"Genetic SD-card": Scientists obtained new methods to improve the genome editing system
Researchers take a step in the development of genome editing technology.
2021-02-02
(Press-News.org) Researchers from Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) in collaboration with colleagues from Belgium take a step in the development of genome editing technology. Currently it is possible to deliver genetic material of different sizes and structures to organs and tissues. This is the key to eliminating DNA defects and treating more patients. The project is guided by Professor Gleb Sukhorukov and supported by the Russian Science Foundation. Research results were published in Particle & Particle Systems Characterization journal.
An international research group developed a polymer carrier with a number of unique properties, several types of genetic material can be loaded in its structure. In particular, the scientists managed to load genetic material of various sizes and structures into "universal containers". From small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to messenger RNAs (mRNAs). The efficiency of delivery was demonstrated on human stem cells.
"Nowadays most of the vaccines, including those for COVID-19, are made on the basis of mRNA. This is a kind of "genetic SD-card" with information which activates human immune system, thus teaches it how to deal with the "enemy proteins" of the virus. Typically, for medical purposes, different types of carriers are used to deliver specific molecules, we proved that it is possible to deliver genetic materials of different sizes using one type of carrier. This technology opens up new horizons for the development of non-viral delivery systems", - notes Alexander Timin, head of the Laboratory for microencapsulation and controlled delivery of biologically active compounds at St. Petersburg Polytechnic University.
Scientists added that the micron-scaled carrier with incorporated genetic material can be delivered by systemic administration, or locally (directly into the tumor focus for cancer).
"The study is conducted jointly with the Raisa Gorbacheva Memorial Research Institute of Children Oncology, Hematology and Transplantation, which provided the patients'mesenchymal stem cells (cells building organs and tissues) for the experiments. In the future, we plan to conduct experiments on tumor-bearing laboratory animals in order to find out how the genetic material delivered to the tumor will be managed, "- said Igor Radchenko, director of the "RASA-Polytech" center.
INFORMATION:
The Raisa Gorbacheva Memorial Research Institute of Children Oncology, Hematology and Transplantation is interested in the early implementation of these developments in order to fulfill the recommendations and medical protocols that will be introduced into medical practice.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-02
Semiconducting 2D alloys could be key to overcoming the technical limitations of modern electronics. Although 2D Si-Ge alloys would have interesting properties for this purpose, they were only predicted theoretically. Now, scientists from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology have realized the first experimental demonstration. They have also shown that the Si to Ge ratio can be adjusted to fine tune the electronic properties of the alloys, paving the way for novel applications.
Alloys--materials composed of a combination of different elements or compounds--have played a crucial role in the technological development of humans since the Bronze Age. Today, ...
2021-02-02
The Bronze Age (2200 to 800 BC) marked a decisive step in the technological and economic development of ancient societies. People living at the time faced a series of challenges: changes in the climate, the opening up of trade and a degree of population growth. How did they respond to changes in their diet, especially in Western Switzerland? A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, and Pompeu Fabra University (UPF) in Spain has for the first time carried out isotopic analyses on human and animal skeletons together with plant remains. The scientists discovered that manure use had become widespread over time to improve crop harvests in response to demographic growth. The researchers also found that there had ...
2021-02-02
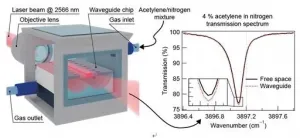
Optical waveguides suspended in air are capable to beat free-space laser beams in light-analyte interaction even without complex dispersion engineering. This phenomenon has been predicted more than 20 years ago, yet never observed in experiment.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Jana Jágerská from Department of Science and Technology, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, and co-workers have devised a mid-infrared free standing solid core optical waveguide which pushes the light interaction with the surrounding air beyond what has been reported up until now: 107 % interaction strength compared to that of a free-space beam has been demonstrated.
"The guided mode of our thin waveguide ...
2021-02-02
New study found that electrons can reach ultra-relativistic energies for very special conditions in the magnetosphere when space is devoid of plasma.
Recent measurements from NASA's Van Allen Probes spacecraft showed that electrons can reach ultra-relativistic energies flying at almost the speed of light. Hayley Allison, Yuri Shprits and collaborators from the German Research Centre for Geosciences have revealed under which conditions such strong accelerations occur. They had already demonstrated in 2020 that during solar storm plasma waves play a crucial role for that. However, it was previously unclear why such high electron energies are not achieved ...
2021-02-02
The COVID-19 pandemic has upended many parts of daily life, one of them being our work life. Research carried out by the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) has studied the factors that help make efficient work teams. The explanation is multidimensional and multilevel.
"Inspiring leadership builds employees' resilience and willingness to undertake new challenges," said Pilar Ficapal Cusi, professor at the UOC's Faculty of Economics and Business and one of the authors of the study, which was published in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
Viewed from the group and organizational perspective, "the shared vision, the team's belief in its own creative effectiveness, the ability to reflect openly about how their members connect to adapt ...
2021-02-02
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have discovered the individual traits of fungi, and how their hyphae - that is, the fungal threads that grow in soil - behave very differently as they navigate through the earth's microscopic labyrinths.
The study was performed in a lab environment, and the underground system constructed synthetically from silicone. Using a microscope, researchers were able to follow seven species and compare their behaviour. How do they react when the maze they grow in turns sharply and forces the hyphae to grow in the direction it came from? What happens when a large space opens up in front of them?
"Under a microscope, their behaviour becomes much more personal than you can ever imagine. ...
2021-02-02
Parasitic worms could hold the key to living longer and free of chronic disease, according to a review article published today in the open-access eLife journal.
The review looks at the growing evidence to suggest that losing our 'old friend' helminth parasites, which used to live relatively harmlessly in our bodies, can cause ageing-associated inflammation. It raises the possibility that carefully controlled, restorative helminth treatments could prevent ageing and protect against diseases such as heart disease and dementia.
"A decline in exposure to commensal microbes and gut helminths in developed countries ...
2021-02-02
A greater exposure to air pollution at the very start of life was associated with a detrimental effect on people's cognitive skills up to 60 years later, the research found.
Researchers at the University of Edinburgh tested the general intelligence of more than 500 people aged approximately 70 years using a test they had all completed at the age of 11 years.
The participants then repeated the same test at the ages of 76 and 79 years.
A record of where each person had lived throughout their life was used to estimate the level of air pollution they had experienced in their early years.
The team used statistical models to analyse the relationship between a person's exposure to air pollution ...
2021-02-02
To evaluate the chemical composition of food from a physiological point of view, it is important to know the functions of the receptors that interact with food ingredients. These include receptors for bitter compounds, which first evolved during evolution in bony fishes such as the coelacanth. What 400 million years of evolutionary history reveal about the function of both fish and human bitter receptors was recently published in the journal Genome Biology and Evolution by a team of researchers led by the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich and the University of Cologne.
Evolutionarily, bitter receptors are a relatively recent invention of nature compared ...
2021-02-02
A process that releases iron in response to stress may contribute to heart failure, and blocking this process could be a way of protecting the heart, suggests a study in mice published today in eLife.
People with heart failure often have an iron deficiency, leading some scientists to suspect that problems with iron processing in the body may play a role in this condition. The study explains one way that iron processing may contribute to heart failure and suggests potential treatment approaches to protect the heart.
"Iron is essential for many processes in the body including oxygen transport, but too much iron can lead to a build-up of unstable oxygen molecules that can kill cells," says ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] "Genetic SD-card": Scientists obtained new methods to improve the genome editing system
Researchers take a step in the development of genome editing technology.