(Press-News.org) NEW YORK, NY (Feb. 1, 2021)--Errors in the way chromosomes are packed into antibody-producing B cells appear to play a role in the development of B cell-related blood cancers, according to a new study by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
The findings could lead to new biomarkers for predicting the onset of these cancers and to a new class of cancer therapies that prevent or correct harmful changes in genome architecture.
The study was published online Feb. 1 in the journal Nature Genetics.
Antibodies are made by immune cells called B cells through a series of carefully controlled chromosome rearrangements and "good" mutations that allow the cell to make a wide array of different antibodies. "Although these changes are essential for generating the vast diversity of antibodies, there is a risk that 'bad' mutations will occur and lead to B cell-derived cancers," says study leader Uttiya Basu, PhD, professor of microbiology & immunology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
Basu's new study shows that a protein called DIS3 is critical in maintaining genomic architecture and preventing uncontrolled chromosome rearrangements that have the potential to cause cancer.
These new studies with mice reveal that B cells become destabilized, have more detrimental chromosomal rearrangements, and are less capable of generating specific antibodies when DIS3 is missing.
DIS3 stabilizes chromosomes by preventing the buildup of noncoding RNAs (RNAs that do not code for proteins), the study also reveals.
"The massive accumulation of these RNAs perturbs the way the genome is packed in the nucleus and leaves the genome vulnerable to DNA translocations," Basu says.
Because DIS3 mutations are common in people with multiple myeloma--a type of blood cancer that stems from B cells--the study may explain why these mutations contribute to the disease.
"It's possible that multiple myeloma treatment could require therapeutic interventions that prevent RNA accumulation and its effect on genome architecture," says Basu.
Future studies will focus on how genome architectural changes could be used to predict the onset of various B cell malignancies, which sometimes start out as relatively benign conditions.
The study also brings to light the role of genomic architecture maintenance for the prevention of cancer and the role of noncoding RNA in the normal production of antibodies.
INFORMATION:
More Information
The study is titled "Noncoding RNA processing by DIS3 regulates chromosomal architecture and somatic hypermutation in B cells."
The other contributors are Brice Laffleur (Columbia), Junghyun Lim (Columbia and Jeonbuk National University, South Korea), Wanwei Zhang (Columbia), Yiyun Chen (Hong Kong University of Science and Technology), Evangelos Pefanis (Columbia and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals), Jonathan Bizarro (Columbia), Carolina R. Batista (Columbia), Lijing Wu (Columbia), Aris N. Economides (Regeneron), and Jiguang Wang (Hong Kong University of Science and Technology).
The study was supported by grants from the National Insitutes of Health (RO1AI099195, RO1AI134988, and RO1AI143897), Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, Pershing Square Sohn Cancer Research Alliance, and an EMBO fellowship.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Columbia University Irving Medical Center provides international leadership in basic, preclinical, and clinical research; medical and health sciences education; and patient care. The medical center trains future leaders and includes the dedicated work of many physicians, scientists, public health professionals, dentists, and nurses at the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, the Mailman School of Public Health, the College of Dental Medicine, the School of Nursing, the biomedical departments of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, and allied research centers and institutions. Columbia University Irving Medical Center is home to the largest medical research enterprise in New York City and State and one of the largest faculty medical practices in the Northeast. For more information, visit cuimc.columbia.edu or columbiadoctors.org.
Taking a particular type of medication to treat enlarged prostate is associated with a reduced risk of developing Parkinson's disease, according to a large observational study led by researchers at the University of Iowa, with colleagues in Denmark and China.
The findings, published Feb. 1 in JAMA Neurology, provide compelling evidence that terazosin, and similar medications, might have the potential to prevent or delay the development of Parkinson's disease.
The new study used data on almost 300,000 older men from two large, independent patient datasets--the Truven ...
A new kind of wearable health device would deliver real-time medical data to those with eye or mouth diseases, according to Huanyu 'Larry' Cheng, Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Professor in the Penn State Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics (ESM).
Cheng recently published a paper in Microsystems & Nanoengineering on new micro- and nano-device technology that could revolutionize how certain health conditions are monitored and treated.
"We sought to create a device that collects both small and large substances of biofluids such as tears and saliva, which can be analyzed for certain conditions on a rapid, continuous basis, rather than waiting on test results from samples in a lab," he said.
