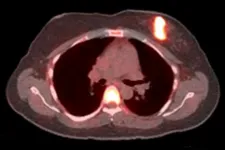
(Press-News.org) DALLAS, Feb. 2, 2021 — Young, Black adults are more than twice as likely to die in the first year after a heart transplant when compared to same-age, non-Black heart transplant recipients, according to new research published today in Circulation: Heart Failure, an American Heart Association journal.
Research has consistently shown that Black heart transplant recipients have a higher risk of death following heart transplantation compared to non-Black recipients. Black patients have higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease at younger ages, and therefore, they may need heart transplants at younger ages. Researchers hypothesized that studies focused on disparities among Black heart transplant recipients may be missing an even greater disparity – younger Black patients.
“Generally, older patients are at a higher risk of having worse outcomes following a major procedure,” said Errol L. Bush, M.D., senior author of the study, associate professor of surgery and surgical director of the Advanced Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Program at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland. “Organ transplantation, however, is a complex operation that requires lifelong, specialized medical and surgical care. Continued access to the health care system and financial resources such as insurance may be unfairly limited in younger patients, potentially leading to worse outcomes.”
Researchers analyzed the outcomes of almost 23,000 adults (median age 56, 25% female) who had a heart transplant between Jan. 1, 2005 and Jan. 31, 2017. Patient information was obtained from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients, a registry that includes data on all transplant donors, wait-listed patients and recipients in the United States. Risks of mortality were compared between Black and non-Black transplant recipients in four different age groups (18-30 years, 31-40 years, 41-60 years and 61-80 years).
The researchers found that when compared to other heart transplant recipients:
Across all age groups, Black heart transplant recipients had approximately a 30% higher risk of death.
However, when examined by age groups, the risk of death among Black heart transplant recipients was 2 times higher among recipients aged 18-30 years and 1.5 times higher among recipients aged 31-40 years.
Among Black heart transplant recipients aged 18-30, the risk of death was primarily during the first year after transplant, with Black recipients having 2.3 times higher risk of death in this time period.
“Our study is the first to highlight young, Black recipients as a subgroup at a higher risk of death during the first year after a heart transplant,” said Hasina Maredia, M.D., first author of the study whose interest in health disparities inspired her to initiate and lead the project as a medical student at Johns Hopkins. “Our findings indicate clinical research moving forward should focus attention on young, Black recipients during this high-risk period so that longstanding racial disparities seen in heart transplant survival can be improved.”
In the study, young, Black heart transplant recipients differed from young, non-Black recipients in several ways, including being more likely to have diabetes and/or high blood pressure; have a weakened heart muscle (cardiomyopathy); and be insured by Medicaid rather than a private insurer. More serious illness and additional medical problems prior to surgery might increase the risk of death from surgical complications, and financial constraints might make it more difficult for younger recipients with limited insurance to access specialized care and take the medications needed to prevent organ rejection, according to the researchers’ discussion of possible mechanisms for the disparity.
“The high risk associated with Black race is not specifically due to race itself; it is a marker of systemic racism and inequities that have resulted in significant health care disparities,” said Bush and Maredia.
The American Heart Association recently published a presidential advisory that addresses structural racism as a cause of poor health and premature death from heart disease and stroke. The advisory, titled “Call to Action: Structural Racism as a Fundamental Driver of Health Disparities,” reviews the historical context, current state and potential solutions to address structural racism in the U.S. and outlines steps the Association is taking to address and mitigate the root causes of health care disparities.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors are Mary Grace Bowring, M.P.H.; Allan B. Massie, Ph.D.; Sunjae Bae, M.P.H.; Amber Kernodle, M.D.; Shakirat Oyetunji, M.D.; Christian Merlo, M.D., M.P.H.; Robert S. D. Higgins, M.D.; and Dorry L. Segev, M.D., Ph.D. Author disclosures are in the manuscript.
The study is funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health.
Additional Resources:
Available multimedia is on right column of release link - https://newsroom.heart.org/news/racial-disparities-young-black-adults-had-significantly-worse-heart-transplant-outcomes?preview=c3fef0124f8206e35b8f7fccd3449124
After Feb. 2, view the manuscript online.
Environment, culture, other social determinants play big role in heart health
Heart transplants from severely obese donors show comparable outcomes for patients
Follow AHA/ASA news on Twitter @HeartNews
Follow news from the AHA’s Circulation: Heart Failure journal @CircHF
Statements and conclusions of studies published in the American Heart Association’s scientific journals are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the Association’s policy or position. The Association makes no representation or guarantee as to their accuracy or reliability. The Association receives funding primarily from individuals; foundations and corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations and fund specific Association programs and events. The Association has strict policies to prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers and health insurance providers are available here, and the Association’s overall financial information is available here.
