Not too big, not too small: Goldilocks analogy found in maze navigation
2021-02-02
(Press-News.org) New research from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) has found a surprising randomness for how fluids choose their path around obstacles that depends on their spacing. This has important implications for a range of scenarios - from oil recovery and groundwater remediation, to understanding the movement of fluids through biological systems. The research was published in Physical Review Letters.
Scientists from OIST's Micro/Bio/Nanofluidics Unit created a tiny set up comprised of two microscopic cylinders, each around the width of a human hair, placed side-by-side in a channel. This created a choice of three possible paths for a fluid to take past the pair of obstacles. A viscoelastic fluid, which is like that found in regular shampoo and conditioner, was run through the set-up at a constant rate and the path it chose around the cylinders was mapped.
"We found this nice Goldilocks analogy," said lead author Dr. Cameron Hopkins. "If the central gap between the cylinders was too small then the fluid would avoid this gap and randomly choose one of the two side paths to go around the cylinders. If the central gap was too large, then the fluid would go through the center and avoid the two side paths. It was only when the gap was just the right size, that the fluid would randomly choose between the three available paths."
Ultimately this research has revealed insights into the complexity of fluid path-selection and the findings can be extended to help understand fluid transport in larger, real-world systems.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-02
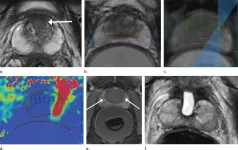
OAK BROOK, Ill. - A technique that delivers high-intensity focused ultrasound to targeted tissue under MRI guidance effectively treats intermediate-risk prostate cancer with minimal side effects, according to a study published in Radiology.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men, aside from non-melanoma skin cancers. Common treatments to the entire gland, such as surgery and radiation therapy, are effective in eliminating the cancer, but they often leave patients with incontinence and sexual dysfunction.
A class of treatments called focal therapy offers an alternative for some men with intermediate-risk disease that is still confined to the prostate. In focal therapy, the cancer is ablated, or destroyed, by either ...
2021-02-02
By late summer 2020, the resurgence of COVID-19 in the United States was largely driven by adults between the ages of 20 and 49, a new study finds. The results indicate that in locations where novel highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 lineages have not yet established, additional interventions among adults of these ages could bring resurgent COVID-19 epidemics under control and avert deaths. Following initial declines in the number of reported SARS-CoV-2 infections and deaths - a result largely attributed to non-pharmaceutical interventions - a resurgence in transmission of COVID-19 occurred in the United States and Europe beginning in August 2020. Understanding the age demographics that drove this is crucial. For example, between August ...
2021-02-02
Laser particles are micrometre and nanometre lasers in the form of particles dispersible in aqueous solution, which have attracted considerable interest in the life sciences as a promising new optical probe. Laser particles emit highly bright light with extremely narrow spectral bandwidth. By transferring laser particles into live cells as shown in Figure 1, individual cells in a heterogeneous population can be tracked using each intracellular particle's specific spectral fingerprint as an optically readable barcode. However, laser particles emit directional light (Figure 2) and freely tumble inside living cells, their orientation varying randomly over time. Therefore optical readout of these labels results ...
2021-02-02
Loess Plateau possesses a particular loess physiognomy with numerous ravines and slopes, and tableland is a typical landform in it. Together, the ununiform in both topographic undulation and land coverage compose the ununiform, complex underlying surface on Loess Plateau. This provides a special platform for research of turbulence above the complex underlying surface.
As the front-edge problem encountered in the atmospheric boundary layer thesis, the turbulence research for complex underlying surface has drawn extensive attention recently. Local similarity has already proven that under certain condition, theories of turbulence based on the uniform underlying surface can also be applied to which for the ununiform underlying surface. ...
2021-02-02
A team from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a portable device that produces high-resolution 3D images of human skin within 10 minutes.
The team said the portable skin mapping (imaging) device could be used to assess the severity of skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis.
3D skin mapping could be useful to clinicians, as most equipment used to assess skin conditions only provide 2D images of the skin surface. As the device also maps out the depth of the ridges and grooves of the skin at up to 2mm, it could also help with monitoring wound healing.
The device presses a specially devised film onto the subject's skin to obtain an imprint of up to 5 by 5 centimetres, which is then ...
2021-02-02
A satellite-based dataset generated by KAUST researchers has revealed the dynamics of dust storm formation and movements over the last decade in the Arabian Peninsula. Analysis of this long-term dataset reveals the connection between the occurrence of extreme dust events and regional atmospheric conditions, a finding that could help improve weather forecasting and air-quality models.
Dust storms occur when strong winds lift tiny particles of sand into the atmosphere. These events often span several miles and can have an enormous impact on daily life, from damaging buildings and disrupting air traffic to triggering respiratory illnesses and other health problems.
The Arabian Peninsula is a global hotspot of extreme dust events, with storms occurring ...
2021-02-02
Residential gardens are a poor substitute for native bushland and increasing urbanisation is a growing threat when it comes to bees, Curtin University research has found.
Published in 'Urban Ecosystems', the research looked at bee visits to flowers, which form pollination networks across different native bushland and home garden habitats.
Lead author, Forrest Foundation Scholar Miss Kit Prendergast, from Curtin's School of Molecular and Life Sciences said the findings highlight the need to prevent destruction of remaining bushland and preserve native vegetation, in order to protect sustainable bee communities and their pollination services.
"Our study involved spending hundreds of hours at 14 sites on the Swan Coastal Plain at Perth, Western Australia, ...
2021-02-02
Researchers have shown how disposable face masks could be recycled to make roads, in a circular economy solution to pandemic-generated waste.
Their study shows that using the recycled face mask material to make just one kilometre of a two-lane road would use up about 3 million masks, preventing 93 tonnes of waste from going to landfill.
Developed by researchers at RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, the new road-making material is a mix of shredded single-use face masks and processed building rubble designed to meet civil engineering safety standards. ...
2021-02-02
Researchers from Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) in collaboration with colleagues from Belgium take a step in the development of genome editing technology. Currently it is possible to deliver genetic material of different sizes and structures to organs and tissues. This is the key to eliminating DNA defects and treating more patients. The project is guided by Professor Gleb Sukhorukov and supported by the Russian Science Foundation. Research results were published in Particle & Particle Systems Characterization journal.
An international research group developed a polymer ...
2021-02-02
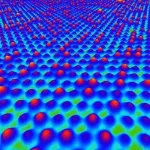
Semiconducting 2D alloys could be key to overcoming the technical limitations of modern electronics. Although 2D Si-Ge alloys would have interesting properties for this purpose, they were only predicted theoretically. Now, scientists from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology have realized the first experimental demonstration. They have also shown that the Si to Ge ratio can be adjusted to fine tune the electronic properties of the alloys, paving the way for novel applications.
Alloys--materials composed of a combination of different elements or compounds--have played a crucial role in the technological development of humans since the Bronze Age. Today, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Not too big, not too small: Goldilocks analogy found in maze navigation