(Press-News.org) To date, research in the field of combinatorial catalysts has relied on serendipitous discoveries of catalyst combinations. Now, scientists from Japan have streamlined a protocol that combines random sampling, high-throughput experimentation, and data science to identify synergistic combinations of catalysts. With this breakthrough, the researchers hope to remove the limits placed on research by relying on chance discoveries and have their new protocol used more often in catalyst informatics.
Catalysts, or their combinations, are compounds that significantly lower the energy required to drive chemical reactions to completion. In the field of "combinatorial catalyst design," the requirement of synergy--where one component of a catalyst complements another--and the elimination of ineffective or detrimental combinations are key considerations. However, so far, combinatorial catalysts have been designed using biased data or trial-and-error, or serendipitous discoveries of combinations that worked. A group of researchers from Japan has now sought to change this trend by trying to devise a repeatable protocol that relied on a screening instrument and software-based analysis.
Their new study, published in ACS Catalysis, details the identification of effective catalyst combinations, using the proposed protocol, for the oxidative coupling of methane (OCM). OCM is a widely used chemical reaction used to convert methane into useful gases in the presence of oxygen and the catalyst. Elaborating on the motivations behind the study, Dr. Toshiaki Taniike, Professor at the School of Materials Science, Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology and corresponding author of the study, says, "Combinatorial catalyst design is hardly generalizable, and the empirical aspect of the research has biased the literature data toward accidentally found combinations".
To derive a bias-free dataset from OCM for devising the protocol, the researchers sampled randomly 300 solid catalysts from a vast materials space containing upwards of 36,000 catalysts! Screening such a large number of catalysts is near impossible by human standards. Hence, the team used a high-throughput screening instrument to evaluate their performance at facilitating OCM. The obtained dataset was used to outline the novel protocol, aimed at providing a guideline for catalyst design. This was implemented in the form of a "decision tree classification," which is a form of machine learning that helped in understanding the efficiency of the selected catalyst combinations, in giving better OCM yield. This, in turn, helped in drawing up the required catalyst design guidelines.
Interestingly, the results showed that, even with random sampling, 51 out of the 300 catalysts gave a better OCM yield when compared to the alternative non-catalytic process. Explaining the potential implications of their discovery, Dr. Keisuke Takahashi, Associate Professor at Hokkaido University and co-author of this study, says, "The combination of high throughput experimentation and data science has already demonstrated the power of bias-free catalyst big data in finding novel catalysts as well as a catalyst design guideline. It is also important to state the essentiality of these approaches for implementing such a demanding study in a realistic time frame. By equipping all the essential techniques of the study, truly nonempirical catalyst developments could be realized".
Indeed, we can hope, along with the scientists, that this strategy will "catalyze" several future material science discoveries!
INFORMATION:
About Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Japan
Founded in 1990 in Ishikawa prefecture, the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) was the first independent national graduate school in Japan. Now, after 30 years of steady progress, JAIST has become one of Japan's top-ranking universities. JAIST counts with multiple satellite campuses and strives to foster capable leaders with a state-of-the-art education system where diversity is key; about 40% of its alumni are international students. The university has a unique style of graduate education based on a carefully designed coursework-oriented curriculum to ensure that its students have a solid foundation on which to carry out cutting-edge research. JAIST also works closely both with local and overseas communities by promoting industry-academia collaborative research.
About Professor Toshiaki Taniike from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Japan
Dr. Toshiaki Taniike is a Professor and the Director of International Research Center for Materials Informatics, at the School of Material Science, Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Japan. Dr. Taniike's specialties include inorganic compounds and materials chemistry. He has more than 140 publications like research articles, review papers etc. in reputed journals, and several books, to his credit. In addition, he is a valuable member of The Japan Petroleum Institute, Materials Life Society, The Society of Polymer Science, Catalysis Society of Japan, and The Surface Science Society of Japan.
Life changes influence the amount of physical activity in a person, according to a recent study by the University of Jyväskylä. The birth of children and a change of residence, marital status and place of work all influence the number of steps of men and women in different ways. For women, having children, getting a job and moving from town to the countryside reduce everyday exercise.
A study conducted by the Faculty of Sports & Health Sciences found that the birth of the first child significantly reduces the number of everyday steps in women. As children grow, women's aerobic steps, in turn, increase. Although the birth of children did not have a statistically significant effect on the number of steps in men, changes were also observed ...
Use of waste heat contributes largely to sustainable energy supply. Scientists of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and T?hoku University in Japan have now come much closer to their goal of converting waste heat into electrical power at small temperature differences. As reported in Joule, electrical power per footprint of thermomagnetic generators based on Heusler alloy films has been increased by a factor of 3.4. (DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2020.10.019)
Many technical processes only use part of the energy consumed. The remaining fraction leaves the system ...
