(Press-News.org) Mothers are at increased risk of mental health problems as they struggle to balance the demands of childcare and remote working in COVID-19 lockdowns, according to new research from an international team of researchers.
The findings, published in the journal Psychological Medicine, were drawn from a comprehensive, online survey of mothers in China, Italy and the Netherlands.
Changes to their working lives, family strife and loss of social networks emerged as common factors affecting the mental health of mothers in all three countries.
The study was carried out by a team from Radboud University, Peking University, Tilburg University, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, and Padua University, to compare the factors affecting and protecting mothers' metal health in lockdown across countries and cultures.
A total of 900 Dutch, 641 Italian, and 922 Chinese mothers with children aged between one and 10 years participated in the study and reported on their mental health, family functioning, the support they received, and their demographic characteristics during the first lockdown in April and May 2020.
The researchers found women in all three countries shared three big risk factors: changes to work through unemployment, reduced job security and the shift to remote working; marital problems and conflict with other family members, and what the researchers called pandemic-related distress, caused by reduced access to food and essentials, healthcare and social networks.
There were also smaller risks to mental health, which differed across the three countries.
In the Netherlands, unemployed mothers reported high levels of mental health problems, possibly because of financial insecurity. At the same time, highly educated Dutch mothers also reported more symptoms. The researchers suggest this may be because of the need to combine demanding work, often remotely, with child care responsibilities.
In China, highly educated or high income mothers, single mothers, and mothers with poor physical health all reported more mental health symptoms, while in Italy, lower maternal age and poor physical health emerged as risk factors.
Regardless of country, the researchers found mothers who were more resilient and generally able to cope effectively with stressful events experienced lower mental health problems during the lockdown. In China, a large number of children as well as support in childcare from grandparents living in the same household decreased the risk of mental health problems. The researchers conclude that an extended family may be a source of resilience as the unexpected burden of the pandemic is shared among more people.
Dr Madelon Riem, from Radboud University, said: "With closures of schools and day care centres, COVID-19 continues to drastically impact the lives of parents. The burden of the pandemic may be disproportionality placed on women who are still often the primary caregiver. Mothers are, therefore, at increased risk for mental health problems."
Her colleague, Jing Guo, from Peking University, said: "These findings may inform future interventions aimed at improving maternal mental health during future pandemics. For instance, the current lockdown policies may ignore the advantages of grandparental childcare that support mother's mental health, as shown in China.
"Families without grandparental support show a clear need of childcare facilities during lockdowns. Improving maternal mental health not only benefits mothers, but also their children. For mothers who are disproportionately burdened by the pandemic, good mental health may be a necessary prerequisite for providing adequate care of their children."
INFORMATION:
Scientists from MIPT, Moscow Pedagogical State University and the University of Manchester have created a highly sensitive terahertz detector based on the effect of quantum-mechanical tunneling in graphene. The sensitivity of the device is already superior to commercially available analogs based on semiconductors and superconductors, which opens up prospects for applications of the graphene detector in wireless communications, security systems, radio astronomy, and medical diagnostics. The research results are published in a high-rank journal Nature Communications.
Information transfer in wireless networks is based on transformation of a high-frequency continuous electromagnetic wave into a discrete sequence of bits. This technique is known as signal modulation. ...
People receiving treatment for cancer are known to feel better with physical training. But does it make any difference how vigorously they exercise? A new study by researchers at Uppsala University shows that whether the training is intensive or rather less strenuous, its effect is roughly the same. The results are published in the journal Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports.
Physical activity and training during cancer therapy improve physical and mental health, and may also reduce the most common side effects of the treatment. This has been confirmed in several international studies. Many patients suffer from cancer-related fatigue, and both resistance and endurance training are known to lessen fatigue. ...
