Scientists believe studies by colleagues are more prone to biases than their own studies
2021-02-03
(Press-News.org) The properties of human mind affect the quality of scientific knowledge through the insertion of unconscious cognitive biases. Scientists from the University of Turku, Finland, have found that the current level of awareness about research biases is generally low among ecology scientists. Underestimation of the risks associated with unconscious cognitive biases prevents avoiding these risks in a scientist's own research. Due to unconscious origin of biases, it is impossible to combat them without external intervention.
When scientists use some device in their research, they always account for characteristics of this device, such as accuracy and precision. The human mind is the most important tool in the scientific research. Nevertheless, its properties are rarely taken into account by the ecologists while conducting their research.
The cognitive biases emerge most frequently due to tendency of humans to search for and interpret information in a way that confirms one's pre-existing beliefs or hypotheses.
- For example, an influential theory predicts that pollution increases asymmetry of plant leaves. When two groups of scientists were asked to measure the same set of leaves, the group which was told that leaves originate from a polluted site reported significantly higher asymmetry than the group which was told that leaves originate from a clean site. Thus, the first group of scientists found non-existing effect only because they believed that it should exist, says Adjunct Professor Elena Zvereva from the Department of Biology of the University of Turku.
- This kind of biases may considerably influence the output of the research, generally leading to overestimation of the effects under study. Development of measures for combating cognitive biases in research requires information on the current level of awareness about biases among scientists, Zvereva adds.
Responses of 308 ecology scientists from 40 countries to a web-based questionnaire revealed that knowledge about biases and attitude towards biases depend on the scientist's career stage, gender and affiliation country. Respondents from high GDP countries have better knowledge about biases than respondents from low GDP countries. Early career scientists were more concerned about biases, know more about measures to avoid biases, and twice more often have learned about biases from their university courses when compared with their senior colleagues. This difference indicates current improvement of education about biases and gives hope that their impact on scientific research will decrease in the future.
Ecological scientists estimate that the risk of biases in their own studies is much lower than in science in general and in studies by other scientists working in the same research field. In other words, they "see the speck that is in their brother's eye, but do not notice the log that is in their own eye". The strength of this "bias blind spot" is two times larger in men than in women and two times larger in senior scientists than in early career scientists. These differences suggest that this bias is more typical for persons with high self-confidence and self-esteem.
- Education about biases is necessary, but not yet sufficient, to avoid biases because the unconscious origin of biases necessitates external intervention to combat them. Obligatory reporting of measures taken against biases in all relevant manuscripts will likely increase the quality of scientific publications and enhance the reproducibility of scientific results, concludes Adjunct Professor Mikhail Kozlov from the University of Turku.
INFORMATION:
The study has been published in the Scientific Reports journal.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-03
The findings of a new study examining the behaviours of alligator and caiman hatchlings have enhanced our understanding of how we can conserve, and increase, the population of endangered crocodilian species.
At adult size, there are key differences between the American alligator and the closely related spectacled caiman. However, at the time of hatching both species are tiny and might be expected to show similar behaviours in order to avoid being eaten by almost any carnivore around.
Now, researchers at the Universities of Lincoln and Vienna have conducted comparative studies between the hatchlings of these crocodilian creatures and found that the alligators are more active and likely to explore their surroundings.
The research, conducted at 'Crocodiles of the World', the only zoo ...
2021-02-03
Dr. Mikhail V. Blagosklonny, M.D., Ph.D., Editor-in-Chief of Oncotarget, and Professor, at Roswell Park Cancer Institute, published "The goal of geroscience is life extension" which was selected as the Featured Cover Paper for Volume 12 Issue 3 and reported that although numerous drugs seemingly extend healthspan in mice, only a few extend lifespan in mice and only one does it consistently. Some of them, alone or in combination, can be used in humans, without further clinical trials.
Dr. Mikhail V. Blagosklonny from The Roswell Park Cancer Institute said, "Although we do not know everything about aging, we now know enough to start its pharmacologic suppression using ...
2021-02-03
Massive galaxies with extra-large extended "puffy" disks produced stars for longer than their more compact cousins, new modelling reveals.
In a paper published in the Astrophysical Journal, researchers led by Dr Anshu Gupta and Associate Professor Kim-Vy Tran from Australia's ARC Centre of Excellence in All Sky Astrophysics in 3 Dimensions (ASTRO 3D), show that the sheer size of a galaxy influences when it stops making new stars.
