therapy being administered.
There is evidence that metastases are formed by phenotypically plastic cancer cells with stem-cell-like properties.
Currently, the population structure and growth dynamics ...
Oncotarget: Prognostic biomarker for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
2021-01-25
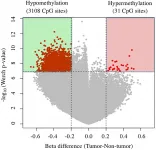
The cover for issue 52 of Oncotarget features Figure 1, "Volcano plots of DNA methylation in tumor tissues compared with nontumor tissue," published in "Reduction of T-Box 15 gene expression in tumor tissue is a prognostic biomarker for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma" by Morine, et al. which reported that the authors conducted a genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation of the tumor and non-tumor tissue of 15 patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and revealed TBX15 was the most hypermethylated gene of the tumor.
Another validation set, which comprised 58 HCC with radical resection, was analyzed to investigate the relationships between tumor phenotype and TBX15 mRNA expression.
TBX15 mRNA levels in tumor tissues were significantly lower compared ...
Aging-US: PAM (PIK3/AKT/mTOR) signaling in glia: potential contributions to brain tumors
2021-01-25
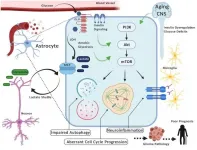
Aging-US Issue 1 Volume 13 features "PAM (PIK3/AKT/mTOR) signaling in glia: potential contributions to brain tumors in aging" which reported that despite a growing proportion of aged individuals at risk for developing cancer in the brain, the prognosis for these conditions remains abnormally poor due to limited knowledge of underlying mechanisms and minimal treatment options.
While cancer metabolism in other organs is commonly associated with upregulated glycolysis and hyperactivation of PIK3/AKT/mTOR pathways, the unique bioenergetic demands of the central nervous system ...
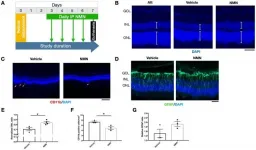
Aging-US: Nicotinamide mononucleotide in degenerative model of retinal detachment
2021-01-25
Aging-US published "Neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of action of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) in a photoreceptor degenerative model of retinal detachment" which reported that here, the authors investigated nicotinamide mononucleotide, a precursor of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, in a retinal detachment induced photoreceptor degeneration.
NMN administration after RD resulted in a significant reduction of TUNEL photoreceptors, CD11b macrophages, and GFAP labeled glial activation; a normalization of protein carbonyl content, and a preservation of the outer nuclear layer thickness.
NMN administration significantly increased NAD levels, SIRT1 protein expression, and heme oxygenase-1 expression.
Delayed NMN administration still exerted protective effects after RD.
This ...
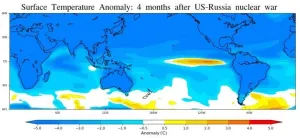
Nuclear war could trigger big El Niño and decrease seafood
2021-01-25
A nuclear war could trigger an unprecedented El Niño-like warming episode in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, slashing algal populations by 40 percent and likely lowering the fish catch, according to a Rutgers-led study.
The research, published in the journal END ...
Mental health is important to overall health, and heart disease prevention and treatment
2021-01-25
DALLAS, Jan. 25, 2021 -- Psychological health can positively or negatively impact a person's health and risk factors for heart disease and stroke, according to "Psychological Health, Well-Being, and the Mind-Heart-Body Connection," a new American Heart Association Scientific Statement, published today in the Association's flagship journal Circulation. The statement evaluates the relationship between psychological health and heart health, summarizing ways to help improve psychological health for people with and at risk for heart disease.
"A person's mind, heart and body are all interconnected and interdependent in what can be termed 'the mind-heart-body-connection,'" said Glenn N. Levine, M.D., FAHA, master clinician and professor of medicine at ...
Despite some advances, women still face disparities of the global burden of stroke
2021-01-25
DALLAS, Jan. 25, 2021 -- The continued global burden of stroke and how it disproportionately affects women are highlighted in new science published online today in the February issue of Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association. Stroke editors selected nine manuscripts focused on stroke disparities in women in this collaboration with Go Red for Women®, the Association's global movement to end heart disease and stroke in women.
"Stroke continues to be a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, with women being more adversely affected by the global burden of stroke," said Stroke Editor-In-Chief Ralph L. Sacco, M.D., M.S., FAHA, ...
Microbes fuelled by wind-blown mineral dust melt the Greenland ice sheet
2021-01-25
Scientists have identified a key nutrient source used by algae living on melting ice surfaces linked to rising sea levels.
The Greenland ice sheet - the second largest ice body in the world after the Antarctic ice sheet - covers almost 80% of the surface of Greenland. Over the last 25 years, surface melting and water runoff from the ice sheet has increased by about 40%.
The international research team, led by the University of Leeds, analysed samples from the southwestern margin on Greenland's 1.7 million km² ice sheet over two years.
They discovered that phosphorus containing minerals may be driving ever-larger algal blooms on the Greenland Ice Sheet. As the algal blooms grow they darken the ice surface, decreasing albedo - ...