How will seafarers fare once automated ships take over? Scientists predict the future
Scientists simulate trends in maritime employment over the next 15 years following ship automation
2021-01-25
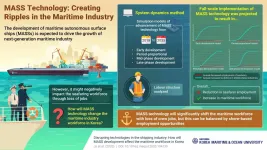
(Press-News.org) Artificial intelligence and automation are changing the world, one industry at a time! Whatever humans can do, machines are learning to also do effectively, with lower costs and fewer errors. The maritime shipping industry is no different. Ships are now increasingly automated (called maritime autonomous surface ships or MASSs), reducing the need for human input. While this bodes well for labor and fuel costs, the question naturally raised is, what happens to the jobs of seafarers, the chief workforce of the shipping industry, once MASSs take over.
To find out, researchers from Korea used complex mathematical models and simulations to determine the effect of MASS technology on jobs lost and gained over time. In their study published in Marine Policy, Assistant Professor Sohyun Jo from Korea Maritime and Ocean University--the lead scientist on this study and a former navigation officer--simulated four possible scenarios depicting varying speeds of growth of MASS technology. The projected outcomes in all the scenarios were consistent; in all examined scenarios, the number of seafarer jobs decreased, but at least fifty times as many shore-based jobs as the lost seafarer jobs were newly created.
These findings are encouraging, but not the endpoint, believes Dr. Jo "This indicates an overall increase in the number of jobs, but we need to nevertheless be prepared; specific and dynamic education, training and development of human resource policies for skills development should be introduced," she says. Other countries that provide manpower for the maritime industry can benefit from this study by introducing "political willingness and technical ability" to adapt to the changing employment sphere. Technology development and timely training internationally competitive human resources is also essential.
"Moreover, to ensure that the marine industry grows sustainably in a new business ecosystem, preemptive efforts to create new business opportunities incorporating ICT technologies are needed," Dr. Jo suggests.
Technology is changing the marine industry for the better, but people can also grow with it, by find their place in this new automated world.
INFORMATION:
Reference
Authors: Sohyun Jo
Title of original paper: Disrupting technologies in the shipping industry: How will MASS development affect the maritime workforce in Korea
Journal: Marine Policy
DOI: 10.1016/j.marpol.2020.104139
Affiliations: Division of Maritime Transportation Science, Korea Maritime and Ocean University, Busan, Republic of Korea
About National Korea Maritime & Ocean University
South Korea's most prestigious university for maritime studies, transportation science and engineering, the National Korea Maritime & Ocean University is located on an island in Busan. The university was established in 1945 and since then has merged with other universities to currently being the only post-secondary institution that specializes in maritime sciences and engineering. It has four colleges that offer both undergraduate and graduate courses.
Website: http://www.kmou.ac.kr/english/main.do
About the author
Dr. Sohyun Jo is an Assistant Professor at Korea Maritime and Ocean University, where she teaches subjects like maritime transport, shipping management, cargo handling, ship simulation, shipping and other safety management. Dr. Jo graduated from Korea Maritime and Ocean University in Korea, majoring in Navigation. She received her MSc in the maritime safety environment and administration at World Maritime University in 2010. She received her doctorate from Korea Maritime and Ocean University in Korea.
She worked in the shipping company as a navigation officer from 3rd to chief mate for 7 years after she graduated KMOU. She is a Master Mariner who holds a 1st license of navigation for deck department.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-25
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- Design of Army aerial vehicles and weapon systems relies on the ability to predict aerodynamic behavior, often aided by advanced computer simulations of the flow of air over the body. High-fidelity simulations assist engineers in maximizing how much load a rotorcraft can lift or how far a missile can fly, but these simulations aren't cheap.
The simulations that designers currently use require extensive data processing on supercomputers and capture only a portion of vortex collision events - which can cause significant performance degradation, from loss of lift on a rotor to complete loss of control of a munition. A new turbulence model could change that.
The Army Research Office, an ...
2021-01-25
Teenagers with happy childhood memories are likely to drink less, take fewer drugs and enjoy learning, according to research published in the peer-reviewed journal END ...
