Deep-sea plastic accumulations by turbidity currents: NW South China sea
New study published in Geology
2021-01-27
(Press-News.org) Boulder, Colo., USA: Benthic plastic litter is a main source of pollutants in oceans, but how it disperses is largely unknown. This study by Guangfa Zhong and Xiaotong Peng, published today in Geology, presents novel findings on the distribution patterns and dispersion mechanisms of deep-sea plastic waste in a submarined canyon located in the northwestern South China Sea.
Evidence collected from a series of manned submersible dives indicate that the plastic litter items transported and deposited in the canyon are most likely controlled by turbidity currents. Here the plastic litter items are highly heterogeneously distributed: Up to 89% of them occur in a few scours of the canyon.
The plastic items are mostly accumulated in longitudinal litter piles of 2-61 m long, 0.5-8 m wide, and 0.1-1.2 m high on average (Figures 1 and 2). Plastic particles and fragments generally occurred on the upstream-facing sides of large boulders and other topographic obstacles, indicating obstruction during down-valley transportation (Figure 1). Furthermore, the litter piles were mostly distributed in the up-valley dipping slopes downstream of the scour centers (Figure 3), which is tentatively linked to the deceleration of turbidity currents after shedding down the steep upstream slopes of the scours and undergoing a hydraulic jump at the scour centers. This interpretation is supported by the sedimentological evidence from grain-size analysis of associated seabed sediment.
The results of this study lend support to the hypothesis of turbidity-current-controlled dispersion of plastic litter and bear implications on deep-sea environmental protection and surveillance. The focused and patterned distribution of benthic plastics in the canyon that can be reasonably explained by morphodynamic interactions sheds light on monitoring or even removal of deep-sea macro-plastic pollutants.
INFORMATION:
FEATURED ARTICLE
Transport and accumulation of plastic litter in submarine canyons--The role of gravity flows
Guangfa Zhong; Xiaotong Peng
Contact: gfz@tongji.edu.cn, State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology, Tongji University, School of Ocean and Earth Science, Shanghai
Article URL: https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article/doi/10.1130/G48536.1/594238/Transport-and-accumulation-of-plastic-litter-in
GEOLOGY articles are online at http://geology.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent. Representatives of the media may obtain complimentary articles by contacting Kea Giles kgiles@geosociety.org. Please discuss articles of interest with the authors before publishing stories on their work, and please make reference to GEOLOGY in articles published. Non-media requests for articles may be directed to GSA Sales and Service, gsaservice@geosociety.org.
https://www.geosociety.org
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-27
JANUARY 26, 2021, NEW YORK - A study led by Ludwig Chicago Co-director Ralph Weichselbaum and Yang-Xin Fu of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center has shown how bacteria in the gut can dull the efficacy of radiotherapy, a treatment received by about half of all cancer patients. Their findings appear in the current issue of the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
"Our study identifies two families of gut bacteria that interfere with radiotherapy in mice and describes the mechanism by which a metabolite they produce--a short chain fatty acid called butyrate--undermines the therapy," said Weichselbaum.
A wide variety of commensal bacteria inhabit ...
2021-01-27
Birds play an underrecognized role in spreading tickborne disease due to their capacity for long-distance travel and tendency to split their time in different parts of the world - patterns that are shifting due to climate change. Knowing which bird species are able to infect ticks with pathogens can help scientists predict where tickborne diseases might emerge and pose a health risk to people.
A new study published in the journal Global Ecology and Biogeography used machine learning to identify bird species with the potential to transmit the Lyme disease bacterium (Borrelia burgdorferi) to feeding ticks. The team developed a model that identified birds known to spread Lyme disease with 80% accuracy and flagged 21 new species that should be prioritized for surveillance.
Lead author Daniel ...
2021-01-27
The rapid development of two-dimensional quantum materials, such as twisted bilayer graphene, monolayer copper superconductors, and quantum spin Hall materials, has demonstrated both important scientific implications and promising application potential. To characterize the electronic structure of these materials/devices, angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) is commonly used to measure the energy and momentum of electrons photoemitted from samples illuminated by X-ray or vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light sources. Although the X-ray-based spatially resolved ARPES has the highest spatial resolution (~100 nm) benefitting from the relatively short wavelength, its energy resolution is typically mediocre (>10 meV), ...
