RUDN University linguists conducted comprehensive study of how Russian speakers perceive Greek sound
2021-01-25
(Press-News.org) Linguists from RUDN University found out how Russian speakers differentiate between similar consonants of the Greek language and associate them with Russian sounds. The results of the study were published in the Speech Communication journal.
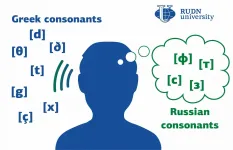
Efficient learning of a foreign language depends on a student's mother tongue and similarities between the sounds of the two languages. If they have a lot of similar sounds, foreign speech is perceived better, and if a student's mother tongue has no or few sounds similar to those of a foreign language, the progress will be slower. For example, it could be quite difficult for a Russian speaker to learn Greek, as some Greek consonants don't have Russian analogs. Linguists from RUDN University were the first to conduct a comprehensive study of these consonants and to identify what sounds Russian speakers associate them with.
"Our study covered several Greek consonants that do not have direct analogs in the Russian language. Our goal was to find out what Russian sounds they are usually associated with. Moreover, we assessed the ability of Russian speakers to differentiate between similar Greek sounds and perceive them in syllables that begin either with a consonant or a vowel," said Georgios Georgiou, Ph.D., a postdoc, and a researcher at the Institute of Modern Languages, Intercultural Communication and Migration at RUDN University.
Unlike Greek, the Russian language doesn't have fricative sounds [θ] and [ð], palatal plosive [?], or palatal fricative [ç]. For their study, the team chose 16 Russian-speaking students that never learned Greek before. The students were asked to listen to a recording with fragments of Greek words, specifically, syllables containing the sounds [θ], [t], [ð], [d], [?], [g], [ç], [x]. After that, the students were asked to match the Greek sounds with Russian ones that could potentially be used to replace them. Also, the students stated the acoustical differences between the sounds in the pairs [θ]-[t], [ð]-[d], [?]-[g], and [ç]-[x].
The students were quite successful in differentiating between similar Greek sounds regardless of the types of syllables they were used in. Traditionally, scientists believe that Russian speakers find the Greek sound [θ] similar to Russian [t]. However, the majority of participants decided it was similar to [f]. As for the sound [ð], the participants found it similar to [z] both vowel and consonant initially.
"Previously, we thought that in the Russian language [θ] was most likely to be replaced with [t], and [ð] with [d]. This is because this occurs in some linguistic borrowings from Greek to Russian, such as the word "????????????????" - "orthodoxy". It is still unknown why the experiment showed a different result. It may be due to the fact that in addition to Russian the participants spoke basic English which gave an additional dimension to their perception of foreign sounds. Another possibility is that some of the participants came from regions of Russia and initially spoke Russian dialects that were quite different from the literary norm. Regardless of the reason, this is an interesting result, and we plan to study this issue further," added Georgios Georgiou from RUDN University.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- U.S. counties with higher income inequality faced higher rates of COVID-19 infections and deaths in the first 200 days of the pandemic, according to a new study. Counties with higher proportions of Black or Hispanic residents also had higher rates, the study found, reinforcing earlier research showing the disparate effects of the virus on those communities.
The findings, published last week by JAMA Network Open, were based on county-level data for all 50 states and Washington, D.C. Data sources included the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, USAFacts and the U.S. Census Bureau.
The lead author of the study, Tim Liao, head of the sociology department at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, initiated the study last summer after noticing that ...
2021-01-25
When it launches in the mid-2020s, NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will explore an expansive range of infrared astrophysics topics. One eagerly anticipated survey will use a gravitational effect called microlensing to reveal thousands of worlds that are similar to the planets in our solar system. Now, a new study shows that the same survey will also unveil more extreme planets and planet-like bodies in the heart of the Milky Way galaxy, thanks to their gravitational tug on the stars they orbit.
"We were thrilled to discover that Roman will be able to offer even more information about the planets throughout our galaxy than originally planned," said Shota ...
2021-01-25
Hitting a pothole on the road in just the wrong way might create a bulge on the tire, a weakened spot that will almost certainly lead to an eventual flat tire. But what if that tire could immediately begin reknitting its rubber, reinforcing the bulge and preventing it from bursting?
