(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. - Fortune 500 firms with strong growth profiles are more susceptible to "cooking the books" than smaller, struggling companies, according to a recent study published in Justice Quarterly.
Researchers from Washington State University, Pennsylvania State University and Miami University examined the characteristics of more than 250 U.S. public corporations that were involved in financial securities fraud identified in Securities and Exchange Commission filings from 2005-2013. They were then compared to a control sample of firms that were not named in SEC fraud filings.
Clear trends emerged in the risk of fraud including corporations that were listed in the Fortune 500, traded on the New York Stock Exchange and had strong growth expectations.
"Prestigious companies, those that are household names, were actually more prone to engage in financial fraud, which was very surprising," said Jennifer Schwartz, WSU sociologist and lead author on the study. "We thought it would be companies that were struggling financially, that were nearing bankruptcy, but it was quite the opposite. It was the companies that thought they should be doing better than they were, the ones with strong growth imperatives--those were the firms that were most likely to cheat."
Corporate financial securities fraud involves attempts to manipulate financial markets in a business' favor by using faulty accounting practices, providing false or incomplete information or otherwise misrepresenting the company's financial status.
The researchers noted that this type of elite, white-collar crime is understudied especially when compared with street crime even though it has more wide-reaching consequences.
"What these companies were doing was essentially fudging the numbers, lying to investors, other companies and the SEC," said Schwartz. "Eventually, you have to make up for the money that was lost, that really never existed, so shareholders lose money, people lose retirement plans, people lose jobs. It's very, very damaging."
Schwartz and her co-authors decided to look at the time period around the global financial crisis that included the fraud scandals of WorldCom and Enron, and the subsequent regulatory Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
The goal was to identify the conditions at publicly traded companies in which there was a greater risk for fraud. The researchers found that companies with Fortune 500 status were represented nearly four times as often among the firms that had committed fraud than in the nonfraudulent control group. Likewise, firms that traded on NYSE were over-represented among fraudulent firms versus non-fraud - by nearly two to one, a higher rate than those that trade on other exchanges like the NASDAQ or OTC.
The study also revealed that fraud occurred more often in firms where the CEO was also the chair of the board, a potential connection that Schwartz and her colleagues are investigating further.
"We need to look more at corporate leadership arrangements, and the responsibility of individuals in creating the culture of the company itself," she said. "How can leaders encourage companies to be more successful not only in terms of profit or growth but also in terms of corporate social responsibility?"
INFORMATION:
(LOS ANGELES) - There are many mechanisms by which the body responds to foreign invaders. One of these involves the T-cells of the immune system, which have a number of different proteins on their surface called "checkpoint proteins." These checkpoint proteins bind to proteins on the surface of other cells and can result in either stimulation or suppression of T-cell activity. Normally, surface proteins on foreign or invading cells will produce a stimulation of T-cell activity against these cells, while T-cell suppression is a built-in mechanism to prevent the immune system from attacking the body's own normal cells.
Tumor cells, ...
Australia's and New Zealand's first set of clinical guidelines for children's head injuries has been created by a network of specialists based at the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI).
The guidelines, developed by the Paediatric Research in Emergency Departments International Collaborative (PREDICT) and published in Emergency Medicine Australasia, will allow emergency department clinicians to best diagnose and treat children's head injuries while reducing unnecessary exposure to radiation from CT scans. They also address head injuries in children with underlying problems, such as a bleeding disorder.
Matthew ...
PITTSBURGH, 2 February, 2021 - Researchers seeking to develop on-demand and behaviorally congruent HIV prevention options for people who practice anal sex are reporting the results of three early phase clinical trials of rectal microbicides at this week's HIV Research for Prevention (HIV R4P) Virtual Conference. The Phase I studies, led by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded Microbicide Trials Network (MTN), found both of two gel-based products well-tolerated, with higher doses of the active drugs likely required to provide protection from HIV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The results are being presented ...
