(Press-News.org) The overuse of antibiotics occurs due to the mistaken widespread belief that they are beneficial for a broad array of conditions and because many physicians are willing to prescribe antibiotics if patients ask for the medication, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in the journal BioEssays, reviewed more than 200 peer-reviewed studies to examine the causes behind antibiotic overuse, which can lead harmful bacteria to become drug-resistant and cause harmful effects on the microbiome, the collection of beneficial germs that live in and on our bodies.
Martin Blaser, director of the Center for Advanced Biotechnology and Medicine at Rutgers and lead author, said the global use of antibiotics between 2000 and 2015 increased 39 percent, with a 77 percent increase in low- and middle-income countries. He discusses the study's findings.
What health concerns result from the disruption of the microbiome by antibiotics?
In children, improper antibiotic use can alter the microbiome while their immunological, metabolic and neural systems are developing. Epidemiological studies associate antibiotic exposure with an increased risk of disease of allergic, metabolic and cognitive disorders that have grown more common in children during the antibiotic era.
In adults, there is increasing evidence that antibiotics may enhance risk for metabolic and neoplastic diseases, including diabetes, kidney stones and growths in the colon and rectum that can lead to cancer.
What are the trends you found in antibiotic use?
Studies in the United States, United Kingdom and China found numerous online pharmacies selling antibiotics without a prescription. This problem also is large in Iow- to middle-income countries, where 60 percent of antibiotics are sold without prescriptions, often by untrained medical practitioners.
Perhaps of special concern during the COVID-19 pandemic is the finding that telemedicine services are another potential source of questionable antibiotic sales in the United States. A recent analysis found that patients with acute respiratory infections were more often prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics if they had a tele-health doctor visit, compared to an in-person visit.
Worldwide, antibiotic use is highest in young children, especially in low-income areas. This is often in response to the fact that young children are prone to have four to six upper respiratory tract infections each year. Although most of these infections are treated by antibiotics, 80 percent are not caused by bacteria and would therefore derive no benefit from antibiotics.
Are some practitioners more likely to prescribe antibiotics?
Our findings are consistent with the hypothesis that older physicians are more likely than their younger colleagues to prescribe antibiotics. For example, one study found that physicians over 30 were several times more likely to prescribe antibiotics for common respiratory conditions that do not necessarily require them. Another study found that physicians with over 25 years in practice were disproportionately likely to issue prescriptions of more than eight days.
What misinformation did you find among the public?
Many people believe that antibiotics are effective against bacterial and viral illnesses, lumping all types of pathogens together and adopting a "germs are germs" attitude. Others believe that taking antibiotics can't hurt. Across Europe, for example, 57 percent of people surveyed were unaware that antibiotics were ineffective against viruses, and 44 percent did not know that antibiotics have no effect against colds or influenza.
What other reasons did you find for inappropriate prescription of antibiotics?
Antibiotics are commonly used across the world to self-treat health problems for which they were never intended, such as in Nigeria, where women are increasingly using antibiotics to reduce menstrual cramps. In low- to middle-income countries, antibiotics are often seen as strong, magical medicines, capable of both curing and preventing a range of illness. In many countries people also take them to return to work or school when ill. One of the studies found that 63 percent of Chinese university students kept a personal antibiotic stock at home.
Parents may appeal for an antibiotic for their children so that they can go to work or for the children to return to school or daycare. A U.S. study found that 43 percent of parents of a child with cold symptoms believed that antibiotics were necessary.
In addition, some doctors are inclined to prescribe an antibiotic to maintain a good relationship with patients who expect to receive medication. Patients may not demand antibiotics outright, but rather infer their need for them by how they describe the severity of their illness or note that they worked in the past for a similar issue. People have become less willing to wait and let an illness run its course. The perception that there is a pill for ills of all kinds leads the public to demand immediate relief for symptoms from practitioners and to self-medicate.
Every time an antibiotic is given, money changes hands. This is especially a problem in low- and middle-income countries, where pharmacists are happy to dispense without a prescription to their customers. The rural health practitioners in China are paid every time they dispense an antibiotic as well. Such monetary incentives favor the wide use of antibiotics.
How can antibiotic overuse be addressed?
Clinicians need to be better educated about the long-term effects on the microbiome and learn about better ways to speak with their patients about antibiotic risks and benefits. They also need to improve their communication about the consequences of antibiotic treatments and identify antibiotic alternatives.
INFORMATION:
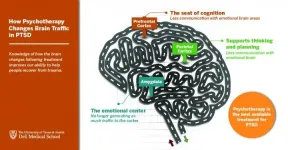
p>AUSTIN, Texas -- Trauma-focused psychotherapy is widely considered the best available treatment for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). However, the ways in which this method affects the brain to promote recovery from PTSD are not well understood. In a END ...
