INFORMATION:
Mallampalli reports a financial interest in the compound licensed to the University of Pittsburgh.
This work is support by the American Heart Association; U.S. Department of Health & Human Services; U.S. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; National Institutes of Health and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute; United States Department of Veterans Affairs and Veterans Health Administration.
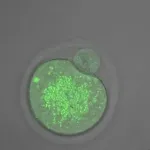
Mouse study identifies novel compound that may help develop diabetes drugs
2021-01-26
(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio - Research led by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine identified a new compound that might serve as a basis for developing a new class of drugs for diabetes.
Study findings are published online in the journal Nature Chemical Biology.
The adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (Ampk) is a crucial enzyme involved in sensing the body's energy stores in cells. Impaired energy metabolism is seen in obesity, which is a risk factor for diabetes. Some medications used to treat diabetes, such as metformin, work by increasing the activity of Ampk.
"In our study, we discovered a protein that is involved in removing Ampk from cells called Fbxo48. We designed and tested a compound termed, BC1618, that blocks Fbxo48 and was much more potent than metformin in increasing Ampk function. BC1618 improved responses to insulin, a measure of effectiveness for diabetes medicines, in obese mice," said Dr. Rama K. Mallampalli, senior author and chair of the department of internal medicine at Ohio State.
Mallampalli began this research at The University of Pittsburgh before joining Ohio State, and continued collaborating with researchers there to complete the study.
"This study builds on our prior research to understand how critical proteins in the body are removed or degraded. The research team had previously designed and produced a family of anti-inflammatory drugs that are FDA approved and are poised to enter Phase 1 studies," Mallampalli said. "Using this new compound as a backbone, our team including Dr. Bill Chen and Dr. Yuan Liu at Pittsburgh will make other compounds that are more potent and safe in animal models and then test them in diabetes animal models. Eventually we aim to obtain FDA approval for human testing."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drug to treat rare genetic disease may help control transmission of African Trypanosomiasis
2021-01-26
African trypanosomiasis (also known as sleeping sickness) is a disease transmitted by tsetse flies and is fatal to humans and other animals; however, there is currently no vaccine, this disease is mainly controlled by reducing insect populations and patient treatment. A study published in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Alvaro Acosta-Serrano at Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine and an international team of researchers suggests that the approved drug nitisinone could be repurposed to kill tsetse flies without harming important pollinator insects.
Currently, the most effective method of controlling the transmission of African trypanosomiasis is by employing insecticide-based vector control campaigns (traps, targets, ...
Compelling evidence of neutrino process opens physics possibilities
2021-01-26
The COHERENT particle physics experiment at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory has firmly established the existence of a new kind of neutrino interaction. Because neutrinos are electrically neutral and interact only weakly with matter, the quest to observe this interaction drove advances in detector technology and has added new information to theories aiming to explain mysteries of the cosmos.
"The neutrino is thought to be at the heart of many open questions about the nature of the universe," said Indiana University physics professor Rex Tayloe. He led the installation, operation and data analysis of a cryogenic liquid argon ...
Study helps understand why kids of obese mothers may be susceptible to metabolic diseases
2021-01-26
A Brazilian study published in the journal Molecular Human Reproduction helps understand why obese mothers tend to have children with a propensity to develop metabolic disease during their lifetime, as suggested by previous research.
According to the authors, "transgenerational transmission of metabolic diseases" may be associated with Mfn2 deficiency in the mother's oocytes (immature eggs). Mfn2 refers to mitofusin-2, a protein involved in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. It is normally found in the outer membrane of mitochondria, ...
Rates of skin cancer have increased dramatically over recent decades
2021-01-26
Incidence rates of skin cancer (cutaneous malignant melanoma) have increased more than 550% in males and 250% in females since the early 1980s in England - according to a new study by Brighton and Sussex Medical School (BSMS).
Published in the new Lancet journal, The Lancet Regional Health - Europe, the study analysed data on more than 265,000 individuals diagnosed with skin cancer in England over the 38-year period, 1981-2018.
