Borderline personality disorder: Don't ignore it
Diagnose it, treat it and teen patients improve
2021-01-25
(Press-News.org) For many years, clinicians have been hesitant to diagnose adolescents with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD), believing it was a mental health "death sentence" for a patient because there was no clear treatment. Carla Sharp, professor of psychology and director of the Developmental Psychopathology Lab at the University of Houston, begs to differ.
And her new research, published in Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology backs her up.
"Like adult BPD, adolescent BPD appears to be not as intractable and treatment resistant as previously thought," reports Sharp. "That means we should not shy away from identifying BPD in adolescents and we shouldn't shy away from treating it."
Borderline Personality Disorder is marked by patterns of varying moods, self-image and behavior, and it results in impulsive actions, problems in relationships and a tendency to think in purely black and white. People with BPD may experience intense episodes of anger, depression and anxiety that can last from a few hours to days.
Sharp said Borderline Personality Disorder is treatable, therapy helps, and early intervention for adolescents is of critical importance.
"We ignore Borderline Personality Disorder at our peril, because compared with other mental disorders, BPD is among the leading causes of suicidal behaviors and self-harm in young people," she said. Up to 10% of BPD patients will die by suicide.
Sharp's research is the first study to show that adolescent borderline pathology follows a similar downward course after discharge from inpatient treatment previously demonstrated for adults. Her conclusions come after examining data collected from 500 adolescent inpatients and following them every six months over an 18-month follow-up period to measure their symptoms of BPD.
The results showed a significant downward trend of BPD features across all time points and across both parent-and adolescent self-reporting which mirrors the reduction in BPD symptomology reported for adults with BPD. Interestingly, the teens Sharp studied were not undergoing specialized treatment for BPD and yet they still improved.
"It sends a message to clinicians: 'Don't put your head in the sand!' If the pathology is there, diagnose it and treat it with your best evidence-based treatment," said Sharp emphatically. The standard therapies for BPD in adults and adolescents currently are dialectical behavior therapy and mentalization-based therapy. But even if clinicians are not trained in those specialized treatments, it would be ethically appropriate to make use of best available scientific evidence to inform practice, consistent with practice-based evidence recommendations from the American Psychological Association, she said.
"Our work contributes to the growing consensus that the discrimination and stigmatization of BPD are not justified. Instead, a clinical course very similar to adult BPD is described which highlights the potential therapeutic rewards of diagnosing and treating adolescent patients with BPD," said Sharp.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-25
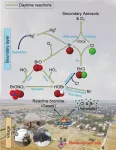
Halogen atoms (Cl and Br) strongly influence the atmospheric chemical composition. Since 1970s, scientists discovered that these atoms were responsible for depletion of ozone in the stratosphere and ground-level ozone of the Arctic. In the past decade, there is emerging recognition that halogen atoms also play important roles in tropospheric chemistry and air quality. However, the knowledge of halogen atoms in continental regions is still incomplete.
"In the troposphere, halogen atoms can kick start hydrocarbon oxidation that makes ozone, modify the oxidative capacity, perturb ...
2021-01-25
A survey of dog owners from across the U.S. shows that when it comes to seeking veterinary care for dogs, barriers to access - including a lack of trust - have more effect on the decision-making process than differences in race, gender or socioeconomic status. The results could aid veterinarians in developing outreach strategies for underserved communities.
"I was interested in how different demographic groups viewed health care and how those views might affect relationships between veterinarians and their clients," says Rachel Park, a Ph.D. student at North Carolina State University and first author of a paper describing the work. "The existing literature wasn't national in scope and hadn't accounted for multiple identities held, such as one's socioeconomic status or ...
2021-01-25
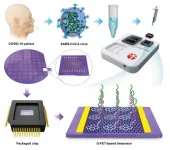
In the past 20 years, humans have suffered several serious epidemics from emerging viruses, such as SARS, swine flu, Ebola, MERS and (most recently) SARS-CoV-2. During each epidemic, an accurate, rapid, and accessible molecular diagnostic test is highly essential for the control and prevention of viral diseases. In particular, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading rapidly in most countries, resulting in a severe global pandemic, which has a profound impact on the world economy and people's normal life. Accurate and rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 has been the most crucial measure for controlling the ...