A research group from Kumamoto University (Japan) has developed an automated measurement system to assess healthy lifespans using nematodes (C. elegans). Based on qualitative differences in lifespans, this system can classify populations of nematodes that are, on average, healthy and long-lived, healthy and die prematurely, and living with long periods of poor health. Since there are many similarities between the mechanisms that determine the lifespan of C. elegans and humans, the researchers believe that this system will make it easier to develop drugs and find foods that extend the ...
A tree grows strong from years of generating its own food. Now imagine if products could be strengthened with the same living materials that provide nutrients to strengthen trees. This is the work of USC Viterbi School of Engineering Civil and Environmental Engineering Professor Qiming Wang whose research lab is one of the first to infuse 3-D printer ink with living material. The material has potential for greater strength, to be flexible and self-heal. The work is documented in a paper published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The idea for this bio-inspired ink came from trees that harness the power of photosynthesis to produce glucose that transform to ...
In our body, unnecessary cells are removed by regulated cell death. Understanding of the mechanism underlying regulated cell death is critical for the development of therapies for many diseases. Professor Nakano's research group has demonstrated that Mind bomb-2 (MIB2), a ubiquitin ligase, binds to and directly ubiquitinates the cell death suppressor protein cFLIP (Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein). cFLIP is encoded by CFLAR gene; alternative splicing results in two forms, the long form (cFLIPL) and the short form (cFLIPs). cFLIPL plays a dominant role in suppression ...
January 27, 2021 - For many of us, as we get older the skin on our face begins to sag and we seem to lose volume around our eyes, cheeks and chin. Is gravity taking its toll in our later years or do we lose fat over the course of several years that many of us associate with youth, vibrancy and energy? Understanding the cause is paramount to how plastic surgeons treat the signs of facial aging.
The traditional theory is sagging: the facial soft tissues simply yield to the effects of gravity over time. And while the idea that weakening ligaments in the midface could result in soft tissue descent still has merit, more recent studies point in another direction. Perhaps the real culprit behind facial aging ...
Speaking is something that comes across as an effortless process, almost working by itself. Our brain, however, has a lot of work to do when we construct a sentence. "In addition, languages differ in myriad ways and this also means that there are differences in how we plan what we want to say in different languages," says Balthasar Bickel, senior author of the study and a professor at the University of Zurich.
And if some languages seem easier, it is because they make fewer distinctions in their grammar. While English always uses the (e.g., in "The tree is tall" and "Snow covers the tree"), German makes a distinction between der (subject) and den (object) (e.g., in "Der Baum ist groß" and ...
A fifth basic flavour has crept into our conceptualisation of foods in recent years--umami. In Japanese, umami translates roughly to 'savoury deliciousness'.
It is often associated with the earthy flavours of meat, mushrooms, broths and vine-ripened tomatoes. It enhances saltiness and sweetness, while reducing bitterness, which is why most people love it.
But does umami exist in beverages? And if so, which fermented beverage has the most umami potential: wine, beer, sake or champagne? And, what happens to flavours when these beverages are paired with foods?
Three researchers from the University of Copenhagen's ...
Researchers from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKSUST) and the University of Hong Kong (HKU) recently demonstrated that the selectivity determinant of Origin Recognition Complex (ORC) for DNA binding lies in a 19-amino acid insertion helix in the Orc4 subunit, which is present in yeast but absent in human. Removal of this motif from Orc4 transforms the yeast ORC, which selects origins based on base-specific binding at defined locations, into one whose selectivity is dictated by chromatin landscape (genomic nucleosome profile), a characteristic feature shared by human ORC.
Further understanding of the preferred DNA shapes and nucleosome positioning requirements will provide new insights for the plasticity of the human ORC in selecting replication ...
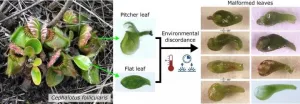
Plants and other organisms can adapt their phenotypes to fluctuating environmental conditions within certain limits. The leaves of the dandelion, for example, are much more small in sunny locations than in shady places. In the sun, less leaf area is adequate to drive sufficient photosynthesis. This makes sense and is part of the dandelion's genetic programming.
However, plants can deviate from their normal programming if they are under constant heat stress or other extreme factors that endanger their survival. They then develop, for example, a wide range of leaf shapes that are extremely rare under natural conditions. In this case, scientists ...
Contracting COVID-19 while pregnant can have deadly consequences for the mother, a new study published today in END ...