The IBeA research group from the University of the Basque Country's Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, is participating in NASA's Mars2020 space mission, which is scheduled to touch down on Mars in February this year. Specifically, the group has participated in constructing and verifying the chemical homogeneity of the templates included on the calibration card of the SuperCam instrument mounted on the Perseverance. 'We made a set of pads perfectly characterised in accordance the instruments we have here, in order to enable us to verify that the LIBS and Raman spectroscopy measurements taken by the SuperCam are correct,' explains Doctor Cristina García-Florentino. 'Raman spectroscopy is a technique ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound effect on higher education -- shifting classes online, canceling events, and putting financial strain on institutions.
One area of academia that has actually shown positive increases, however, is the submission of research papers. A study conducted by Michelle Bell, Mary E. Pinchot Professor of Environmental Health at the Yale School of the Environment (YSE), and postdoctoral associate Kelvin C. Fong found the rate of manuscript submission to a major peer-reviewed journal (American Journal of Public Health) were higher during the pandemic -- but also revealed ...
In the wake of repeated school shootings across the United States, today's youth have been called the mass shooting generation. A new study examined public support for arming school employees. The study found consensus for arming school resource officers, but division over whether to arm teachers and nonteaching staff. The research has clear implications for policy, including the possibility that support for arming school staff may diminish over time as young people (who are less supportive) make up a larger share of voters.
The study was conducted ...
The properties of human mind affect the quality of scientific knowledge through the insertion of unconscious cognitive biases. Scientists from the University of Turku, Finland, have found that the current level of awareness about research biases is generally low among ecology scientists. Underestimation of the risks associated with unconscious cognitive biases prevents avoiding these risks in a scientist's own research. Due to unconscious origin of biases, it is impossible to combat them without external intervention.
When scientists use some device in their research, they always account for characteristics of this device, such as accuracy and precision. The human mind is the ...
The findings of a new study examining the behaviours of alligator and caiman hatchlings have enhanced our understanding of how we can conserve, and increase, the population of endangered crocodilian species.
At adult size, there are key differences between the American alligator and the closely related spectacled caiman. However, at the time of hatching both species are tiny and might be expected to show similar behaviours in order to avoid being eaten by almost any carnivore around.
Now, researchers at the Universities of Lincoln and Vienna have conducted comparative studies between the hatchlings of these crocodilian creatures and found that the alligators are more active and likely to explore their surroundings.
The research, conducted at 'Crocodiles of the World', the only zoo ...
Dr. Mikhail V. Blagosklonny, M.D., Ph.D., Editor-in-Chief of Oncotarget, and Professor, at Roswell Park Cancer Institute, published "The goal of geroscience is life extension" which was selected as the Featured Cover Paper for Volume 12 Issue 3 and reported that although numerous drugs seemingly extend healthspan in mice, only a few extend lifespan in mice and only one does it consistently. Some of them, alone or in combination, can be used in humans, without further clinical trials.
Dr. Mikhail V. Blagosklonny from The Roswell Park Cancer Institute said, "Although we do not know everything about aging, we now know enough to start its pharmacologic suppression using ...
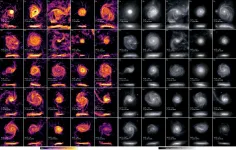
Massive galaxies with extra-large extended "puffy" disks produced stars for longer than their more compact cousins, new modelling reveals.
In a paper published in the Astrophysical Journal, researchers led by Dr Anshu Gupta and Associate Professor Kim-Vy Tran from Australia's ARC Centre of Excellence in All Sky Astrophysics in 3 Dimensions (ASTRO 3D), show that the sheer size of a galaxy influences when it stops making new stars.
"There's a period in the life of the Universe known as the 'cosmic noon', which occurred about 10 billion years ago," said Dr Gupta.
"That was when star formation in massive galaxies was at ...
New research suggests that the rate of rainfall within a storm system is linked to the structure and form of the precipitation area as seen on radar. This discovery relies heavily on the "morphology" of radar signatures, including shape (big, small), and size (high, short or plump, thin). Compared to buying diamonds, morphological characteristics are an important reference factor for pricing. Fascinated by "popcorn-shaped" clouds over the Tibetan Plateau, atmospheric scientists have been inspired to study the relationship between cloud shape, precipitation intensity, and the morphology ...