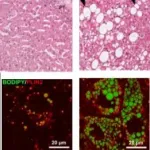
(Press-News.org) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a widespread condition in the Western World. Around 30% of the population have lipid droplets stored in their liver which diminish its function in the long term. Main causes for NAFLD are our high-caloric diet in combination with a sedentary lifestyle. Hitherto, researchers have not fully understood the cause of this disease and despite the high number of affected individuals, there is no approved therapy.
In order to improve our understanding of the basic mechanisms underlying the etiology of NAFLD, Dr. Nina Graffmann, Prof. James Adjaye and the team of the Institute for Stem Cell research and Regenerative Medicine from the University Hospital Duesseldorf differentiated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from healthy donors and NAFLD patients into hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs). The HLCs were stimulated with fatty acids to mimic a scenario where an individual consumes excess fat in their diet. The lipid droplets produced in HLCs are akin to lipid droplets seen in the livers of NAFLD patients.
The analysis of fat incorporation was carried out in collaboration with Prof. Beller of the Systems Biology of Lipid Metabolism group - Heinrich-Heine-University Duesseldorf, Germany.
The recent publication in Biology Open (Publisher-Company of Biologists) demonstrates a strong heterogeneity between cell lines, regarding gene expression and lipid droplet morphology. The scientists think that this is due to the plethora of metabolic networks involved in the development of the disease. It also mirrors the multifaceted, patient-dependent phenotypes which make NAFLD a highly complex disease as the group has shown in an earlier study (Wruck et al, 2015). Nonetheless, the scientists could identify gene expression patterns that correlate with disease severity.
Adiponectin is a molecule synthesized by human fat cells, which has been shown to positively influence hepatocyte metabolism. In the institute for Organic Chemistry and Macromolecular Chemistrymof Heinrich-Heine-University Duesseldorf, Prof. Constantin Czekelius and his team produced a synthetic analogue called AdipoRon for this study. AdipoRon has been first used in mice, were it had a significant anti-diabetic effect (Okada-Iwabu et al, 2013).
Treating HLCs with AdipoRon again resulted in cell line / genetic background specific effects. In addition, AdipoRon affected transcription of genes associated with metabolism, transport, immune system, cell stress and signalling.
"We could recapitulate important aspects of NAFLD with our stem cell based cell culture model. We are going to use it for further studies, because established animal models cannot reproduce the complex human metabolic pathways involved in the development of the disease," explains Dr. Graffmann.
"Once again we have shown that although iPSC- derived hepatocyte-like cells are immature in nature, i.e. fetal, these cells still have immense usefulness in their application in drug discovery and for dissecting disease mechanisms such as NAFLD" says Prof. James Adjaye.
INFORMATION:
References:
Graffmann, N., Ncube, A., Martins, S., Fiszl, A., Reuther, P., Bohndorf, M., Wruck, W., Beller, M., Czekelius, C. & Adjaye, J. (2020) A stem cell based in vitro model of NAFLD enables the analysis of patient specific individual metabolic adaptations in response to a high fat diet and AdipoRon interference. Biology open.
Okada-Iwabu, M., Yamauchi, T., Iwabu, M., Honma, T., Hamagami, K., Matsuda, K., Yamaguchi, M., Tanabe, H., Kimura-Someya, T., Shirouzu, M., Ogata, H., Tokuyama, K., Ueki, K., Nagano, T., Tanaka, A., Yokoyama, S. & Kadowaki, T. (2013) A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Nature, 503(7477), 493-9.
Wruck, W., Graffmann, N., Kawala, M. A. & Adjaye, J. (2017) Concise Review: Current Status and Future Directions on Research Related to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Stem Cells, 35(1), 89-96.
Wruck, W., Kashofer, K., Rehman, S., Daskalaki, A., Berg, D., Gralka, E., Jozefczuk, J., Drews, K., Pandey, V., Regenbrecht, C., Wierling, C., Turano, P., Korf, U., Zatloukal, K., Lehrach, H., Westerhoff, H. V. & Adjaye, J. (2015) Multi-omic profiles of human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease tissue highlight heterogenic phenotypes. Scientific Data, 2, 150068.
Using a combination of telescopes, including the Very Large Telescope of the European Southern Observatory (ESO's VLT), astronomers have revealed a system consisting of six exoplanets, five of which are locked in a rare rhythm around their central star. The researchers believe the system could provide important clues about how planets, including those in the Solar System, form and evolve.
The first time the team observed TOI-178, a star some 200 light-years away in the constellation of Sculptor, they thought they had spotted two planets going around it in the same orbit. However, a closer look revealed something entirely ...