2021-01-27
The overuse of antibiotics occurs due to the mistaken widespread belief that they are beneficial for a broad array of conditions and because many physicians are willing to prescribe antibiotics if patients ask for the medication, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in the journal BioEssays, reviewed more than 200 peer-reviewed studies to examine the causes behind antibiotic overuse, which can lead harmful bacteria to become drug-resistant and cause harmful effects on the microbiome, the collection of beneficial germs that live in and on our bodies.
Martin Blaser, director of the Center for Advanced Biotechnology and Medicine at Rutgers and lead author, said the global use of antibiotics between 2000 and 2015 increased 39 percent, with ...
2021-01-27
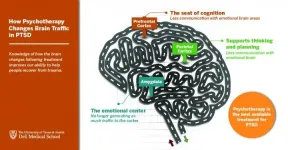
p>AUSTIN, Texas -- Trauma-focused psychotherapy is widely considered the best available treatment for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). However, the ways in which this method affects the brain to promote recovery from PTSD are not well understood. In a END ...
2021-01-27
A research group from Kumamoto University (Japan) has developed an automated measurement system to assess healthy lifespans using nematodes (C. elegans). Based on qualitative differences in lifespans, this system can classify populations of nematodes that are, on average, healthy and long-lived, healthy and die prematurely, and living with long periods of poor health. Since there are many similarities between the mechanisms that determine the lifespan of C. elegans and humans, the researchers believe that this system will make it easier to develop drugs and find foods that extend the ...
2021-01-27
A tree grows strong from years of generating its own food. Now imagine if products could be strengthened with the same living materials that provide nutrients to strengthen trees. This is the work of USC Viterbi School of Engineering Civil and Environmental Engineering Professor Qiming Wang whose research lab is one of the first to infuse 3-D printer ink with living material. The material has potential for greater strength, to be flexible and self-heal. The work is documented in a paper published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The idea for this bio-inspired ink came from trees that harness the power of photosynthesis to produce glucose that transform to ...
2021-01-27
In our body, unnecessary cells are removed by regulated cell death. Understanding of the mechanism underlying regulated cell death is critical for the development of therapies for many diseases. Professor Nakano's research group has demonstrated that Mind bomb-2 (MIB2), a ubiquitin ligase, binds to and directly ubiquitinates the cell death suppressor protein cFLIP (Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein). cFLIP is encoded by CFLAR gene; alternative splicing results in two forms, the long form (cFLIPL) and the short form (cFLIPs). cFLIPL plays a dominant role in suppression ...
2021-01-27
January 27, 2021 - For many of us, as we get older the skin on our face begins to sag and we seem to lose volume around our eyes, cheeks and chin. Is gravity taking its toll in our later years or do we lose fat over the course of several years that many of us associate with youth, vibrancy and energy? Understanding the cause is paramount to how plastic surgeons treat the signs of facial aging.
The traditional theory is sagging: the facial soft tissues simply yield to the effects of gravity over time. And while the idea that weakening ligaments in the midface could result in soft tissue descent still has merit, more recent studies point in another direction. Perhaps the real culprit behind facial aging ...
2021-01-27
Speaking is something that comes across as an effortless process, almost working by itself. Our brain, however, has a lot of work to do when we construct a sentence. "In addition, languages differ in myriad ways and this also means that there are differences in how we plan what we want to say in different languages," says Balthasar Bickel, senior author of the study and a professor at the University of Zurich.
And if some languages seem easier, it is because they make fewer distinctions in their grammar. While English always uses the (e.g., in "The tree is tall" and "Snow covers the tree"), German makes a distinction between der (subject) and den (object) (e.g., in "Der Baum ist groß" and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Deep-sea plastic accumulations by turbidity currents: NW South China sea
New study published in Geology