2021-01-25
FINDINGS
A study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center found shortening a traditional 45-day course of radiation to a five-day course delivered in larger doses is safe and as effective as conventional radiation for men with high-risk forms of prostate cancer.
The findings show the five-day regimen of stereotactic body radiotherapy, a form of external beam radiation therapy that uses a higher dose of radiation, had a four-year cure rate of 82%. Severe side effects were also rare. Around 2% experienced urinary issues and less than 1% had bowel side effects.
BACKGROUND
Building on previous UCLA research that provided significant evidence that a shortened regimen of radiation could be ...
2021-01-25
(Boston)--Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a higher risk of complications including ischemic stroke, cognitive decline, heart failure, myocardial infarction and death. AF frequently is undetected until complications such as stroke or heart failure occur.
While the public and clinicians have an intense interest in detecting AF earlier, the most appropriate strategies to detect undiagnosed AF and medical prognosis and therapeutic implications of AF detected by screening are uncertain.
A new report led by Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) researcher Emelia J. Benjamin, MD, ScM, builds upon a recently conducted National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's virtual workshop that focused on identifying key research priorities related to AF screening.
Global experts reviewed ...
2021-01-25
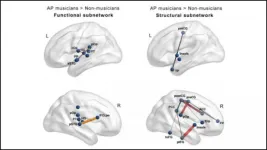
The brains of musicians have stronger structural and functional connections compared to those of non-musicians, regardless of innate pitch ability, according to new research from JNeurosci.
Years of musical training shape the brain in dramatic ways. A minority of musicians -- with Mozart and Michael Jackson in their ranks -- also possess absolute pitch, the ability to identify a tone without a reference. But, it remains unclear how this ability impacts the brain.
In the biggest sample to date, Leipold et al. compared the brains of professional musicians, some with absolute pitch and some without, to non-musicians. To the team's surprise, there were no strong differences ...
2021-01-25
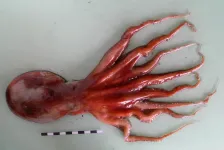
An extensive review of cephalopod fauna from the Northwest African Atlantic coast was performed by researchers from the University of Vigo (Spain) and the Spanish Institute of Oceanography ( END ...
2021-01-25
A team led by plant biologists at the Universities of Freiburg and Göttingen in Germany has shown for the first time that mosses have a mechanism to protect them against cold that was previously known only in flowering plants. Professor Ralf Reski at the Cluster of Excellence Centre for Integrative Biological Signalling Studies (CIBSS) at the University of Freiburg and Professor Ivo Feussner at the Center for Molecular Biosciences (GZMB) at the University of Göttingen have also demonstrated that this mechanism has an evolutionarily independent origin - mosses and flowering ...
2021-01-25
Every living organism has DNA, and every living organism engages in DNA replication, the process by which DNA makes an exact copy of itself during cell division. While it's a tried-and-true process, problems can arise.
Break-induced replication (BIR) is a way to solve those problems. In humans, it is employed chiefly to repair breaks in DNA that cannot be fixed otherwise. Yet BIR itself, through its repairs to DNA and how it conducts those repairs, can introduce or cause genomic rearrangements and mutations contributing to cancer development.
"It's kind of a double-edged sword," says Anna Malkova, professor in the Department of Biology at the University of Iowa, who has studied ...
2021-01-25
Quantum physics allows to make statements about the behaviour of a wide variety of many-particle systems at the atomic level, from salt crystals to neutron stars. In quantum systems, many parameters do not have concrete values, but are distributed over various values with certain probabilities. Often this distribution takes the form of a simple Gaussian bell curve that is encountered also in classical systems for example the distribution of balls in the Galton box experiment. However, not all quantum systems follow this simple behavior and some might deviate from the Gaussian distribution due to interactions.
Prof. Dr. Jens Eisert, who heads a joint research group on theoretical physics at the Freie Universität Berlin and the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, argues that once interactions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Borderline personality disorder: Don't ignore it
Diagnose it, treat it and teen patients improve