The sensors would be placed near the tear duct or mouth to collect samples, ...
Winter survival of honey bee colonies is strongly influenced by summer temperatures and precipitation in the prior year, according to Penn State researchers, who said their findings suggest that honey bees have a "goldilocks" preferred range of summer conditions outside of which their probability of surviving the winter falls.
The results of this study, which used several years of survey data provided by the Pennsylvania State Beekeeper's Association and its members, enabled the development of a tool for forecasting honey bee winter survival to support beekeepers' management decisions, the researchers said.
Honey bees contribute more than $20 billion in pollination services to agriculture in the United States and generate another ...
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems are now known to negatively control plasmid replication, according to Thomas Wood, Biotechnology Endowed Chair and professor of chemical engineering in the Penn State College of Engineering.
Plasmids, or extra-chromosomal bits of DNA, allow bacteria to evade antibiotics, making the antibiotics ineffective in halting a bacterial infection.
The presence or absence of plasmids impacts a bacterium's resistance to antibiotics and its ability to cause infection -- important points related to fighting bacterial infections, according to Wood.
"Each year, there are at least 700,000 deaths worldwide because of bacterial infections, a growing number that is projected to increase to 10 million by 2050," Wood said. "And of course, the effectiveness ...
February 1, 2021 - Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) is a potentially lifesaving treatment for patients in cardiac arrest when the circulation can't be restored by conventional CPR. New guidelines for ECPR in adults and children, developed by the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO), are presented by the ASAIO Journal, official journal of the American Society for Artificial Internal Organs. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
A specialized application of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), ECPR is increasingly being used to provide a chance ...
Imagine a rubber band that was capable of snapping itself many times over, or a small robot that could jump up a set of stairs propelled by nothing more than its own energy. Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have discovered how to make materials that snap and reset themselves, only relying upon energy flow from their environment. The discovery may prove useful for various industries that want to source movement sustainably, from toys to robotics, and is expected to further inform our understanding of how the natural world fuels some types of movement.
Al Crosby, a professor of polymer science and engineering in the College of Natural Sciences at UMass Amherst, ...
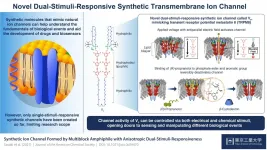
A key thread that holds together the delicate balance of a complex biological system is the transmembrane ion channel. These are supramolecular, or multi-molecule, ion and molecule exchange routes embedded within cell membranes to ensure essential chemical transport to and from the cell and facilitate cell signaling.
In recent years, synthetic biomolecules that mimic the structures and functions of natural ion channels have garnered much interest among molecular biology researchers as models for studying the fundamentals of these channels and perhaps, even creating drug alternatives or developing advanced biosensors.
However, although ...
Social media is increasingly used to spread fake news. The same problem can be found on the capital market - criminals spread fake news about companies in order to manipulate share prices. Researchers at the Universities of Göttingen and Frankfurt and the Jožef Stefan Institute in Ljubljana have developed an approach that can recognise such fake news, even when the news contents are repeatedly adapted. The results of the study were published in the Journal of the Association for Information Systems.
In order to detect false information - often fictitious data that presents a company in a positive light - the scientists used machine learning methods and ...
The adoption of recommended changes in concussion management led to a reduction in the length of symptoms among 11- to 18-year-old athletes with first-time, sports-related concussions, according to new research in the Journal of Osteopathic Medicine. These outcomes support the widespread adoption of the updated concussion guidelines.
Researchers conducted a retrospective review of the medical records of athletes who sustained a concussion between 2016 and 2018 and were treated by a physician who used the revised approach to concussion management. They then compared the data with a previously published data set from athletes who sustained a concussion between 2011 and 2013 and whose physicians followed older guidelines for concussion ...
ITHACA, NY - When it comes to saving endangered species of a certain size, conservationists often have to think outside the box.
This was reinforced by a recent study published in the Journal of Wildlife Diseases, led by faculty in the College of Veterinary Medicine, which analyzed the effects of hanging tranquilized black rhinoceroses upside down by their feet.
"We found that suspending rhinos by their feet is safer than we thought," said Dr. Robin Radcliffe, senior lecturer in wildlife and conservation medicine and first author of the study.
While ...