CHICAGO (January 25, 2021; 9 am CST): A new study finds that older cancer patients are less likely to have optimal results following their cancer operation if they live in an area highly affected by social challenges, especially if they are racial-ethnic minorities. The study was selected for the 2020 Southern Surgical Association Program and published as an "article in press" on the Journal of the American College of Surgeons website in advance of print.
Study investigators from The Ohio State University (OSU) used a novel risk stratification tool called the social vulnerability index (SVI), a composite measure of 15 social and economic factors. ...
The key factor in preventing non-communicable diseases is lifestyle management at the individual level with a focus on such innovations, which can help increase the awareness of risk factors management in society, claim an international team of researchers, among them - scientists from Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania in a recent study. According to them, the management of cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases requires many strategies from several perspectives and on different levels.
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, are medical conditions that are ...
What happened to the promised applications of graphene and related materials? Thanks to initiatives like the European Union's Graphene Flagship and heavy investments by leading industries, graphene manufacturing is mature enough to produce prototypes and some real-life niche applications. Now, researchers at Graphene Flagship partner The Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research (ISI) in Karlsruhe, Germany, have published two papers that roadmap the expected future mass introduction of graphene and related materials in the market.
Back in 2004, graphene was made by peeling off atomically thin layers from a graphite block. Now, thanks to the advances pioneered by the Graphene Flagship, among ...
A team from the Computer Vision Center (CVC) and the University of Barcelona has published the results of a study that evaluates the accuracy and bias in gender and skin colour of automatic face recognition algorithms tested with real world data. Although the top solutions exceed the 99.9% of accuracy, researchers have detected some groups that show higher false positive or false negative rates.
Face recognition has been routinely used by both private and governmental organizations worldwide. Automatic face recognition can be used for legitimate and beneficial purposes (e.g. to improve security) but at the same time its power and ubiquity increases a potential negative ...
Small-scale optical devices capable of using photons for high-speed information processing can be fabricated with unprecedented ease and precision using an additive manufacturing process developed at KAUST.
Fiber optics are conventionally produced by drawing thin filaments out of molten silica glass down to microscale dimensions. By infusing these fibers with long narrow hollow channels, a new class of optical devices termed "photonic crystal fibers" were introduced. The periodic arrangement of air holes in these photonic crystal fibers act like near-perfect mirrors, allowing trapping and long propagation of light in their central core.
"Photonic crystal fibers allow you to confine light in very tight spaces, increasing the optical ...
Skeletal muscle is the largest tissue in the human body and is responsible not only for locomotion but for energy metabolism and heat production. Age-related muscle atrophy reduces motor function and contributes to the need for nursing care. In addition, muscle atrophy associated with various chronic diseases is known to be a risk factor for life expectancy. Myoblasts, the progenitor cells of muscle, play an important role in maintaining muscle homeostasis. However, it has been reported that the differentiation ability of myoblasts decreases with age and disease, and this is thought to be one of the causes of muscle atrophy. In order to prevent or treat muscle atrophy, a research team led by Assistant Professor Tomohide Takaya of Shinshu University, Faculty of Agriculture studied ...
Laser beams can be used to precisely measure an object's position or velocity. Normally, however, a clear, unobstructed view of this object is required - and this prerequisite is not always satisfied. In biomedicine, for example, structures are examined, which are embedded in an irregular, complicated environment. There, the laser beam is deflected, scattered and refracted, often making it impossible to obtain useful data from the measurement.
However, Utrecht University (Netherlands) and TU Wien (Vienna, Austria) have now been able to show that meaningful results can be obtained even in such complicated environments. Indeed, there is a way to specifically modify ...
Depression, especially in urban areas, is on the rise, now more than ever. Mental health outcomes are influenced by, among other things, the type of environment where one lives. Former studies show that urban greenspace has a positive benefit on people experiencing mental ill health, but most of these studies used self-reported measures, which makes it difficult to compare the results and generalise conclusions on the effects of urban greenspace on mental health.
An interdisciplinary research team of UFZ, iDiv and Leipzig University tried to improve this issue by involving an objective indicator: prescriptions of antidepressants. To find out whether a specific type of 'everyday' green space - street trees dotting the neighbourhood sidewalks ...
A lot is known about galaxies. We know, for instance, that the stars within them are shaped from a blend of old star dust and molecules suspended in gas. What remains a mystery, however, is the process that leads to these simple elements being pulled together to form a new star.
But now an international team of scientists, including astrophysicists from the University of Bath in the UK and the National Astronomical Observatory (OAN) in Madrid, Spain have taken a significant step towards understanding how a galaxy's gaseous content becomes organised into a new generation of stars.
Their findings have important implications for our understanding of how stars formed during the early days of the universe, when galaxy collisions were frequent and dramatic, and star and galaxy formation ...