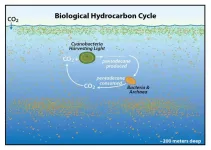
Hydrocarbons and petroleum are almost synonymous in environmental science. After all, oil reserves account for nearly all the hydrocarbons we encounter. But the few hydrocarbons that trace their origin to biological sources may play a larger ecological role than scientists originally suspected.
A team of researchers at UC Santa Barbara and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution investigated this previously neglected area of oceanography for signs of an overlooked global cycle. They also tested how its existence might impact the ocean's response to oil spills.
"We demonstrated that there is a massive and rapid hydrocarbon cycle that occurs in the ocean, and that it is distinct from the ocean's capacity to respond to petroleum input," said Professor David Valentine(link ...
A new Veterans Affairs study finds that delays in undergoing colonoscopy following an abnormal stool test increase the risk of a colorectal cancer diagnosis and cancer-related death.
The results appeared online in the journal Gastroenterology in January 2021.
In a retrospective study of more than 200,000 Veterans, the researchers found that patients who received colonoscopy more than 13 months after an abnormal stool blood test were up to 1.3 times more likely to have colorectal cancer, compared with those who had colonoscopy up to three months after the stool test. Odds of an advanced stage of cancer at diagnosis were up to 1.7 times higher when colonoscopy was delayed beyond 16 months.
The findings also ...
The complex mechanics determining how galaxies spin, grow, cluster and die have been revealed following the release of all the data gathered during a massive seven-year Australian-led astronomy research project.
The scientists observed 13 galaxies at a time, building to a total of 3068, using a custom-built instrument called the Sydney-AAO Multi-Object Integral-Field Spectrograph (SAMI), connected to the 4-metre Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT) at Siding Spring Observatory in New South Wales. The telescope is operated by the Australian National University.
Overseen by the ARC Centre of Excellence for All Sky Astrophysics ...
A combination of genetic mutations may explain the higher incidence of and poorer outcomes from pediatric leukemia in Hispanic and Latino children, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers. They said a novel therapeutic drug combination - as well as testing for these mutations - may help address the disparity.
Hispanic and Latino children are between 1.2 and 1.75 times more likely to develop B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the most common childhood cancer, than non-Hispanic and Latino children. They also have a 40% higher death rate than their counterparts after correcting for socioeconomic factors. Dr. Sinisa Dovat, a researcher and pediatric ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - People who start adulthood with a body mass index (BMI) in the normal range and move later in life to being overweight - but never obese - tend to live the longest, a new study suggests.
Adults in this category lived longer than even those whose BMI stayed in the normal range throughout their life. Those who started adulthood as obese and continued to add weight had the highest mortality rate.
"The impact of weight gain on mortality is complex. It depends on both the timing and the magnitude of weight gain and where BMI started," said Hui Zheng, lead author of the study and associate ...
According to the Barker hypothesis (Hales and Barker 1992) (also referred to as "small baby syndrome"), infants with too low body weight have an increased risk of suffering from cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, diabetes and chronic kidney diseases in adulthood. According to this hypothesis, fetal protective mechanisms enable adaptation to unfavorable intrauterine conditions (chronic oxygen or nutrient deficiency) and allow for fetal survival. At the same time, however, they lead to permanent structural and functional strains and changes into adulthood. The comprehensive study recently published in Nature Communications now clarifies central mechanisms of this phenomenon.
Fetuin-A plays a key role
Under the program of the Swiss National ...
ATLANTA - FEBRUARY 2, 2021 - A new study finds that long-term aspirin use before a diagnosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) may be associated with lower CRC-specific mortality. The report that appears in JNCI: The Journal of the National Cancer Institute, suggests that the findings for pre-diagnosis aspirin use might help reduce CRC mortality in the overall population by limiting metastatic spread of colorectal tumors before diagnosis. Preventing distant metastases leads to fewer deaths from colorectal cancer.
The study, led by Peter T. Campbell, PhD, of the American Cancer Society, used data from men and women enrolled in the American Cancer Society's Cancer Prevention Study-II (CPS-II) Nutrition Cohort who were cancer-free ...