"There's a period in the life of the Universe known as the 'cosmic noon', which occurred about 10 billion years ago," said Dr Gupta.
"That was when star formation in massive galaxies was at ...
2021-02-03
New research suggests that the rate of rainfall within a storm system is linked to the structure and form of the precipitation area as seen on radar. This discovery relies heavily on the "morphology" of radar signatures, including shape (big, small), and size (high, short or plump, thin). Compared to buying diamonds, morphological characteristics are an important reference factor for pricing. Fascinated by "popcorn-shaped" clouds over the Tibetan Plateau, atmospheric scientists have been inspired to study the relationship between cloud shape, precipitation intensity, and the morphology ...
2021-02-03
Hokkaido University scientists show that under laboratory conditions, ultraviolet light reacts with nitrophenol to produce smog-generating nitrous acid.
An advanced laser technique has allowed researchers to observe, in real-time, the decomposition of a pollutant into atmospheric nitrous acid, which plays a key role in the formation of ozone and photochemical smog. The technique, described by Hokkaido University researchers in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, could be used in a wide range of applications.
Nitrophenols are a type of fine particulate matter found in the atmosphere that form as a result of fossil fuel combustion and from forest fires. It is hypothesised that light interacts with nitrophenols and breaks them down into nitrous acid; atmospheric nitrous ...
2021-02-03
Social interaction may help reverse food and cigarette cravings triggered by being in social isolation, a UNSW study in rats has found.
The study, published in Scientific Reports, used an animal model of drug addiction to show that a return to social interaction gives the same result as living in a rich, stimulating environment in reducing cravings for both sugar and nicotine rewards.
"This was an animal study, but we can probably all relate to the mental health benefits of being able to go for a coffee with our friends and having a chat," lead author Dr Kelly Clemens from UNSW Sydney's School of Psychology ...
2021-02-03
The SARS-CoV-2, the new coronavirus behind the current pandemic, infects humans by binding its surface-exposed spike proteins to ACE2 receptors exposed on the cell membranes.
Upon a vaccination or a real infection, it takes several weeks before the immunity develops antibodies that can selectively bind to these spike proteins. Such antibody-labeled viruses are neutralized by the natural killer and T cells operated by the human immunity.
An alternative approach to train the immunity response is offered by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago and California State University at Sacramento who have developed a novel strategy that redirects antibodies for other diseases existing in humans to the spike proteins ...
2021-02-03
A higher diversity of flowering plants increases the breeding success of wild bees and may help compensate for the negative effects of insecticides. This is what researchers from the Universities of Göttingen and Hohenheim, as well as the Julius Kühn Institute, have found in a large-scale experimental study. The results have been published in the scientific journal Ecology Letters.
In their experiment, the researchers investigated how successfully the wild bee Osmia bicornis (red mason bee) reproduced. Red mason bees are important for both ecological and economic ...
2021-02-03
Researchers in Costa Rica have found that some bacteria on the skin of amphibians prevent growth of the fungus responsible for what has been dubbed 'the amphibian apocalypse'.
Published in the journal Microbiology, the research identified a number of bacteria which could growth of the fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd). One particularly dangerous strain of the fungus, called BdGPL-2, is responsible for mass amphibian die-offs around the world.
The fungus infects the skin of amphibians, breaking down the cells. As amphibians breathe and regulate water through their skin, infection is often deadly. It is believed that almost 700 species of amphibian are vulnerable to the ...
2021-02-03
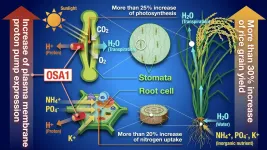
A group of scientists led by Drs Toshinori Kinoshita and Maoxing Zhang (Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules,Nagoya University, Japan) and Dr Yiyong Zhu (Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Solid Organic Waste Utilization, Nanjing Agricultural University, China) have developed a method which, by increasing the number of a plasma membrane proton pump gene in rice, simultaneously increases nutrient uptake through the roots and stomatal opening, thus increasing the yield of paddy field grown rice by over 30%.
In their previous research, the group had found that the plasma membrane proton pump played an important role in influencing stomatal opening. When they created a variant of rice with an overexpression of a particular plasma membrane proton pump gene, they found ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists believe studies by colleagues are more prone to biases than their own studies