Cholesterol starvation kills lymphoma cells
How new experimental drug could work in other cancers with an appetite for cholesterol
2021-01-26
(Press-News.org) Nanoparticle is first therapy to trigger this novel way to kill lymphoma cells
Drug is being developed for clinical trials
Drug selectively attacks cancer cells, leaves normal cells unharmed
CHICAGO --- Scientists at Northwestern Medicine have developed a novel therapy to trick cancer cells into gobbling up what they think is their favorite food - cholesterol - which actually triggers their destruction. What appears to them as a cholesterol-loaded particle is actually a synthetic nanoparticle that binds to the cancer cells and starves them to death.
Although the research looked at lymphoma cells, scientists say the new experimental drug from Northwestern could be effective in other cancers with a similar appetite for cholesterol, such as kidney and ovarian cancer.
The study was published this month in the Journal of Biological Chemistry and builds upon prior work published by the group.
"Our ability to identify the novel mechanism of cell death gets us closer to translation to the bedside, where we can use this approach in patients with lymphoma who are not responding to more standard therapy," said co-corresponding author Dr. Leo I. Gordon, the Abby and John Friend Professor of Cancer Research at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a Northwestern Medicine physician. "These data also provide a rationale to extend these observations to other cholesterol-addicted cancers, such as ovarian and kidney cancer."
This new therapy may work because the scientists also demonstrated cholesterol metabolism is quite different in target cancer cells from that of normal cells. That enables the experimental drug to selectively attack and kill vulnerable cancer cells while leaving normal cells unharmed.
New therapies are urgently needed to treat up to 40% of lymphomas that are aggressive and do not respond to current therapies. Also, SCARB1, the target of the drug which is involved in keeping cholesterol balanced in the cell, is present on other cancer cells that share the same appetite for cholesterol.
"Our therapy targets cancer cells that are dependent upon cholesterol uptake and perturbs the overall balance of cholesterol in the cell," said co-corresponding author Dr. C. Shad Thaxton, an associate professor of urology at Northwestern. "We discovered the cell tries to compensate by turning off pathways it requires to stay alive. We hope that this novel mechanism may be a blueprint for targeting other types of cancer."
The synthetic biologic nanoparticle therapy is the first of its kind to target cancer cells, specifically modulate cell cholesterol metabolism, and then trigger this novel way to kill cells. In addition, the scientists show the drug is not toxic to normal cells that do not harbor the same disruptions in cholesterol metabolism as the cancer cells do.
For the study, Northwestern scientists demonstrated the efficacy of the experimental drug and how it works in human cancer cell models, in animal models and in cancer cells obtained from patients with lymphoma.
The group will continue development of the drug so they can apply to begin Phase I clinical trials in patients. They also initiated a process of scaling up production of the drug to conduct studies in larger animals.
INFORMATION:
Gordon and Thaxton also are members of the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University.
Other Northwestern authors include Jonathan S. Rink, Adam Yuh Lin, Kaylin M. McMahon, Andrea E. Calvert, Shuo Yang, Tim Taxter, Jonathan Moreira, Amir Behdad and Reem Karmali.
Thaxton, Gordon and McMahon are cofounders of a biotechnology company that licensed the HDL nanoparticle technology from Northwestern University.
This work was in part supported by grant T32HL094293 from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, grant R01CA167041 from the National Cancer Institute, both of the National Institutes of Health, and a Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center Support Grant.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-26
A study performed by the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) provided eight recommendations for improving the online technology to help with the treatment and diagnosis of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs). The analysis, presented in a recent open-access publication, was performed by UOC researchers Carme Carrion and Marta Aymerich from the eHealth Lab and Noemí Robles from the eHealth Center, together with José Antonio Ruiz Postigo from the World Health Organization and Oriol Solà de Morales from the Health Innovation Technology Transfer Foundation. In the study, the authors looked at the context of the existing apps and identified their weaknesses.
The ...
2021-01-26
Announcing a new publication for BIO Integration journal. In this opinion article the authors Tianhong Yao, Huirong Lin, Jingsong Mao, Shuaidong Huo and Gang Liu from Xiamen University, Xiamen, China discuss CT imaging features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus.
Novel coronavirus pneumonia is an acute, infectious pneumonia caused by a novel coronavirus infection. Computed tomographic (CT) imaging is one of the main methods to screen and diagnose patients with this disease. In this article the authors discuss the importance and clinical value of chest ...