In the race to stop the spread of COVID-19, a three-layer cloth mask that fits well can effectively filter COVID particles, says a group of UBC researchers.
After testing several different mask styles and 41 types of fabrics, they found that a mask consisting of two layers of low-thread-count quilting cotton plus a three-ply dried baby wipe filter was as effective as a commercial non-surgical mask at stopping particles--and almost as breathable.
The cloth masks filtered out up to 80 per cent of 3-micron particles, and more than 90 per cent of 10-micron particles.
"We focused on particles larger than one micron because these are likely most important to COVID-19 transmission," explains researcher Dr. Steven Rogak, a professor of mechanical engineering who ...
The genus Ficus (figs) and their agaonid pollinating fig wasps are a classic example of coevolution. It represents perhaps the most extreme and ancient (about 75 million years) obligate pollination mutualism known.
Previous studies have suggested that pollinator host-switching and hybridization existed in some fig taxa with genetic evidence based on relatively few genes. However, those cases were mainly treated as rare exceptions, and strict-sense coevolution was still treated as the dominate coevolution model for the codiversification of this "extreme" obligate pollination system with high species richness.
Together with colleagues from 11 institutions from home and abroad, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical ...
Scientists at Scripps Research have clarified the workings of a mysterious protein called Gαo, which is one of the most abundant proteins in the brain and, when mutated, causes severe movement disorders.
The findings, which appear in Cell Reports, are an advance in the basic understanding of how the brain controls muscles and could lead to treatments for children born with Gαo-mutation movement disorders. Such conditions--known as GNAO1-related neurodevelopmental disorders--were discovered only in the past decade, and are thought to affect at least hundreds of children around the world. Children with the disease suffer from severe developmental ...
World-first 3D printed oesophageal stents developed by the University of South Australia could revolutionise the delivery of chemotherapy drugs to provide more accurate, effective and personalised treatment for patients with oesophageal cancer.
Fabricated from polyurethane filament and incorporating the chemotherapy drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), the new oesophageal stents are the first to contain active pharmaceutical ingredients within their matrix .
Their unique composition allows them to deliver up to 110 days of a sustained anti-cancer medication directly to the cancer site, restricting further tumour growth.
Importantly, the capabilities of 3D printing enabling rapid creation of individually tailored stents with patient-specific geometries and drug dosages.
PhD ...
The COVID-19 pandemic is a great example of the importance of access to the Internet and to digital health information. Unfortunately, historical disparities in health care appear to be reflected in computer ownership, access to the Internet and use of digital health information. However, few studies have qualitatively explored reasons for digital health information disparity, especially in older adults.
A study led by Florida Atlantic University's Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing in collaboration with the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and the University of Massachusetts Medical ...
A 30-year high in East African rainfall during 2018 and 2019 resulted in rising water levels and widespread flooding. The new study shows that emissions of methane - the second most important greenhouse gas - from flooded East African wetlands were substantially larger following these extreme rainfall events.
The study, led by Dr Mark Lunt from the University of Edinburgh's School of GeoSciences, used data from two different satellites in combination with an atmospheric model to evaluate methane emissions from East Africa. This included data from the European TROPOMI satellite instrument, launched in 2017, which provides information about atmospheric methane at ...
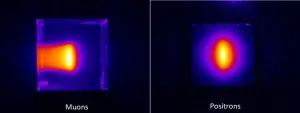
A new technique has taken the first images of muon particle beams. Nagoya University scientists designed the imaging technique with colleagues in Osaka University and KEK, Japan and describe it in the journal Scientific Reports. They plan to use it to assess the quality of these beams, which are being used more and more in advanced imaging applications.
Muons are charged particles that are 207 times the mass of electrons. They naturally form when cosmic rays strike atoms in the upper atmosphere, showering down onto every part of Earth's surface. They can penetrate through hundreds of meters of solids before being absorbed.
Scientists have used naturally ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Although exercise is known to enhance cognitive function and improve mental health, the neurological mechanisms of this link are unknown. Now, researchers from Japan have found evidence of the missing link between aerobic fitness and cognitive function.
In a study published in Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, researchers from the University of Tsukuba revealed that spontaneous eye blink rate (sEBR), which reflects activity of the dopamine system, could be used to understand the connection between cognitive function and aerobic fitness.
The dopaminergic system is known to be involved in physical activity and exercise, and previous researchers have proposed that exercise-induced changes in cognitive function might be mediated by activity ...