(Press-News.org) Amsterdam, NL, January 26, 2021 - With medicinal cannabis now legalized in many parts of the world, there is growing interest in its use to alleviate symptoms of many illnesses including Parkinson's disease (PD). According to results of a survey of PD patients in Germany in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease, over 8% of patients with PD reported using cannabis products and more than half of those users (54%) reported a beneficial clinical effect.
Cannabis products containing THC (tetrahydrocannabinol, the main psychoactive compound of cannabis) can be prescribed in Germany when previous therapies are unsuccessful or not tolerated, and where cannabis can be expected with not a very unlikely chance to relieve disabling symptoms. CBD (pure cannabidiol, derived directly from the hemp plant, a cousin of the marijuana plant) is available without a prescription from pharmacies and on the internet.
"Medical cannabis was legally approved in Germany in 2017 when approval was given for therapy-resistant symptoms in severely affected patients independent of diagnosis and without clinical evidence-based data," explained lead investigator Prof. Dr. med. Carsten Buhmann, Department of Neurology, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany. "PD patients fulfilling these criteria are entitled to be prescribed medical cannabis, but there are few data about which type of cannabinoid and which route of administration might be promising for which PD patient and which symptoms. We also lack information about the extent to which the PD community is informed about medicinal cannabis and whether they have tried cannabis and, if so, with what result."
Investigators aimed to assess patient perceptions of medicinal cannabis as well as evaluate the experiences of patients already using cannabis products. They performed a nationwide, cross-sectional, questionnaire-based survey among members of the German Parkinson Association (Deutsche Parkinson Vereinigung e.V.), which is the largest consortium of PD patients in German-speaking countries with nearly 21,000 members. Questionnaires were sent out in April 2019 with the association's membership journal and were also distributed in the investigators' clinic.
Over 1,300 questionnaires were analyzed; results showed that interest in the PD community in medical cannabis was high, but knowledge about different types of products was limited. Fifty-one percent of respondents were aware of the legality of medicinal cannabis, and 28% were aware of the various routes of administration (inhaling versus oral administration), but only 9% were aware of the difference between THC and CBD.
More than 8% of patients were already using cannabinoids and more than half of these users (54%) reported that it had a beneficial clinical effect. The overall tolerability was good. Over 40% of users reported that it helped manage pain and muscle cramps, and more than 20% of users reported a reduction of stiffness (akinesia), freezing, tremor, depression, anxiety, and restless legs. Patients reported that inhaled cannabis products containing THC were more efficient in treating stiffness than oral products containing CBD but were slightly less well tolerated.
Patients using cannabis tended to be younger, living in large cities, and more aware of the legal and clinical aspects of medicinal cannabis. Sixty-five percent of non-users were interested in using medicinal cannabis, but lack of knowledge and fear of side effects were reported as main reasons for not trying it.
"Our data confirm that PD patients have a high interest in treatment with medicinal cannabis but lacked knowledge about how to take it and especially the differences between the two main cannabinoids, THC and CBD," noted Prof. Dr. med. Buhmann. "Physicians should consider these aspects when advising their patients about treatment with medicinal cannabis. The data reported here may help physicians decide which patients could benefit, which symptoms could be addressed, and which type of cannabinoid and route of administration might be suitable."
"Cannabis intake might be related to a placebo effect because of high patient expectations and conditioning, but even that can be considered as a therapeutic effect. It has to be stressed, though, that our findings are based on subjective patient reports and that clinically appropriate studies are urgently needed," he concluded.
Bastiaan R. Bloem, MD, PhD, Director, Radboudumc Center of Expertise for Parkinson & Movement Disorders, Nijmegen, The Netherlands, and Co-Editor-in Chief of the Journal of Parkinson's Disease, added: "These findings are interesting in that they confirm a widespread interest among patients in the use of cannabis as a potential treatment for people living with PD. It is important to emphasize that more research is needed before cannabis can be prescribed as a treatment, and that guidelines currently recommend against the use of cannabis, even as self-medication, because the efficacy is not well established, and because there are safety concerns (adverse effects include among others sedation and hallucinations). As such, the present paper mainly serves to emphasize the need for carefully controlled clinical trials to further establish both the efficacy and safety of cannabis treatment."
INFORMATION:
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Research led by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine found that the widely prescribed pain-relief drug gabapentin can prevent harmful structural changes in the injured spinal cords of mice, and also block cardiovascular changes and immune suppression caused by spinal cord injury.
"Gabapentin is often prescribed as a treatment for pain, but if it is given early after injury - before symptoms develop - it can also limit structural changes in nerve cells. We show that these benefits remain even one month after stopping gabapentin treatment in spinal injured mice. We believe that gabapentin could be repurposed as a prophylactic therapy that can prevent autonomic dysfunction in ...
