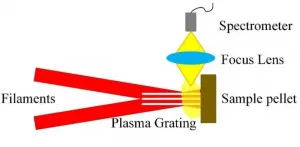
(Press-News.org) Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a rapid chemical analysis tool. A powerful laser pulse is focused on a sample to create a microplasma. The elemental or molecular emission spectra from that microplasma can be used to determine the elemental composition of the sample.
Compared with more traditional technology, like atomic absorption spectroscopy and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES), LIBS has some unique advantages: no sample pretreatment, simultaneous multi-element detection, and real-time noncontact measurements. These advantages make it suitable for practical analysis of solids, gases, and liquids.
Traditional LIBS and extensions
Traditional LIBS systems based on a nanosecond pulse laser (ns-LIBS) have some disadvantages due to laser power intensity, long pulse duration, and the plasma shielding effect. These issues adversely affect its reproducibility and signal-to-noise ratio. Femtosecond LIBS (fs-LIBS) can exclude the plasma shielding effect since the ultrashort pulse duration limits the laser-matter interaction time. The femtosecond pulse has a high power density so materials can be effectively ionized and dissociated, leading to a higher signal-to-background ratio and more precise spectral resolution.
Filament-induced breakdown spectroscopy (FIBS) combines the LIBS technique with a femtosecond laser filament. A single laser filament results from the interplay between the Kerr self-focusing and plasma defocusing mechanisms present in the propagation of an ultrashort, high-intensity beam in a transparent medium such as atmospheric air. The femtosecond laser filament produces a long and stable laser plasma channel, which guarantees the stability of the laser power density and can improve measurement stability. However, the power and electron densities saturate when the laser energy increases. This is known as laser intensity clamping effect, and it limits the detection sensitivity of FIBS.
Plasma grating
Fortunately, the laser intensity clamping effect can be overcome through a plasma grating induced by the nonlinear interaction of multiple femtosecond filaments. The electron density in the plasma grating has been proven to be an order of magnitude higher than that in a filament.
Based on that insight, researchers under the leadership of Heping Zeng at East China Normal University in Shanghai END
Breakthrough for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
Overcoming limitations inherent in other LIBS techniques, plasma-grating-induced breakdown spectroscopy enhances signal intensity by more than three times
2021-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Harnessing the power of AI to understand warm dense matter
2021-01-28
The study of warm dense matter helps us understand what is going on inside giant planets, brown dwarfs, and neutron stars. However, this state of matter, which exhibits properties of both solids and plasmas, does not occur naturally on Earth. It can be produced artificially in the lab using large X-ray experiments, albeit only at a small scale and for short periods of time. Theoretical and numerical models are essential to evaluate these experiments, which are impossible to interpret without formulas, algorithms, and simulations. Scientists at the Center for Advanced Systems Understanding (CASUS) at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) have now developed a method to evaluate such ...
National laboratories' look to the future of light sources with new magnet prototype
2021-01-28
With a powerful enough light, you can see things that people once thought would be impossible. Large-scale light source facilities generate that powerful light, and scientists use it to create more durable materials, build more efficient batteries and computers, and learn more about the natural world.
When it comes to building these massive facilities, space is money. If you can get higher-energy beams of light out of smaller devices, you can save millions on construction costs. Add to that the chance to significantly improve the capabilities of existing light sources, and you have the motivation behind a project that has brought scientists at three U.S. Department of Energy national laboratories together.
This team has just achieved an important milestone ...
Genetic analysis of symptoms yields new insights into PTSD
2021-01-28
Attempts to identify the genetic causes of neuropsychiatric diseases such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) through large-scale genome-wide analyses have yielded thousands of potential links. The challenge is further complicated by the wide range of symptoms exhibited by those who have PTSD. For instance, does extreme arousal, anger, or irritation experienced by some have the same genetic basis as the tendency to re-experience traumatic events, another symptom of the disorder?
A new study led by researchers at Yale and the University of California-San Diego (UCSD) provides answers to some of these questions and uncovers intriguing genetic similarities between PTSD and other mental health disorders such as anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. ...
