Retrained generic antibodies can recognize SARS-CoV-2
2021-02-03
(Press-News.org) The SARS-CoV-2, the new coronavirus behind the current pandemic, infects humans by binding its surface-exposed spike proteins to ACE2 receptors exposed on the cell membranes.
Upon a vaccination or a real infection, it takes several weeks before the immunity develops antibodies that can selectively bind to these spike proteins. Such antibody-labeled viruses are neutralized by the natural killer and T cells operated by the human immunity.
An alternative approach to train the immunity response is offered by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago and California State University at Sacramento who have developed a novel strategy that redirects antibodies for other diseases existing in humans to the spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2.
In their study published by the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, the team proposes using peptide-based double-faced "booster" inhibitors, with one face binding to the spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and the other face binding to generic hepatitis B antibodies.
"Once the SARS-CoV-2 viruses become labeled by the hepatitis B antibodies via intermediate boosters, the viruses will be neutralized. This universal approach allows a dramatic shortening of the response time upon real infections, which can be critical in certain patients or conditions," said Petr Král, UIC professor of chemistry, physics, pharmaceutical sciences and chemical engineering, and senior author on the paper.
Král and Yanxiao Han, who recently earned a Ph.D. in chemistry at UIC and is first author on the paper, believe the study could provide guidance in the preparation of generic therapeutics against emerging pathogens with the combined advantages of small-protein and antibody therapies.
"The dramatic impact which novel viruses can have on humans could be fast mitigated in the absence of their vaccination if generic antibodies present within them are temporarily retrained to recognize these viruses," the researchers wrote.
In a study published last spring, Král and Han extracted different peptides from ACE2 that interact directly with the viral spike protein.
"We investigated potential COVID-19 therapeutics using computer simulations based on the X-ray crystal structure of the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 when it is bound to ACE2," Král said. "Similar to our latest study, identifying these kinds of inhibitors could lead to new treatments to combat the coronavirus."
INFORMATION:
Co-author on the paper is Katherine McReynolds of California State University at Sacramento.
This work is supported by funding from the UIC Center for Clinical and Translational Science.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-03
A higher diversity of flowering plants increases the breeding success of wild bees and may help compensate for the negative effects of insecticides. This is what researchers from the Universities of Göttingen and Hohenheim, as well as the Julius Kühn Institute, have found in a large-scale experimental study. The results have been published in the scientific journal Ecology Letters.
In their experiment, the researchers investigated how successfully the wild bee Osmia bicornis (red mason bee) reproduced. Red mason bees are important for both ecological and economic ...
2021-02-03
Researchers in Costa Rica have found that some bacteria on the skin of amphibians prevent growth of the fungus responsible for what has been dubbed 'the amphibian apocalypse'.
Published in the journal Microbiology, the research identified a number of bacteria which could growth of the fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd). One particularly dangerous strain of the fungus, called BdGPL-2, is responsible for mass amphibian die-offs around the world.
The fungus infects the skin of amphibians, breaking down the cells. As amphibians breathe and regulate water through their skin, infection is often deadly. It is believed that almost 700 species of amphibian are vulnerable to the ...
2021-02-03
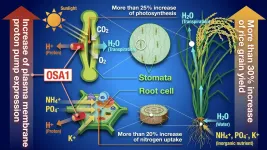
A group of scientists led by Drs Toshinori Kinoshita and Maoxing Zhang (Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules,Nagoya University, Japan) and Dr Yiyong Zhu (Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Solid Organic Waste Utilization, Nanjing Agricultural University, China) have developed a method which, by increasing the number of a plasma membrane proton pump gene in rice, simultaneously increases nutrient uptake through the roots and stomatal opening, thus increasing the yield of paddy field grown rice by over 30%.
In their previous research, the group had found that the plasma membrane proton pump played an important role in influencing stomatal opening. When they created a variant of rice with an overexpression of a particular plasma membrane proton pump gene, they found ...