Skin cancer is the fifth most common cancer in the UK, with about 16,200 new cases each year.
Excessive exposure to UV radiation from the sun (or sunlight) is the main environmental risk factor for developing skin cancer. It is estimated that about 86% of all skin cancers in the UK are ...
Avoid repeating old mistakes
2021-01-26
Since the founding of the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, member states have regularly agreed on global strategies to bring the increasingly rapid loss of biodiversity to a halt. In 2002, the heads of state adopted the so-called 2010 biodiversity targets. Eight years later, little progress had been made and 20 new, even more ambitious goals were set for the next ten years. Last year, it became clear that this target had been missed, too. The loss of biodiversity continues unabated.
This year, new targets are being negotiated again - this time for 2030. The decisions are to be made at the Conference of the Parties (COP15) in Kunming, China. To ...
For older adults, specific Facebook activities more important than overall use
2021-01-26
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- The actions that older adults take on Facebook may be more important to their user experience and well-being than their overall use of the site, according to researchers.
In a study conducted by a team that included researchers from Penn State, older adults experienced different levels of competence, relatedness and autonomy on Facebook based on the types of their activities on the site.
Specifically, older adults who posted more pictures to Facebook felt more competent, which led to significantly higher levels of well-being in general, ...
'Tri-active' contraceptive gel combines spermicidal, anti-viral, libido-enhancing agents
2021-01-26
Researchers from North Carolina State University have created a trifunctional contraceptive gel that contains spermicidal, anti-viral and libido-enhancing agents in one formulation. When tested in a rat model, the gel both enhanced male libido and prevented pregnancy in 100% of cases, as compared to an average 87% effective rate with a commercially available contraceptive gel.
"We are using three pharmacological agents in a new formulation," says Ke Cheng, Randall B. Terry, Jr. Distinguished Professor in Regenerative Medicine at NC State's College of Veterinary Medicine, professor in the NC State/UNC Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering and corresponding author of a paper describing the work. "Our hope ...
TGen-led study results suggest more accurate diagnostic for breast cancer
2021-01-26
PHOENIX, Ariz. -- Jan. 26, 2021 -- Breast cancer, even at its initial stages, could be detected earlier and more accurately than current techniques using blood samples and a unique proteomics-based technology, according to findings of a study led by the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope.
Patrick Pirrotte, Ph.D., an Assistant Professor and Director of TGen's Collaborative Center for Translational Mass Spectrometry, and an international team of researchers developed a test that can detect infinitesimally small breast cancer biomarkers that are shed into the bloodstream from cells surrounding cancer known as extracellular matrix (ECM), according to the findings of their study recently published in the scientific journal Breast Cancer Research.
For ...
Two anti-viral enzymes transform pre-leukemia stem cells into leukemia
2021-01-26
Since stem cells can continually self-regenerate, making more stem cells, and differentiate into many different specialized cell types, they play an important role in our development and health. But there can also be a dark side -- stem cells can sometimes become cancer stem cells, proliferating out of control and leading to blood cancers, such as leukemia and multiple myeloma. The self-renewing nature of cancer stem cells makes them particularly hard to eradicate, and they're often the reason a blood cancer reoccurs.
Researchers at UC San Diego Health and University of California San Diego School of Medicine are ...
Over half of cannabis users with Parkinson's disease report clinical benefits
2021-01-26
Amsterdam, NL, January 26, 2021 - With medicinal cannabis now legalized in many parts of the world, there is growing interest in its use to alleviate symptoms of many illnesses including Parkinson's disease (PD). According to results of a survey of PD patients in Germany in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease, over 8% of patients with PD reported using cannabis products and more than half of those users (54%) reported a beneficial clinical effect.
Cannabis products containing THC (tetrahydrocannabinol, the main psychoactive compound of cannabis) can be prescribed in Germany when previous therapies are unsuccessful or not tolerated, and where cannabis can be expected with not a very unlikely ...