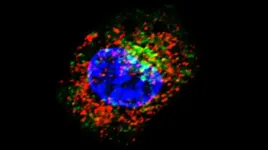
(Press-News.org) Washington, DC - January 28, 2021 - Self swabs and caregiver swabs are effective at detecting multiple pathogens and are just as accurate as those taken by healthcare workers, according to a team of Australian researchers. The research appears in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology, a publication of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Across the range of pathogens and swab types, there was high agreement between results from self- or caregiver swabs and those performed by a healthcare worker, even when different sites were swabbed (e.g. nasopharyngeal vs. nasal)," said principal investigator Joshua Osowicki, BMedSci, MBBS, FRACP, a Pediatric Infectious Diseases physician in the Murdoch Children's Research Institute's Tropical Diseases research group, Melbourne, Australia.
"We found a pooled sensitivity of 91% and specificity of 98% for self- or caregiver-collected upper airway swabs compared to [healthcare worker] swabs," the investigators wrote. (Sensitivity refers to the proportion of those who test positive that are correctly identified, and specificity the proportion testing negative that are correctly identified.)
"Findings were similar when only SARS-CoV-2 data were considered," the researchers wrote. "This level of diagnostic performance should reassure clinicians, researchers, and public health officials that diagnostic performance is not necessarily compromised by self- or caregiver swabbing."
Pathogens swabbed in the study include SARS-CoV-2, influenza, group A Streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, pharyngeal Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and a panel of respiratory viruses.
The study was a systematic review and meta-analysis of 20 previous studies comprising swabs of more than 3,500 individuals, comparing self- or caregiver swabs with swabs collected by healthcare workers for diagnosis of a range of upper airway pathogens. "We searched for previous studies that included both kinds of swabs collected from the same individuals," said Dr. Osowicki. "For each study, we considered the sensitivity and specificity of self- or caregiver swabs compared to swabs by healthcare workers, and the agreement between the two kinds of swabs.
Self- and caregiver swabbing offer a number of advantages over swabbing by healthcare workers, including less likelihood of transmission, reduced expenses, conservation of personal protective equipment, and less discomfort to patients. An online survey of patients with SARS-CoV-2 symptoms found a much higher proportion willing to be tested via a self-collected saliva sample (92%) or a nasal swab (88%) than by a drive-through healthcare worker swab collection (71%)," according to the investigators.
When the plans of then medical student and first author Ciara Harrison to complete an immunology laboratory project were derailed by the pandemic, Dr. Harrison, now a first-year physician, pivoted to this systematic review and meta-analysis.
INFORMATION:
The American Society for Microbiology is one of the largest professional societies dedicated to the life sciences and is composed of 30,000 scientists and health practitioners. ASM's mission is to promote and advance the microbial sciences.
ASM advances the microbial sciences through conferences, publications, certifications and educational opportunities. It enhances laboratory capacity around the globe through training and resources. It provides a network for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings. Additionally, ASM promotes a deeper understanding of the microbial sciences to diverse audiences.
Despite long-standing ideas about the importance of thumb evolution in tool use and development, questions remain about exactly when human-like manual dexterity and efficient thumb use arose--and which hominin species was the first to have this ability. Now, researchers who've analyzed the biomechanics and efficiency of the thumb across different fossil human species using virtual muscle modeling have new insight into when these abilities first arose and what they've meant for the development of more complex human culture. The findings, appearing January 28 in the journal Current Biology, suggest that a fundamental aspect of human thumb opposition first appeared approximately 2 million years ago and was not found ...
What makes one person drive above the speed limit while another navigates steadily in the right lane? What motivates someone to leave a job with a steady paycheck to launch their own business while the other sticks to one employer for an entire career?
"People have different tendencies to engage in behavior that risks their health or that involve uncertainties about the future," says Gideon Nave, an assistant professor of marketing in Penn's Wharton School.
Yet explaining the origin of those tendencies, both in the genome and in the brain, has been challenging for researchers, partly because previous studies on ...