That's exactly what blood vessels can do after an aneurysm forms, according to new research led by the University of Pittsburgh's Swanson School of Engineering and in partnership with the Mayo Clinic. Aneurysms are abnormal bulges in artery walls that can form in brain arteries. Ruptured brain aneurysms are fatal in almost 50% of cases.
The research, recently published in Experimental Mechanics, is the first to show that there are two phases of wall restructuring after an aneurysm forms, the first ...
2021-01-25
PHILADELPHIA (January 25, 2021) - While eating less and moving more are the basics of weight control and obesity treatment, finding ways to help people adhere to a weight-loss regimen is more complicated. Understanding what features make a diet easier or more challenging to follow can help optimize and tailor dietary approaches for obesity treatment.
A new paper from the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing (Penn Nursing) analyzed different dietary approaches and clinical trials to better understand how to optimize adherence and subsequent weight reduction. The findings have been published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
"There is not convincing evidence that one diet is universally easier to adhere to than another for extended periods, a feature necessary for long-term ...
2021-01-25
Research by an international team of medical experts has found cancer patients could be up to four times more likely to die following cancer surgery in low to lower-middle income countries than in high-income countries. It also revealed lower-income countries are less likely to have post-operative care infrastructure and oncology services.
The global observational study, published in The Lancet, explored global variation in post-operative complications and deaths following surgery for three common cancers. It was conducted by researchers from the GlobalSurg Collaborative and NIHR Global Health Unit on Global Surgery - led by the University of Edinburgh, with analysis and support from the University of Southampton.
Between April 2018 and January 2019, researchers enrolled 15,958 ...
2021-01-25
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Older minority cancer patients with poor social determinants of health are significantly more likely to experience negative surgical outcomes compared to white patients with similar risk factors, according to a new study published by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center - Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC - James).
A new retrospective analysis of more than 200,000 patients conducted by researchers with the OSUCCC - James suggests that minority patients living in high socially vulnerable neighborhoods had a 40% increased risk of a complication ...
2021-01-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Absent a widely available vaccine, mitigation measures such as stay-at-home mandates, lockdowns or shelter-in-place orders have been the major public health policies deployed by state governments to curb the spread of COVID-19.
But given the uncertain duration of such policies, questions have been raised about the potential negative mental health consequences of extended lockdowns with indefinite end dates. But according to new research co-written by a team of University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign experts who study the intersection of health care and public policy, the negative mental health effects of ...
2021-01-25
ITHACA, N.Y. - Researchers from Cornell University and the National Park Service have pinpointed and confirmed the location of the remnants of a wooden fort in Alaska - the Tlingit people's last physical bulwark against Russian colonization forces in 1804 - by using geophysical imaging techniques and ground-penetrating radar.
The fort was the last physical barrier to fall before Russia's six-decade occupation of Alaska, which ended when the United States purchased Alaska in 1867 for $7 million.
The Tlingit built what they called Shiskinoow - the "sapling fort" - on a peninsula in modern-day Sitka, Alaska, ...
2021-01-25
During epileptic seizures, a large number of nerve cells in the brain fire excessively and in synchrony. This hyperactivity may lead to uncontrolled shaking of the body and involve periods of loss of consciousness. While about two thirds of patients respond to anti-epileptic medication, the remainder is refractory to medical treatment and shows drug-resistance. These patients are in urgent need for new therapeutic strategies.
Together with colleagues in Japan, Prof. Dr. Christine Rose and her doctoral student Jan Meyer from the Institute of Neurobiology at HHU have performed a study to address the cellular mechanisms that promote the development of epilepsy. While up to now, most studies and anti-epileptic drugs targeted nerve cells (neurons), ...
2021-01-25
Findings of a new study published by researchers from Trinity College Dublin and St James's Hospital outline the health impacts faced by older people while cocooning during the Covid-19 pandemic. The findings are published in the Quarterly Journal of Medicine here: https://bit.ly/3qGKJoI.
Cocooning involves staying at home and reducing face-to-face interaction with other people and is an important part of the response to the COVID-19 pandemic, with an overall aim to prevent transmission to vulnerable older people. However, concerns exist regarding the long-term adverse effects ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] RUDN University linguists conducted comprehensive study of how Russian speakers perceive Greek sound