Nanoparticle is first therapy to trigger this novel way to kill lymphoma cells
Drug is being developed for clinical trials
Drug selectively attacks cancer cells, leaves normal cells unharmed
CHICAGO --- Scientists at Northwestern Medicine have developed a novel therapy to trick cancer cells into gobbling up what they think is their favorite food - cholesterol - which actually triggers their destruction. What appears to them as a cholesterol-loaded particle is actually a synthetic nanoparticle that binds to the cancer cells and starves them to death. ...
A study performed by the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) provided eight recommendations for improving the online technology to help with the treatment and diagnosis of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs). The analysis, presented in a recent open-access publication, was performed by UOC researchers Carme Carrion and Marta Aymerich from the eHealth Lab and Noemí Robles from the eHealth Center, together with José Antonio Ruiz Postigo from the World Health Organization and Oriol Solà de Morales from the Health Innovation Technology Transfer Foundation. In the study, the authors looked at the context of the existing apps and identified their weaknesses.
The ...
Announcing a new publication for BIO Integration journal. In this opinion article the authors Tianhong Yao, Huirong Lin, Jingsong Mao, Shuaidong Huo and Gang Liu from Xiamen University, Xiamen, China discuss CT imaging features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus.
Novel coronavirus pneumonia is an acute, infectious pneumonia caused by a novel coronavirus infection. Computed tomographic (CT) imaging is one of the main methods to screen and diagnose patients with this disease. In this article the authors discuss the importance and clinical value of chest ...
Damage to the brain gray matter plays an important role in the progression of multiple sclerosis. This study now shows that such damage can be caused by inflammatory reactions that lead to loss of synapses, which impairs neural activity.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the central nervous system, in which nerve cells are attacked by the patient's own immune system. In many cases, the disease develops into a progressive form, which is characterized by a shift of pathology from the white matter to the gray matter, ...
Every year, more than 400,000 people die from malaria, the majority are children under the age of five years old, who die from a disease which affects more than 200 million people a year.
The most serious form of the disease is cerebral malaria which may cause severe neurological consequences and, in the worst-case scenario, result in death. The precise mechanism behind cerebral malaria has remained a mystery - until now, says a research group from the Department of Immunology and Microbiology at the University of Copenhagen.
'In our study, we show that a certain type of the malaria parasite can cross the blood-brain barrier by utilising ...
Mangrove ecosystems are at particular risk of being polluted by plastic carried from rivers to the sea. Fifty-four per cent of mangrove habitat is within 20 km of a river that discharges more than a tonne of plastic waste a year into the ocean, according to a new paper published in the journal Science of the Total Environment. Mangroves in southeast Asia are especially threatened by river-borne plastic pollution, the researchers found.
The paper, written by scientists at GRID-Arendal and the University of Bergen, is the first global assessment of coastal environments' exposure to river-borne plastic pollution. The majority of plastic waste carried to sea by rivers ends up trapped along coastlines, but some types ...
FORT LAUDERDALE/DAVIE, Fla. - Global warming or climate change. It doesn't matter what you call it. What matters is that right now it is having a direct and dramatic effect on marine environments across our planet.
"More immediately pressing than future climate change is the increasing frequency and severity of extreme 'underwater heatwaves' that we are already seeing around the world today," Lauren Nadler, Ph.D., who is an assistant professor in Nova Southeastern University's (NSU) Halmos College of Arts and Sciences . "This phenomenon is what we wanted to both simulate and understand."
Nadler is a co-author of a new study on this topic, which you can find published online ...
Scientists have designed a single-dose universal vaccine that could protect against the many forms of leptospirosis bacteria, according to a study published today in eLife.
An effective vaccine would help prevent the life-threatening conditions caused by leptospirosis, such as Weil's disease and lung haemorrhage, which are fatal in 10% and 50% of cases, respectively.
Leptospirosis is caused by a diverse group of spirochetes called leptospires. A broad range of mammals, including rats, harbour the bacteria in their kidneys and release them into the environment through their urine. Humans and animals can then get infected after coming into contact with contaminated water or soil. In addition to having a major impact on the health of vulnerable human populations, ...
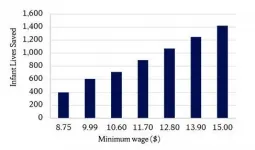
Syracuse, N.Y. - As President Joe Biden seeks to raise the federal minimum wage, a new study published recently by researchers from Syracuse University shows that a higher minimum wage will reduce infant deaths.
In the study, "Effects of US state preemption laws on infant mortality," Syracuse University professors found that each additional dollar of minimum wage reduces infant deaths by up to 1.8 percent annually in large U.S. cities. The study was published recently by Preventive Medicine.
The federal minimum wage has not been increased since 2009, and Biden's $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan to aid those hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic calls for Congress to raise the minimum wage from $7.25 ...