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public’s health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for nearly a century. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, Twitter or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
Hormone therapy commonly is given as a targeted treatment for women whose cancer cells carry receptors for estrogen. But the therapy only works for about half of all patients. Until now, there hasn't been a good way to reliably predict who will benefit and who will not.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown they can distinguish patients likely or unlikely to benefit from hormone therapy using an imaging test that measures the function of the estrogen receptors in their cancer cells. In a small phase 2 clinical trial, the researchers showed that the cancers of all patients with working estrogen receptors remained stable or improved on hormone therapy, and progressed in all women with nonfunctional ...
A new method for constructing special solar cells could significantly increase their efficiency. Not only are the cells made up of thin layers, they also consist of specifically arranged nanoblocks. This has been shown in a new study by an international research team led by the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), which was published in the scientific journal Nano Letters.
Commercially available solar cells are mostly made of silicon. "Based on the properties of silicon it's not feasible to say that their efficiency can be increased indefinitely," says Dr Akash Bhatnagar, a physicist from the Centre for Innovation Competence (ZIK) "SiLi-nano" at MLU. ...
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (FEBRUARY 2, 2021). Researchers in the United Kingdom (UK) conducted a randomized controlled trial in 47 patients with lumbar spinal stenosis to compare treatment outcomes and costs of two competing surgical procedures: insertion of the X-Stop® (Medtronic) interspinous distractor device and open decompression surgery with laminectomy. Both procedures improved the patients' quality of life; however, overall, laminectomy gave patients a better quality of life and was also more cost-effective.
Detailed findings of this study can be found in a new article, "A randomized controlled trial of the X-Stop interspinous ...
Abu Dhabi, UAE, February 2, 2021: Adolescent mothers often fall through the cracks of educational programming. This is highly problematic given that globally an estimated 12 million girls between the ages of 15-19, and 777,000 girls under the age of 15, give birth each year. In populations affected by conflict and displacement, adolescent girls have an increased likelihood of becoming mothers due to various factors, such as disruptions to schooling, the loss of family members, poverty, gender-based violence, and poor access to healthcare and sexual and reproductive services and resources. There is a lack of support programs for these young mothers, and a continuing need for educational programming. ...
Temperature rise due to climate change has negatively affected labour productivity in the past decades and will keep damaging it, potentially at a higher extent than what has been estimated in the literature up to now. In South Africa, a future scenario with severe climate change will feature a reduction of per capita GDP of up to 20% by the end of the century, compared to an idealized future without the impacts of a changing climate.
This is what emerges from the study "Climate change and development in South Africa: the impact of rising temperatures on economic productivity and labour availability", coordinated by the ...
Many household products contain ingredients to protect them against sun damage. These UV filters are found in plastics, paints and textiles, as well as personal care products such as sunscreens and moisturizers. UV filters are entering the aquatic environment in rivers, lakes and oceans. Consider for a moment a beach goer swimming in the ocean or rain washing over plastic playground equipment and running into a stormwater drain - either directly or indirectly, UV filters end up making their way to a waterway.
UV filters are chemicals that work by either physically blocking or absorbing UV rays. There are two main types of UV filters: inorganic forms, which contain metal particles, ...
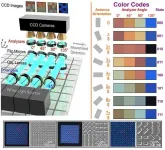
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Purdue University innovators have created technology aimed at replacing Morse code with colored "digital characters" to modernize optical storage. They are confident the advancement will help with the explosion of remote data storage during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Morse code has been around since the 1830s. The familiar dots and dashes system may seem antiquated given the amount of information needed to be acquired, digitally archived and rapidly accessed every day. But those same basic dots and dashes are still used in many optical media to aid in storage.
A new technology developed at Purdue is aimed at ...
As the U.S. confronts a bitter election season, political unrest and violence, a shaky economy, and a soaring death toll due to COVID-19, 84% of U.S. adults say the country has serious societal issues that we need to address, according to a new poll.
At the same time, 9 in 10 adults say they hope that the country moves toward unity, according to Stress in AmericaTM: January 2021 Stress Snapshot, conducted by The Harris Poll on behalf of the American Psychological Association.
The survey found that the average reported stress level during the prior month was 5.6, (on a scale from 1 to 10 where ...
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, IL (Feb. 2, 2021) - As the number of states increase where medical and recreational cannabis use is legal, so does the importance that physicians discuss with patients the effects of cannabis on those with asthma. A new survey in Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific journal of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, shows that of those who used cannabis, about half smoked it while a third vaped - both "inhalation routes" likely to affect one's lungs.
"It surprised me that over half of the cannabis users in this study who have asthma were smoking it," said Joanna Zeiger, PhD, principal investigator for the study. "And further, of those with uncontrolled asthma, ...
A new study shows that the mating behaviour of crickets is significantly affected by traffic noise and other man-made sounds - a finding that could have implications for the future success of the species.
The research, published in the journal Behavioral Ecology, was carried out at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), and involved studying the mating choices of female field crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus) under different acoustic conditions.
When a female cricket is nearby, male crickets will perform a courtship song by rubbing their wings together. The song is energetically costly to produce and so contains ...