2021-01-26
Damage to the brain gray matter plays an important role in the progression of multiple sclerosis. This study now shows that such damage can be caused by inflammatory reactions that lead to loss of synapses, which impairs neural activity.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the central nervous system, in which nerve cells are attacked by the patient's own immune system. In many cases, the disease develops into a progressive form, which is characterized by a shift of pathology from the white matter to the gray matter, ...
2021-01-26
Every year, more than 400,000 people die from malaria, the majority are children under the age of five years old, who die from a disease which affects more than 200 million people a year.
The most serious form of the disease is cerebral malaria which may cause severe neurological consequences and, in the worst-case scenario, result in death. The precise mechanism behind cerebral malaria has remained a mystery - until now, says a research group from the Department of Immunology and Microbiology at the University of Copenhagen.
'In our study, we show that a certain type of the malaria parasite can cross the blood-brain barrier by utilising ...
2021-01-26
Mangrove ecosystems are at particular risk of being polluted by plastic carried from rivers to the sea. Fifty-four per cent of mangrove habitat is within 20 km of a river that discharges more than a tonne of plastic waste a year into the ocean, according to a new paper published in the journal Science of the Total Environment. Mangroves in southeast Asia are especially threatened by river-borne plastic pollution, the researchers found.
The paper, written by scientists at GRID-Arendal and the University of Bergen, is the first global assessment of coastal environments' exposure to river-borne plastic pollution. The majority of plastic waste carried to sea by rivers ends up trapped along coastlines, but some types ...
2021-01-26
FORT LAUDERDALE/DAVIE, Fla. - Global warming or climate change. It doesn't matter what you call it. What matters is that right now it is having a direct and dramatic effect on marine environments across our planet.
"More immediately pressing than future climate change is the increasing frequency and severity of extreme 'underwater heatwaves' that we are already seeing around the world today," Lauren Nadler, Ph.D., who is an assistant professor in Nova Southeastern University's (NSU) Halmos College of Arts and Sciences . "This phenomenon is what we wanted to both simulate and understand."
Nadler is a co-author of a new study on this topic, which you can find published online ...
2021-01-26
Scientists have designed a single-dose universal vaccine that could protect against the many forms of leptospirosis bacteria, according to a study published today in eLife.
An effective vaccine would help prevent the life-threatening conditions caused by leptospirosis, such as Weil's disease and lung haemorrhage, which are fatal in 10% and 50% of cases, respectively.
Leptospirosis is caused by a diverse group of spirochetes called leptospires. A broad range of mammals, including rats, harbour the bacteria in their kidneys and release them into the environment through their urine. Humans and animals can then get infected after coming into contact with contaminated water or soil. In addition to having a major impact on the health of vulnerable human populations, ...
2021-01-26
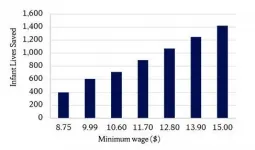
Syracuse, N.Y. - As President Joe Biden seeks to raise the federal minimum wage, a new study published recently by researchers from Syracuse University shows that a higher minimum wage will reduce infant deaths.
In the study, "Effects of US state preemption laws on infant mortality," Syracuse University professors found that each additional dollar of minimum wage reduces infant deaths by up to 1.8 percent annually in large U.S. cities. The study was published recently by Preventive Medicine.
The federal minimum wage has not been increased since 2009, and Biden's $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan to aid those hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic calls for Congress to raise the minimum wage from $7.25 ...
2021-01-26
CAMBRIDGE, MD (January 26, 2021)--The Chesapeake Bay has a long history of nutrient pollution resulting in degraded water quality. However, scientists from the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science are reporting some improvements in the Choptank River on Maryland's Eastern Shore.
The Choptank is a tributary of Chesapeake Bay, and its watershed lies primarily in the state of Maryland, with a portion in Delaware. There are strong similarities between the Choptank basin and the Chesapeake as a whole, which enables the Choptank to be used as a model for progress in the Bay.
The Chesapeake Bay is an estuary which has undergone considerable ...
2021-01-26
Researchers from McGill University have discovered, for the first time, one of the possible mechanisms that contributes to the ability of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) to increase social interaction. The findings, which could help unlock potential therapeutic applications in treating certain psychiatric diseases, including anxiety and alcohol use disorders, are published in the journal PNAS.
Psychedelic drugs, including LSD, were popular in the 1970s and have been gaining popularity over the past decade, with reports of young professionals claiming to regularly take small non-hallucinogenic micro-doses of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cholesterol starvation kills lymphoma cells
How new experimental drug could work in other cancers with an appetite for cholesterol