2021-01-25
New Orleans, LA - An analysis by Nicholas Gilpin, PhD, Professor of Physiology and Associate Director of the Alcohol and Drug Abuse Center of Excellence at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, and Michael Taffe, PhD, Professor of Psychiatry at the University of California San Diego, summarizes long-standing racial inequities in federal funding for biosciences research from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Their report describes prior failures to correct these racial inequities and offers strategies that may be effective in eliminating these disparities. Their paper, published online in the open-access ...
2021-01-25
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a widespread condition in the Western World. Around 30% of the population have lipid droplets stored in their liver which diminish its function in the long term. Main causes for NAFLD are our high-caloric diet in combination with a sedentary lifestyle. Hitherto, researchers have not fully understood the cause of this disease and despite the high number of affected individuals, there is no approved therapy.
In order to improve our understanding of the basic mechanisms underlying the etiology of NAFLD, Dr. Nina Graffmann, Prof. James Adjaye and the team of the Institute for Stem Cell research and Regenerative Medicine from the University Hospital Duesseldorf differentiated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from healthy ...
2021-01-25
Using a combination of telescopes, including the Very Large Telescope of the European Southern Observatory (ESO's VLT), astronomers have revealed a system consisting of six exoplanets, five of which are locked in a rare rhythm around their central star. The researchers believe the system could provide important clues about how planets, including those in the Solar System, form and evolve.
The first time the team observed TOI-178, a star some 200 light-years away in the constellation of Sculptor, they thought they had spotted two planets going around it in the same orbit. However, a closer look revealed something entirely ...
2021-01-25
CHICAGO (January 25, 2021; 9 am CST): A new study finds that older cancer patients are less likely to have optimal results following their cancer operation if they live in an area highly affected by social challenges, especially if they are racial-ethnic minorities. The study was selected for the 2020 Southern Surgical Association Program and published as an "article in press" on the Journal of the American College of Surgeons website in advance of print.
Study investigators from The Ohio State University (OSU) used a novel risk stratification tool called the social vulnerability index (SVI), a composite measure of 15 social and economic factors. ...
2021-01-25
The key factor in preventing non-communicable diseases is lifestyle management at the individual level with a focus on such innovations, which can help increase the awareness of risk factors management in society, claim an international team of researchers, among them - scientists from Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania in a recent study. According to them, the management of cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases requires many strategies from several perspectives and on different levels.
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, are medical conditions that are ...
2021-01-25
What happened to the promised applications of graphene and related materials? Thanks to initiatives like the European Union's Graphene Flagship and heavy investments by leading industries, graphene manufacturing is mature enough to produce prototypes and some real-life niche applications. Now, researchers at Graphene Flagship partner The Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research (ISI) in Karlsruhe, Germany, have published two papers that roadmap the expected future mass introduction of graphene and related materials in the market.
Back in 2004, graphene was made by peeling off atomically thin layers from a graphite block. Now, thanks to the advances pioneered by the Graphene Flagship, among ...
2021-01-25
A team from the Computer Vision Center (CVC) and the University of Barcelona has published the results of a study that evaluates the accuracy and bias in gender and skin colour of automatic face recognition algorithms tested with real world data. Although the top solutions exceed the 99.9% of accuracy, researchers have detected some groups that show higher false positive or false negative rates.
Face recognition has been routinely used by both private and governmental organizations worldwide. Automatic face recognition can be used for legitimate and beneficial purposes (e.g. to improve security) but at the same time its power and ubiquity increases a potential negative ...
2021-01-25
Small-scale optical devices capable of using photons for high-speed information processing can be fabricated with unprecedented ease and precision using an additive manufacturing process developed at KAUST.
Fiber optics are conventionally produced by drawing thin filaments out of molten silica glass down to microscale dimensions. By infusing these fibers with long narrow hollow channels, a new class of optical devices termed "photonic crystal fibers" were introduced. The periodic arrangement of air holes in these photonic crystal fibers act like near-perfect mirrors, allowing trapping and long propagation of light in their central core.
"Photonic crystal fibers allow you to confine light in very tight spaces, increasing the optical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How will seafarers fare once automated ships take over? Scientists predict the future
Scientists simulate trends in maritime employment over the next 15 years following ship automation