New research about emerging 'COVID-19 personality types'
2021-01-29
(Press-News.org) New research by Mimi E. Lam (University of Bergen) just published in Humanities and Social Sciences Communications identifies and explores the impacts of salient viral or COVID-19 behavioural identities that are emerging.
"These emergent COVID-19 behavioural identities are being hijacked by existing social and political identities to politicize the pandemic and heighten racism, discrimination, and conflict," says Lam. She continues: "the COVID-19 pandemic reminds us that we are not immune to each other. To unite in our fight against the pandemic, it is important to recognize the basic dignity of all and value the human diversity currently dividing us."
"Only then, can we foster societal resilience and an ethical COVID-19 agenda. This would pave the way for other global commons challenges whose impacts are less immediate, but no less dire for humanity.
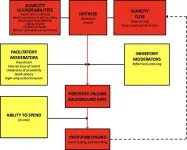
Lam argues that liberal democracies need an ethical policy agenda with three priorities: 1. to recognize the diversity of individuals; 2. to deliberate and negotiate value trade-offs; and 3. to promote public buy-in, trust, and compliance.
Some emergent "COVID-19 personality types":
Deniers: who downplay the viral threat, promoting business as usual
Spreaders: who want it to spread, herd immunity to develop, and normality to return
Harmers: who try to harm others by, for example, spitting or coughing at them
Realists: who recognise the reality of the potential harm and adjust their behaviours
Worriers: who stay informed and safe to manage their uncertainty and fear
Contemplators: who isolate and re?ect on life and the world
Hoarders: who panic-buy and hoard products to quell their insecurity
Invincibles: often youth, who believe themselves to be immune
Rebels: who de?antly ?out social rules restricting their individual freedoms
Blamers: who vent their fears and frustrations onto others
Exploiters: who exploit the situation for power, pro?t or brutality
Innovators: who design or repurpose resources to fight the pandemic
Supporters: who show their solidarity in support of others
Altruists: who help the vulnerable, elderly, and isolated
Warriors: who, like the front-line health-care workers, combat its grim reality
Veterans: who experienced SARS or MERS and willingly comply with restrictions
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-29
Drawing on animal-foraging theory, a new model predicts psychological factors that may lead to panic buying during times of crisis. The model is largely supported by real-world data from the COVID-19 pandemic. Richard Bentall of the University of Sheffield, England, and colleagues presented these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 27.
In the early stages of the pandemic, consumers in several countries around the world engaged in "panic buying" of household items, causing temporary shortages of toilet rolls and other products. Such behavior is typical during times of crisis, but few studies have examined the psychology of crisis-driven over-purchasing.
To better understand this phenomenon, Bentall and colleagues turned to animal-foraging ...
2021-01-29
As one of the most experienced archaeologists studying California's Native Americans, Lynn Gamble(link is external) knew the Chumash Indians had been using shell beads as money for at least 800 years.
But an exhaustive review(link is external) of some of the shell bead record led the UC Santa Barbara professor emerita of anthropology to an astonishing conclusion: The hunter-gatherers centered on the Southcentral Coast of Santa Barbara were using highly worked shells as currency as long as 2,000 years ago.
"If the Chumash were using beads as money 2,000 years ago," Gamble said, "this changes our thinking of hunter-gatherers and sociopolitical and economic complexity. This may be the first example of the use of money anywhere in the ...
2021-01-29
As part of standard patient protocol, doctors inform women of the risks of pregnancy. But there is one exception to this standard: stillbirth.
University of Arkansas law professor Jill Wieber Lens argues that women have a right to know of the risk of stillbirth, and, consistent with the evolution of informed consent law, this right should be enforceable through a medical malpractice tort claim.
Stillbirth, or pregnancy loss after 20 weeks but before birth, is not uncommon. Annually, 26,000 U.S. women give birth to a stillborn baby, or roughly one out every 160 pregnancies. The United States' stillbirth rate ...
2021-01-29
COLLEGE PARK, Md.--The amount of methane released into the atmosphere as a result of coal mining is likely much higher than previously calculated, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American Geophysical Union recently.
The study estimates that methane emissions from coal mines are approximately 50 percent higher than previously estimated. The research was done by a team at the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and others.
The higher estimate is due mainly to two factors: methane that continues to be emitted from thousands of abandoned mines and the higher methane content in coal seams that are ever deeper, according to chief ...
2021-01-29
The Japanese now have their own reference genome thanks to researchers at Tohoku University who completed and released the first Japanese reference genome (JG1).
Their study was published in the journal Nature Communications on January 11, 2021.
"JG1 can aid with the clinical sequence analysis of Japanese individuals with rare diseases as it eliminates the genomic differences from the international reference genome," said Jun Takayama, co-author of the study.
Back in 2003, the Human Genome Project, through a gargantuan global effort, cracked the code of life and mapped all the genes of the human genome.
Since then, more accurate versions of the human reference genome have ...
2021-01-29
The researchers of the Institute for Atmospheric and Earth system research at the University of Helsinki have investigated how atmospheric particles are formed in the Arctic. Until recent studies, the molecular processes of particle formation in the high Arctic remained a mystery.
During their expeditions to the Arctic, the scientists collected measurements for 12 months in total. The results of the extensive research project were recently published in the Geophysical Research Letters journal.
The researchers discovered that atmospheric vapors, particles, and cloud formation have clear differences within various Arctic environments. The study clarifies how Arctic warming and sea ice loss strengthens processes where different vapors are emitted to the atmosphere. The ...
2021-01-29
The Covid-19 pandemic has made home offices, virtual meetings and remote learning the norm, and it is likely here to stay. But are people paying attention in online meetings? Are students paying attention in virtual classrooms? Researchers Jens Madsen and Lucas C. Parra from City College of New York, demonstrate how eye tracking can be used to measure the level of attention online using standard web cameras, without the need to transfer any data from peoples computers, thus preserving privacy. In a paper entitled "Synchronized eye movements predict test scores in online video education," published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, they show that just ...
2021-01-29
Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) and ETH Zurich have developed a process to produce commodity chemicals in a much less hazardous way than was previously possible. Such commodity chemicals represent the starting point for many mass-produced products in the chemical industry, such as plastics, dyes, and fertilizers, and are usually synthesized with the help of chlorine gas or bromine, both of which are extremely toxic and highly corrosive. In the current issue of Science, the researchers report that they have been able to utilize electrolysis, i.e., the application of an electric current, to obtain chemicals known as dichloro and dibromo compounds, which can then be used to synthesize ...
2021-01-29
A new study has found that mobile apps can play a vital role in helping immigrants integrate into new cultures, as well as provide physical and mental health benefits.
Researchers at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) surveyed new migrants and refugees undertaking free beginners' language classes in Greece, often the first destination for people arriving into Europe from Africa and Asia, over a 10-month period.
The findings, published in the journal Computers in Human Behavior, show that those using mobile apps aided by artificial intelligence (AI), such as language assistants, customised information sites, or health symptom trackers, experienced ...
2021-01-29
New research has revealed how an invasion of the alien evergreen tree, Prosopis juliflora seriously diminishes water resources in the Afar Region of Ethiopia, consuming enough of this already scarce resource to irrigate cotton and sugarcane generating some US$ 320 million and US$ 470 million net benefits per year.
A team of Ethiopian, South African and Swiss scientists, including lead author Dr Hailu Shiferaw, Dr Tena Alamirew, and Dr Gete Zeleke from the Water and Land Resource Centre of Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia, and Dr Sebinasi Dzikiti from Stellenbosch University, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New research about emerging 'COVID-19 personality types'