ANN ARBOR, Michigan -- It was an unexpected discovery that started with an analysis of more than 1,000 genes. The question: why game-changing cancer immunotherapy treatments work for only a fraction of patients.
The analysis shone a light on one that popped up repeatedly in patients and mouse models that did not respond to immune checkpoint therapy: stanniocalcin-1, a glycoprotein whose role in both tumors and immunology is largely unknown.
By following the trail from this surprising thread, a University of Michigan Rogel Cancer team uncovered how stanniocalcin-1, or STC1, works inside the cell to block a cellular "eat-me" signal that typically triggers the immune system to produce T cells to fight the tumor. The findings, published in ...
Scientists at the National Eye Institute (NEI) have developed a promising gene therapy strategy for a rare disease that causes severe vision loss in childhood. A form of Leber congenital amaurosis, the disease is caused by autosomal-dominant mutations in the CRX gene, which are challenging to treat with gene therapy. The scientists tested their approach using lab-made retinal tissues built from patient cells, called retinal organoids. This approach, which involved adding copies of the normal gene under its native control mechanism, partially restored CRX function. The study report appears today in Stem ...
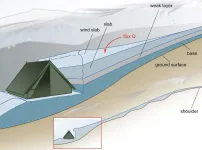
In early October 2019, when an unknown caller rang EPFL professor Johan Gaume's cell phone, he could hardly have imagined that he was about to confront one of the greatest mysteries in Soviet history. At the other end of the line, a journalist from The New York Times asked for his expert insight into a tragedy that had occurred 60 years earlier in Russia's northern Ural Mountains - one that has since come to be known as the Dyatlov Pass Incident. Gaume, head of EPFL's Snow and Avalanche Simulation Laboratory (SLAB) and visiting fellow at the WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, had never heard ...
Researchers at the University of Basel and Ruhr University Bochum have developed a source of single photons that can produce billions of these quantum particles per second. With its record-breaking efficiency, the photon source represents a new and powerful building-block for quantum technologies.
Quantum cryptography promises absolutely secure communications. A key component here are strings of single photons. Information can be stored in the quantum states of these light particles and transmitted over long distances. In the future, remote quantum processors will communicate with each other via single photons. And perhaps the processor itself will use photons as quantum bits for computing.
A basic prerequisite for such applications, however, is an efficient source ...
Using X-ray tomography, a research team has observed the internal evolution of the materials inside solid-state lithium batteries as they were charged and discharged. Detailed three-dimensional information from the research could help improve the reliability and performance of the batteries, which use solid materials to replace the flammable liquid electrolytes in existing lithium-ion batteries.
The operando synchrotron X-ray computed microtomography imaging revealed how the dynamic changes of electrode materials at lithium/solid-electrolyte interfaces determine the behavior of solid-state batteries. The researchers found that battery operation caused voids to form ...
Science is society's best method for understanding the world, yet many people in the field are unhappy with the way it works. Rules and procedures meant to promote innovative research can have perverse side-effects that harm both science and scientists. One of these - the 'priority rule' - rewards scientists who make discoveries with prestige, prizes and better career opportunities, depriving the runners-up of similar perks. Researchers at University of Technology Eindhoven (TU/e) and the Arizona State University in the US have developed a new model to better understand this rule, and see if current reforms to improve the system actually make sense. Their study was published in Nature Human Behaviour.
"Over the past decade, there have been growing concerns that something ...
What The Study Did: This study finds that being a health care worker isn't associated with poorer outcomes among patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Authors: Nauzer Forbes, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Calgary in Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35699)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
Risky behaviors such as smoking, alcohol and drug use, speeding, or frequently changing sexual partners result in enormous health and economic consequences and lead to associated costs of an estimated 600 billion dollars a year in the US alone. In order to define measures that could reduce these costs, a better understanding of the basis and mechanisms of risk-taking is needed.
Functional and anatomical differences
UZH neuro-economists Goekhan Aydogan, Todd Hare and Christian Ruff, together with an international research team looked at the genetic characteristics that correlate with risk-taking behavior. Using a representative sample of 25,000 people, the researchers examined the relationship ...