At-home swabs diagnose infections as accurately as healthcare worker-collected swabs
2021-01-28
Washington, DC - January 28, 2021 - Self swabs and caregiver swabs are effective at detecting multiple pathogens and are just as accurate as those taken by healthcare workers, according to a team of Australian researchers. The research appears in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology, a publication of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Across the range of pathogens and swab types, there was high agreement between results from self- or caregiver swabs and those performed by a healthcare worker, even when different sites were swabbed (e.g. nasopharyngeal vs. nasal)," said principal investigator Joshua Osowicki, BMedSci, MBBS, FRACP, a Pediatric Infectious Diseases physician in the Murdoch Children's Research Institute's ...
Modeling study of ancient thumbs traces the history of hominin thumb dexterity
2021-01-28
Despite long-standing ideas about the importance of thumb evolution in tool use and development, questions remain about exactly when human-like manual dexterity and efficient thumb use arose--and which hominin species was the first to have this ability. Now, researchers who've analyzed the biomechanics and efficiency of the thumb across different fossil human species using virtual muscle modeling have new insight into when these abilities first arose and what they've meant for the development of more complex human culture. The findings, appearing January 28 in the journal Current Biology, suggest that a fundamental aspect of human thumb opposition first appeared approximately 2 million years ago and was not found ...
Risk-taking behavior has a signature in the brain, big data shows
2021-01-28
What makes one person drive above the speed limit while another navigates steadily in the right lane? What motivates someone to leave a job with a steady paycheck to launch their own business while the other sticks to one employer for an entire career?
"People have different tendencies to engage in behavior that risks their health or that involve uncertainties about the future," says Gideon Nave, an assistant professor of marketing in Penn's Wharton School.
Yet explaining the origin of those tendencies, both in the genome and in the brain, has been challenging for researchers, partly because previous studies on ...
How a little-known glycoprotein blocks a cancer cell's immune response
2021-01-28
ANN ARBOR, Michigan -- It was an unexpected discovery that started with an analysis of more than 1,000 genes. The question: why game-changing cancer immunotherapy treatments work for only a fraction of patients.
The analysis shone a light on one that popped up repeatedly in patients and mouse models that did not respond to immune checkpoint therapy: stanniocalcin-1, a glycoprotein whose role in both tumors and immunology is largely unknown.
By following the trail from this surprising thread, a University of Michigan Rogel Cancer team uncovered how stanniocalcin-1, or STC1, works inside the cell to block a cellular "eat-me" signal that typically triggers the immune system to produce T cells to fight the tumor. The findings, published in ...
Researchers use patients' cells to test gene therapy for rare eye disease
2021-01-28
Scientists at the National Eye Institute (NEI) have developed a promising gene therapy strategy for a rare disease that causes severe vision loss in childhood. A form of Leber congenital amaurosis, the disease is caused by autosomal-dominant mutations in the CRX gene, which are challenging to treat with gene therapy. The scientists tested their approach using lab-made retinal tissues built from patient cells, called retinal organoids. This approach, which involved adding copies of the normal gene under its native control mechanism, partially restored CRX function. The study report appears today in Stem ...
Using science to explore a 60-year-old Russian mystery
2021-01-28
In early October 2019, when an unknown caller rang EPFL professor Johan Gaume's cell phone, he could hardly have imagined that he was about to confront one of the greatest mysteries in Soviet history. At the other end of the line, a journalist from The New York Times asked for his expert insight into a tragedy that had occurred 60 years earlier in Russia's northern Ural Mountains - one that has since come to be known as the Dyatlov Pass Incident. Gaume, head of EPFL's Snow and Avalanche Simulation Laboratory (SLAB) and visiting fellow at the WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, had never heard ...
Physicists develop record-breaking source for single photons
2021-01-28
Researchers at the University of Basel and Ruhr University Bochum have developed a source of single photons that can produce billions of these quantum particles per second. With its record-breaking efficiency, the photon source represents a new and powerful building-block for quantum technologies.
Quantum cryptography promises absolutely secure communications. A key component here are strings of single photons. Information can be stored in the quantum states of these light particles and transmitted over long distances. In the future, remote quantum processors will communicate with each other via single photons. And perhaps the processor itself will use photons as quantum bits for computing.
A basic prerequisite for such applications, however, is an efficient source ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
A new Johns Hopkins Medicine study finds sex and menopause-based differences in presentation of early Lyme disease
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
[Press-News.org] Breakthrough for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopyOvercoming limitations inherent in other LIBS techniques, plasma-grating-induced breakdown spectroscopy enhances signal intensity by more than three times