2021-02-03
Modern-day robots are often required to interact with humans intelligently and efficiently, which can be enabled by providing them the ability to perceive touch. However, previous attempts at mimicking human skin have involved bulky and complex electronics, wiring, and a risk of damage. In a recent study, researchers from Japan sidestep these difficulties by constructing a 3D vision-guided artificial skin that enables tactile sensing with high performance, opening doors to innumerable applications in medicine, healthcare, and industry.
Robots have come a long way since their original inception for high-speed automation. Today, robots can be found in a wide variety of roles in medicine, rehabilitation, agriculture, and marine navigation. Since a ...
2021-02-03
Modern immunotherapeutic anti-cancer drugs support a natural mechanism of the immune system to inhibit the growth of cancer cells. They dock onto a specific receptor of the killer cell and prevent it from being switched off by the cancer cells. This is a complex molecular process, which is known but has not yet been fully understood. In a molecular dynamics study conducted by the group led by medical information scientist Wolfgang Schreiner and gynaecologists Heinz Kölbl and Georg Pfeiler from MedUni Vienna, working with biosimulation expert Chris Oostenbrink ...
2021-02-03
What are the reasons for such a contrast in outcomes? A scientist team led by the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) has now analysed the humoral innate immune defence of European greater mouse-eared bats to the fungus. In contrast to North American bats, European bats have sufficient baseline levels of key immune parameters and thus tolerate a certain level of infection throughout hibernation. The results are published in the journal "Developmental and Comparative Immunology".
During infections caused by Pseudogymnoascus destructans (Pd), North American bats arouse frequently from ...
2021-02-03
To date, research in the field of combinatorial catalysts has relied on serendipitous discoveries of catalyst combinations. Now, scientists from Japan have streamlined a protocol that combines random sampling, high-throughput experimentation, and data science to identify synergistic combinations of catalysts. With this breakthrough, the researchers hope to remove the limits placed on research by relying on chance discoveries and have their new protocol used more often in catalyst informatics.
Catalysts, or their combinations, are compounds that significantly lower the energy required to drive chemical reactions to completion. In the field of "combinatorial catalyst design," the requirement of synergy--where one component ...
2021-02-03
Life changes influence the amount of physical activity in a person, according to a recent study by the University of Jyväskylä. The birth of children and a change of residence, marital status and place of work all influence the number of steps of men and women in different ways. For women, having children, getting a job and moving from town to the countryside reduce everyday exercise.
A study conducted by the Faculty of Sports & Health Sciences found that the birth of the first child significantly reduces the number of everyday steps in women. As children grow, women's aerobic steps, in turn, increase. Although the birth of children did not have a statistically significant effect on the number of steps in men, changes were also observed ...
2021-02-03
Use of waste heat contributes largely to sustainable energy supply. Scientists of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and T?hoku University in Japan have now come much closer to their goal of converting waste heat into electrical power at small temperature differences. As reported in Joule, electrical power per footprint of thermomagnetic generators based on Heusler alloy films has been increased by a factor of 3.4. (DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2020.10.019)
Many technical processes only use part of the energy consumed. The remaining fraction leaves the system ...
2021-02-03
In the race to stop the spread of COVID-19, a three-layer cloth mask that fits well can effectively filter COVID particles, says a group of UBC researchers.
After testing several different mask styles and 41 types of fabrics, they found that a mask consisting of two layers of low-thread-count quilting cotton plus a three-ply dried baby wipe filter was as effective as a commercial non-surgical mask at stopping particles--and almost as breathable.
The cloth masks filtered out up to 80 per cent of 3-micron particles, and more than 90 per cent of 10-micron particles.
"We focused on particles larger than one micron because these are likely most important to COVID-19 transmission," explains researcher Dr. Steven Rogak, a professor of mechanical engineering who ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Retrained generic antibodies can recognize SARS-CoV-2