(Press-News.org) More effective antiviral treatments could be on the way after research from The University of Texas at Austin sheds new light on the COVID-19 antiviral drug remdesivir, the only treatment of its kind currently approved in the U.S. for the coronavirus.
The study is END
Scientists discover how remdesivir works to inhibit coronavirus
2021-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Transportation investments could save hundreds of lives, billions of dollars
2021-01-28
BOSTON - Investments in infrastructure to promote bicycling and walking could save as many as 770 lives and $7.6 billion each year across 12 northeastern states and the District of Columbia under the proposed Transportation and Climate Initiative (TCI), according to a new Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health study.
Published in the Journal of Urban Health, the analysis shows that the monetary benefit of lives saved from increased walking and cycling far exceed the estimated annual investment for such infrastructure, without ...
Malaria threw human evolution into overdrive on this African archipelago
2021-01-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- Malaria is an ancient scourge, but it's still leaving its mark on the human genome. And now, researchers have uncovered recent traces of adaptation to malaria in the DNA of people from Cabo Verde, an island nation off the African coast.
An archipelago of ten islands in the Atlantic Ocean some 385 miles offshore from Senegal, Cabo Verde was uninhabited until the mid-1400s, when it was colonized by Portuguese sailors who brought enslaved Africans with them and forced them to work the land.
The Africans who were forcibly brought to Cabo Verde carried ...
Scientists find key function of molecule in cells crucial for regulating immunity
2021-01-28
CHAPEL HILL, NC - Many molecules in our bodies help our immune system keep us healthy without overreacting so much that our immune cells cause problems, such as autoimmune diseases. One molecule, called AIM2, is part of our innate immunity - a defense system established since birth - to fight pathogens and keep us healthy. But little was known about AIM2's contribution to T cell adaptive immunity - defenses developed in response to particular pathogens and health problems we develop over the course of our lives.
Now, UNC School of Medicine scientists led by Jenny Ting, PhD, the William Kenan Distinguished Professor of Genetics, and Yisong Wan, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology, discovered that AIM2 is important for the proper function of regulatory ...
'Be a man': Why some men respond aggressively to threats to manhood
2021-01-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- When their manhood is threatened, some men respond aggressively, but not all. New research from Duke University suggests who may be most triggered by such threats - younger men whose sense of masculinity depends heavily on other people's opinions.
"Our results suggest that the more social pressure a man feels to be masculine, the more aggressive he may be," said Adam Stanaland, a Ph.D. candidate in psychology and public policy at Duke and the study's lead author.
"When those men feel they are not living up to strict gender norms, they may feel the need to act aggressively to prove their manhood -- to 'be a man'."
The pair of studies considered 195 undergraduate students and a random pool of 391 men ages 18 to 56.
Study participants were asked a series ...
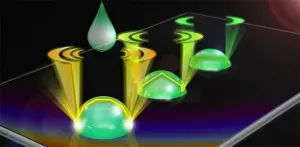
Lasing mechanism found in water droplets
2021-01-28
Tiny molecular forces at the surface of water droplets can play a big role in laser output emissions. As the most fundamental matrix of life, water drives numerous essential biological activities, through interactions with biomolecules and organisms. Studying the mechanical effects of water-involved interactions contributes to the understanding of biochemical processes. According to Yu-Cheng Chen, professor of electronic engineering at Nanyang Technological University (NTU), "As water interacts with a surface, the hydrophobicity at the bio-interface mainly determines the mechanical equilibrium ...
Thick lithosphere casts doubt on plate tectonics in Venus's geologically recent past
2021-01-28
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- At some point between 300 million and 1 billion years ago, a large cosmic object smashed into the planet Venus, leaving a crater more than 170 miles in diameter. A team of Brown University researchers has used that ancient impact scar to explore the possibility that Venus once had Earth-like plate tectonics.
For a study published in Nature Astronomy, the researchers used computer models to recreate the impact that carved out Mead crater, Venus's largest impact basin. Mead is surrounded by two clifflike faults -- rocky ripples frozen in time after the basin-forming impact. The models showed that for those rings to be where they ...
Post-overdose outreach programs in Massachusetts expanding
2021-01-28
BOSTON-Boston Medical Center has released a study that shows post overdose outreach programs in Massachusetts have expanded across the state, as 44 percent of municipalities reported having such programs available - a majority established since 2015 - to reduce risks for those who survive an overdose. The results are published online in the February 2021 issue of Drug and Alcohol Dependence.
These post-overdose outreach programs leverage collaborations between public health overdose prevention practitioners and public safety organizations (police, fire, EMS) to engage overdose survivors and/or their social networks (family, friends, and acquaintances) at their home one to three days after an overdose. ...
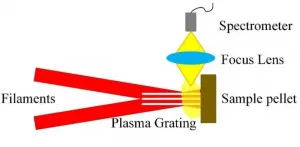
Breakthrough for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
2021-01-28
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a rapid chemical analysis tool. A powerful laser pulse is focused on a sample to create a microplasma. The elemental or molecular emission spectra from that microplasma can be used to determine the elemental composition of the sample.
Compared with more traditional technology, like atomic absorption spectroscopy and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES), LIBS has some unique advantages: no sample pretreatment, simultaneous multi-element detection, and real-time noncontact measurements. These advantages make it suitable for practical analysis of solids, gases, and liquids.
Traditional LIBS and extensions
Traditional ...
Harnessing the power of AI to understand warm dense matter
2021-01-28
The study of warm dense matter helps us understand what is going on inside giant planets, brown dwarfs, and neutron stars. However, this state of matter, which exhibits properties of both solids and plasmas, does not occur naturally on Earth. It can be produced artificially in the lab using large X-ray experiments, albeit only at a small scale and for short periods of time. Theoretical and numerical models are essential to evaluate these experiments, which are impossible to interpret without formulas, algorithms, and simulations. Scientists at the Center for Advanced Systems Understanding (CASUS) at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) have now developed a method to evaluate such ...
National laboratories' look to the future of light sources with new magnet prototype
2021-01-28
With a powerful enough light, you can see things that people once thought would be impossible. Large-scale light source facilities generate that powerful light, and scientists use it to create more durable materials, build more efficient batteries and computers, and learn more about the natural world.
When it comes to building these massive facilities, space is money. If you can get higher-energy beams of light out of smaller devices, you can save millions on construction costs. Add to that the chance to significantly improve the capabilities of existing light sources, and you have the motivation behind a project that has brought scientists at three U.S. Department of Energy national laboratories together.
This team has just achieved an important milestone ...